|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 13(2); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is common disorder of the school-age population. ADHD is familial and genetic studies estimate heritability at 80-90%. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between the genetic type and alleles for RELNgene (rs736707, rs2229864, rs362746, rs362726, rs362691, rs1062831, rs607755, and rs2072403) in Korean children with ADHD.
Methods
The sample consisted of 180 ADHD children and 159 control children. We diagnosed ADHD according to DSM-IV. ADHD symptoms were evaluated with Conners' Parent Rating Scales and Dupaul Parent ADHD Rating Scales. Blood samples were taken from the 339 subjects, DNA was extracted from blood lymphocytes, and PCR was performed for RELN Polymorphism. Alleles and genotype frequencies were compared using the chi-square test. We compared the allele and genotype frequencies of RELN gene polymorphism in the ADHD and control groups.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common childhood neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by behavioral problems such as attention deficit, hyperactivity and impulsivity.1 It has a prevalence of 2-7.6% among children of school age in Korea.23 Family studies reported that ADHD showed a heredity as high as 80-90%,4 and molecular genetic studies are actively carried out accordingly. Recent genetic studies on ADHD have usually been conducted on the dopamine receptors and related neurotransmitters.
Reelin is an extracellular protein that is mainly involved in nerve cell migration, appropriate brain lamination, and synapse formation in the central nervous system.5 For humans, the reelin gene is located at chromosome 7q22.1.6
An animal study reported that the expression of reelin is involved in long term potentiation (LTP) and cognition.78 Reelin promotes hippocampal LTP and this function requires the activity of lipoprotein receptors.910 The role of Reelin in synaptic function is mediated in part through interactions between ApoER2 and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors.11 These proteins form a synaptic complex that controls Ca2+ entry through the NMDA receptor and thus regulate synaptic plasticity. In addition Reelin signaling is also important for the regulation of NMDA receptor subunit composition during hippocampal neuronal maturation, and NMDA receptor-mediated activity in cortical neurons.12 Inattention and partial cognitive decline are characteristic symptoms of ADHD as well as dementia.
Many studies have reported that the abnormality of reelin is associated with autism, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and lissencephaly.13 In previous research, there have been a number of association studies on the reelin gene and autism. Serajee et al.14 and Li et al.15 reported the association of the rs736 707/rs362691 reelin genes with autism, and Ashley-Koch et al.16 reported the association of rs2073559 with autism. Recently, the association between excessive transmission of the allele of RELN SNP rs362719 and bipolar disorder has been reported.17
Consequences of RELN mutation were first characterized in the homozygous reeler mouse which phenotypically exhibited an ataxic gait.181920 A number of abnormalities have been characterized in the brains of homozygous reeler mice. These include a nonfoliated cerebellum and deficits in lamination of the hippocampus and other cortical areas.2122 Most strikingly, in homozygous reeler mice, the cortex has been characterized as a laminar inversion of the typical inside-out pattern of development.18 A recent analysis of neocortex of homozygous reeler mice found an even more complex pattern with evidence of a mirror-image laminar structure and rostrocaudal cell-type-specific differences in laminar phenotype.20
Disorganization of the hippocampus and amygdala were also observed, suggesting pervasive disruption of brain cytoarchitecture as a result of reduced Reelin expression.
To our knowledge, no research has been reported about correlation between ADHD in youths and RELN gene polymorphism. Few studies have been conducted to show the correlation between RELN gene polymorphism and Autism. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between the genetic type and alleles for RELN gene in Korean children with ADHD.
A questionnaire was conducted with about 16,000 elementary school students in a city whose population is about 500,000 from September 2008 and August 2010. A interview was performed randomly with the children whose Korean version of the Dupaul Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scales (K-ARS)23 score was 19 or higher, and 180 ADHD children who consented to the genetic study were selected. For the control group, 159 children in the same area were selected by matching the sex and age of the subjects in the patient group. For both of the patient and control groups, a clinical evaluation and the DSM-IV diagnosis1 were performed by a child psychiatrist. The number of ADHD children was 180, including 132 boys (73.3%) and 48 girls (26.7%), and the mean age was 8.67±0.84. The number of the children in the control group was 159, including 100 boys (62.9%) and 59 girls (37.1%), and the mean age was 8.59±0.79. There was no significant difference in the sex and age between the two groups (Table 1). Subjects were excluded from the study if there was any evidence of conduct disorder, mood disorder, anxiety disorder, Tourette's disorder, pervasive development disorder, mental retardation (IQ <70) and neurological disorders including epilepsy. Both the patient group and control group in this study underwent clinical evaluation and DSM-IV diagnosis by children psychiatrists, applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria strictly, because we will get subject group was composed of pure ADHD diagnosed subjects without major psychiatric disorder and neurological abnormality. None of the children who participated in the study has ever undergone drug treatment before the evaluation. Informed consent was obtained prior to study entry. The study was also approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee. None of the children was taking psychostimulants at the time of the study.
On the day of visiting the hospital, the child psychiatrist performed a clinical interview as well as Kovac's Children's Depression Inventory (CDI),2425 State Anxiety Inventory (SAIC), Trait Anxiety Inventory (TAIC)26 and Dupaul Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Sales (K-ARS),21 computerized ADS (ADHD Diagnostic System)27 as well as completing a questionnaire survey regarding the pregnancy, infancy, developmental history and anamnesis of the children with their parents. Subjects were included from our sample if they had a score over two standard deviations from the norm on the tests for ADS (T-score >70). ADHD had a lot of cormorbid disorders, as depressive disorder and anxiety disorder. So we excluded children with the high score of depressive symptoms and anxiety symptoms. Subjects with high anxiety scores (a Spielberger trait/state anxiety scale score >47/49) on the Korean version of Spielberger trait-state anxiety scale for children were excluded, and subjects with high depression scores (Kovacs depression inventory score >29) on Kovacs depression inventory for children were also excluded. In Cho and Lee23 presented the score over 22 as the mild depressed state, over 26 as the middle depressed state, and over 29 as the severe depressed state in the Korean form of the Kovacs' Childhood Depression Inventory. Also Cho and Choi24 evaluated the reliability of the Korean State Anxiety Inventory for Children, reported that the scores 39-42 indicate a little high trait anxiety, scores 43-46 indicate a considerably high trait anxiety, and scores 47 or higher indicate very high trait anxiety in TAIC scales. In addition, a professional clinical psychologist performed a comprehensive psychological test, including an intelligence test, on each subject.
DNA was extracted from leukocytes using a commercial DNA extraction kit, the Wizard Genomic DNA purification kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The RELN SNP was genotyped by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) according to the protocol described by Li et al.'s studies13
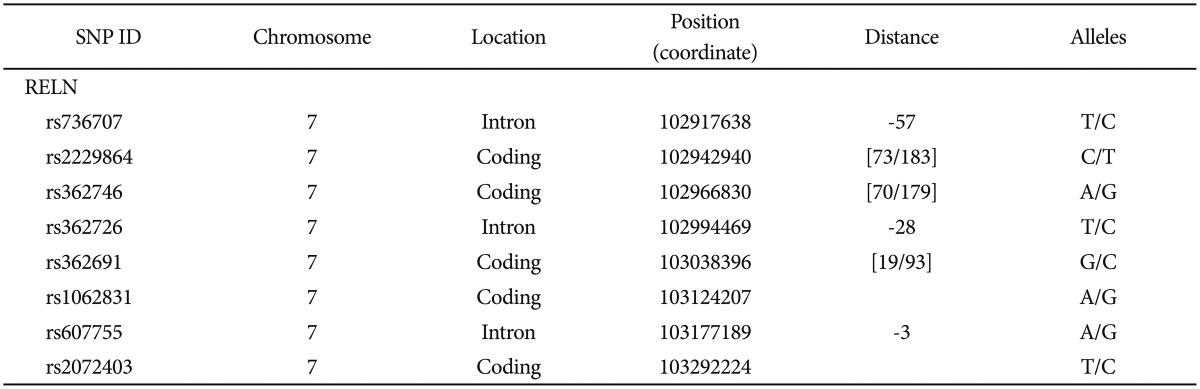
RELN rs736707, rs22 29864, rs362746, rs362726, rs362691, rs1062831, rs607755, and rs2072403 were genotyped by Illumina, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA) through the use of their Integrated Bead Array System (Table 2). We supplied Illumina with barcoded DNA microtiter plates containing the DNA quantified with Pico Green to be at 100 ng/mL and Illumina delivered genotypes with quality scores calculated by proprietary Illumina algorithms.
We performed independent t-tests for age, chi-square tests for sex, and chi-squre tests to compare the results of the control group and the ADHD group through the frequency of the genotypes and alleles. SPSS PC software (version 15.0) was used for the statistical analysis and the significance level was set to the p value being less than 0.05. The calculation revealed that a sample size of 210 subjects is required to obtain a power that is 95% or higher in the chi-square test between the control group and the patients group. Our study was conducted with 339 subjects and the power was 97.41%. This indicates that the association of the RELN gene polymorphism and ADHD can be sufficiently accounted for by the results in this study. However, we performed the power program analysis for the chi-squre test with 339 subjects and the result showed that the effect size was 0.46 (moderate level).
The subjects were a total of 339 children. The children in both of the ADHD group and the control group had never taken any psychostimulant in advance. There was no difference in the age (t=0.06, p=0.813) and sex (χ2=3.79, p=0.052) between the control group and the ADHD children group (Table 2).
The RELN-rs736707 genotypes of the 159 subjects in the control group and the 180 subjects in the ADHD group were T/T alleles (37.58%:31.46%), T/C alleles (47.13%:42.70%) and C/C alleles (15.29%:25.84%), and there was a significant difference in the frequency of genotypes between the two groups (χ2=2.24, df=2, p=0.025). The RELN-rs736707 allele of the 159 subjects in the control group and the 180 subjects in the ADHD group were T alleles (61.15%:52.81%) and C alleles (38.85%:47.19%), and there was a significant difference in the frequency of allele between the two groups (χ2=2.15, df=1, p=0.031) (Table 3).
For the RELN-rs736707 genotypes, the odds ratio was significant at 2.02 (confidence interval: 1.09-3.73, p=0.025). Also for the RELN-rs736707 allele, the odds ratio was significant at 1.40 (confidence interval: 1.03-1.90, p=0.031) (Table 3).
This study is a case-controlled study in which the frequency of the genotypes and alleles of RELN were compared between the ADHD children and the control group in Korea. The correlation between the genotypes and alleles of eight candidate RELN SNPs was investigated. This study showed that there was a significant correlation between the frequencies of the RELN-rs736707. This study showed that there was a significant correlation between the frequencies of the RELN-rs736707 and ADHD, this result is reported for the first time in child ADHD studies.
Li et al.13 reported the association between rs5906883 genetic polymorphism of the RELN gene and Autism was reported first in Asia. But no association has been reported about correlation between ADHD and RELN gene polymorphism. In this study, the correlation between ADHD and RELN-rs736707 genetic polymorphism was found in this study firstly.
Combining the results about the correlation between the RELN rs736707 and ADHD, it can be understood that the failure of RELN regulation may cause the changes in neurodevelopmental process and may be correlated with the vulnerability of various psychiatric diseases including ADHD and movement disorder. These receptors can affect the NMDA-mediating action, which is related with the symptoms found in the children with ADHD. This study also suggests that the failure to regulate the RELN expression causes changes in the synaptogenesis and neural migration and the structural development of the brain regions related with nerve activity, attention and impulsivity. Recently, a very large study by Plessen et al.28 involving children and adolescents with ADHD reported an increased volume of the hippocampus bilaterally in those with the disorder. The hippocampus is known to be involved in attentional processes such as visuospatial working memory29 and in modulating executive functions.30 Disturbances in these functional domains belong to core symptoms of ADHD.24 In the same study, the authors reported indirect evidence of a reduced size of the basolateral amygdala complex in children and adolescents with ADHD. The finding of altered amygdala and hippocampus volumes in ADHD is of particular interest for adult patients with ADHD because affective symptoms, emotional instability and impulsivity often dominate the clinical picture in this age group compared with hyperactivity and inattentiveness, which often play a minor role. Based on previous findings in children with ADHD described by Plessen et al.,26 we suspected that abnormality of the amygdala and the hippocampus have the association RELN polymorphism abnormality. Hence, the correlation between the RELN gene and ADHD should be carefully handled and the result of our study should be verified in the future study with a large number of independent samples.
The limitations of this study are as follows: first, the number of subject children was small. The subjects of this study were 180 ADHD children and 159 children in the control group. Second, the results of this study may not be generalized for the cases of other racial or ethnic groups since the frequency of alleles can vary due to local or racial differences. The distribution of the allele frequency in the ADHD patient children and parents group in this study was also different from that of other countries. Third, only a few SNPs were investigated in this study among the many genes related with the various ADHD phenotypes. Although it is clear that not just one genetic factor causes the increased ADHD vulnerability, we did not consider the interaction with other risk factors.
Despite the methodological limitations described before, this study has several advantages. First, the patient group and the control group were matched so that there was no difference in the frequency of sex and age. The prevalence of ADHD is higher among males and in adolescence; thus, the sex and age characteristics can have a great effect. Considering this, our study was evaluated by matching the age and sex of the patient group and the control group with each other. Second, this study used population-based samples. Previous studies in Korea were hardly considered to represent the general population because the subjects were usually ADHD children who visited hospitals for their clinical symptoms. In this study, the subjects in the risk group were selected by the questionnaire survey from the whole population in a region and the patient and control samples were obtained by random contact. Thus, the subjects in this study may be more appropriate to the characteristics of general population than those of the study performed with the patients who visited hospitals. Third, both the patient group and control group in this study underwent clinical evaluation and DSM-IV diagnosis by children psychiatrists, applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria strictly, and thus the patient group was composed of pure ADHD diagnosed subjects.
We expect that different allele distribution results may be produced from future studies on the quantitative correlation of the ADHD performance in the pure ADHD group from which co-existing diseases are excluded, the patients group composed of only boys or girls, the subtype groups such as hyperactivity dominant group and attention deficiency dominant group, and the drug response group.
References
1. American Psychiatric Association Committee on Nomenclature and Statistics. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Press; 1994.
2. Cho SC, Shin YO. Prevalence of disruptive behavior disorders. J Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1994;5:141-149.
3. Kim JY, Ahn DH, Shin YJ. An epidemiological study of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and learning disabilities in a rural area. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 1999;38:784-793.
4. Faraone SV, Doyle AE. The nature and heritability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 2001;10:299-316. PMID: 11351800.


5. de Bergeyck V, Naerhuyzen B, Goffinet AM, Lambert de Rouvroit C. A panel of monoclonal antibodies against reelin, the extracellular matrix protein defective in reeler mutant mice. J Neurosci Methods 1998;82:17-24. PMID: 10223511.


6. DeSilva U, D'Arcangelo G, Braden VV, Chen J, Miao GG, Curran T, et al. The human reelin gene: isolation, sequencing, and mapping on chromosome 7. Genome Res 1997;7:157-164. PMID: 9049633.


7. Tueting P, Doueiri MS, Guidotti A, Davis JM, Costa E. Reelin down-regulation in mice and psychosis endophenotypes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2006;30:1065-1077. PMID: 16769115.


8. Qiu S, Korwek KM, Pratt-Davis AR, Peters M, Bergman MY, Weeber EJ. Cognitive disruption and altered hippocampus synaptic function in reelin haploinsufficient mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2006;85:228-242. PMID: 16376115.


9. Weeber EJ, Beffert U, Jones C, Christian JM, Forster E, Sweatt JD, et al. Reelin and ApoE receptors cooperate to enhance hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning. J Biol Chem 2002;277:39944-39952. PMID: 12167620.


10. Ventruti A, Kazdoba TM, Niu S, D'Arcangelo G. Reelin deficiency causes specific defects in the molecular composition of the synapses in the adult brain. Neuroscience 2011;189:32-42. PMID: 21664258.


11. Beffert U, Morfini G, Bock HH, Reyna H, Brady ST, Herz J. Reelin-mediated signaling locally regulates protein kinase B/Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Chem 2002;277:49958-49964. PMID: 12376533.


12. Sinagra M, Verrier D, Frankova D, Korwek KM, Blahos J, Weeber EJ, et al. Reelin, very-low-density lipoprotein receptor, and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 control somatic NMDA receptor composition during hippocampal maturation in vitro. J Neurosci 2005;25:6127-6136. PMID: 15987942.



13. Folsom TD, Fatemi SH. The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuropharmacology 2013;68:122-135. PMID: 22981949.


14. Serajee FJ, Zhong H, Mahbubul Huq AH. Association of Reelin gene polymorphisms with autism. Genomics 2006;87:75-83. PMID: 16311013.


15. Li H, Li Y, Shao J, Li R, Qin Y, Xie C, et al. The association analysis of RELN and GRM8 genes with autistic spectrum disorder in Chinese Han population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008;147B:194-200. PMID: 17955477.


16. Ashley-Koch AE, Jaworski J, Ma de Q, Mei H, Ritchie MD, Skaar DA, et al. Investigation of potential gene-gene interactions between APOE and RELN contributing to autism risk. Psychiatr Genet 2007;17:221-226. PMID: 17621165.


17. Goes FS, Willour VL, Zandi PP, Belmonte PL, MacKinnon DF, Mondimore FM, et al. Sex-specific association of the reelin gene with bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2010;153B:549-553. PMID: 19691043.



18. Falconer DS. Two new mutants, trembler and 'reeler', with neurological actions in the house mouse (Mus musculus L.). J Genet 1951;50:192-201. PMID: 24539699.


19. Curran T, D'Arcangelo G. Role of reelin in the control of brain development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 1998;26:285-294. PMID: 9651544.


20. Tissir F, Goffinet AM. Reelin and brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2003;4:496-505. PMID: 12778121.


21. Hamburgh M. Analysis of the postnatal developmental effects of "reeler" a neurological mutation in mice. A study in developmental genetics. Dev Biol 1963;8:165-185. PMID: 14069672.


22. Boyle MP, Bernard A, Thompson CL, Ng L, Boe A, Mortrud M, et al. Cell-type-specific consequences of Reelin deficiency in the mouse neocortex, hippocampus, and amygdala. J Comp Neurol 2011;519:2061-2089. PMID: 21491433.


23. So YK, Noh JS, Kim YS, Kim SG, Ko YJ. The reliability and validity of Korean parent and teacher ADHD Rating Scale. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 2002;41:283-289.
24. Kovacs M. The Children's Depression Inventory: A Self-Rated Depression Scale for School-Aged Youngsters. University of Pittsburgh. Unpublished manuscript; 1983.
25. Cho SC, Lee YS. Development of the Korean form of the Kovacs' Childhood Depression Inventory. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 1990;29:943-956.
26. Cho SC, Choi JS. Development of Korean form of the state-trait anxiety inventory for children. Seoul J Psychiatry 1989;14:150-157.
27. Shin MS, Cho SC, Chun SY, Hong KM. A study of the development and standardization of ADHD diagnostic system. J Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000;11:91-99.
28. Plessen KJ, Bansal R, Zhu H, Whiteman R, Amat J, Quackenbush GA, et al. Hippocampus and amygdale morphology in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:795-807. PMID: 16818869.



29. Bedard AC, Martinussen R, Ickowicz A, Tannock R. Methylphenidate improves visual-spatial memory in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2004;43:260-268. PMID: 15076258.


30. Sergeant JA, Geurts H, Oosterlaan J. How specific is a deficit of executive functioning for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? Behav Brain Res 2002;130:3-28. PMID: 11864714.