 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 15(10); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The present meta-analysis aimed to analyze the cognitive performance of schizophrenia patients measured by Trail Making Tests (TMT) and the contribution of socio-demographic factors to cognitive impairments.
Methods
PubMed and PsycARTICLES databases were searched for the studies published between January 1985 and November 2017. Data were drawn from 19 studies encompassing 1095 patients and 324 controls. The effect size and heterogeneity were assessed with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 2 using random-effect model.
Results
Overall, the results showed that the schizophrenia patients performed significantly (p<0.001) worse than healthy controls in both TMT-A and B. However, concurrent substance abuse, clinical status (inpatient or outpatient), duration of education and duration of illness were not associated with cognitive impairment among the schizophrenia patients.
Cognitive impairments are one of the common neurocognitive abnormalities in schizophrenia [1,2]. The deficits involve a number of cognitive domains such as general intelligence, attention, working memory, verbal fluency, verbal learning and memory as well as executive functioning [3]. These cognitive domains are assessed using several neuropsychological testing batteries. Trail Making Test (TMT) is commonly used to assess motor processing speed, complex visual scanning and cognitive flexibility [4]. TMT-A, which is used to evaluate processing speed, requires the participant to connect the serially numbers that are scattered on a page by drawing a line. Meanwhile, TMT-B is done by alternately linking the sequentially numbers and letters on a page. This will provide information on cognitive flexibility of the individual [5].
Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia patients can be associated with several factors such as age [6], gender [7]. education duration, illness duration [8], age of onset and negative symptoms [9]. However, the effects of these factors on cognitive domains are inconclusive [10-13]. TMT is highly sensitive to attentional and executive impairments, as well as to psychomotor slowing. It is proven that the TMT performance is affected by age, education and intelligence [14,15], where age and education were significantly correlated with TMT-A and TMT-B scores [4]. Although substance-abusing schizophrenia patients had worse clinical outcomes compared to non-substance abusing patients [16], a study demonstrated that schizophrenia patients with substance abuse showed substantially better performance in executive functions measured by TMT-A and B [17]. On the other hand, several studies showed no significant difference in executive functions between these two groups of patients [18,19].
As cognitive impairment has been proposed as putative endophenotypes in schizophrenia [20,21], investigation of factors that may affect the cognitive performance is essential. Thus, the current study aimed to conduct a meta-analysis on cognitive processing speed as well as cognitive flexibility of schizophrenia patients based on TMT-A and TMT-B scores, respectively. Our study also investigated the association of substance abuse, education duration, illness duration and patientsŌĆÖ clinical status with their cognitive performance.
Two databases, PsycARTICLES and PubMed, were searched with these keywords: ŌĆ£trail making test,ŌĆØ ŌĆ£schizophrenia patients,ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£controlled studies.ŌĆØ The search included articles related to human subjects published from 1985 until November 2017 and was not subjected to English-language restriction. At the first stage of screening, a total of 263 studies was identified, including 242 papers from PsycARTICLES and 21 papers from PubMed. Then, non-related articles, such as literature reviews, meta-analysis, interviews, systematic reviews and mathematical model papers were filtered. This led to the retrieval of 32 eligible articles for full-text review (Figure 1).
All the selected articles selected met the following criteria. First, all the patients included in this analysis must be diagnosed within the schizophrenia spectrum i.e. schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and schizophreniform disorder, based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision (ICD-10) criteria. Second, the data for TMT-A and TMT-B must be presented as separated values and completed with mean, standard deviation and total sample number. Third, for randomized trials and pilot studies, only baseline scores were included in the analysis. For this, due to the present of two TMT values in a single article, the article was cited with the addition of ŌĆśaŌĆÖ and ŌĆśbŌĆÖ letter in the parentheses at the end of authorŌĆÖs name. Thus, from the 32 retrieved articles, only 19 of those met the inclusion criteria.
First authorsŌĆÖ names, year of publication, characteristics of participants as well as the mean and standard deviation values of TMT (TMT-A and B) were extracted from each paper (Table 1). Two types of analyses were conducted: 1) comparison between the TMT scores of schizophrenia patients and healthy controls and 2) mean of each of the TMT scores among the patients. Subgroup analyses were performed in order to study the association between cognitive performance of patients and their duration of education, duration of illness as well as their hospital status as inpatients or outpatients. The mean age of the cases ranged between 23.0 years to 43.0 years for patients and 23.8 years to 42.0 years for controls. Meanwhile, the mean education and duration of illness of the patients ranged from 10.0 years to 12.8 years and 1.0 year to 18.2 years, respectively. In terms of drug history, the patients in all but 2 studies were medicated at the time of assessment. In general, the patients from different studies had received one or combination of these therapies: antipsychotic drugs, antidepressant, antiparkinsonian, minor tranquilizers and mood stabilizers.
The cognitive functional areas assessed by TMT-A and TMT-B are the psychomotor processing speed and cognitive flexibility, respectively. All analyses were performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) version 2 (Biostat, Englewood, NJ, USA). Depending on the Q statistic value, either the fixed or random effects model were adopted to calculate the effect sizes (ESs) and 95% confidence. In this study, the ESs were analyzed as standardized difference in means (SMDs). Then, the SMDs of TMT data was used to determine the probability of superiority (PS) [40]. The mean time for TMT-A and B completions were compared to the standard. The standard average time to complete TMT-A and B are 29 seconds and 75 seconds, respectively. However, the cognitive functioning was considered deficit if the time to complete TMT-A and B exceeds 78 seconds and 273 seconds, respectively. If the heterogeneity was considered non-trivial, a random effects model was applied in the meta-analysis. Otherwise, a fixed effects model would be utilized. The heterogeneity between studies was quantified using I-squared (I2) and tau-squared (Žä2) [41]. I2 describes the percentage of observed variance across studies which caused by heterogeneity rather than chance [42]. The magnitude of heterogeneity is divided into 3 levels, which are low (I2Ōēż25%), moderate (25%< I2Ōēż50%) and high (I2>50%). Meanwhile, Žä2 indicates the actual variance between-studies in the random effects model. Subgroup analyses based on the presence or absence of substance abuse disorder, patientsŌĆÖ clinical status (inpatient or outpatient), the duration of their education and illness were conducted in the presence of heterogeneity. The difference in the mean completion time for each subgroups was examined using the StudentŌĆÖs t-test with SPSS 14.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with the significant differences at p<0.050.
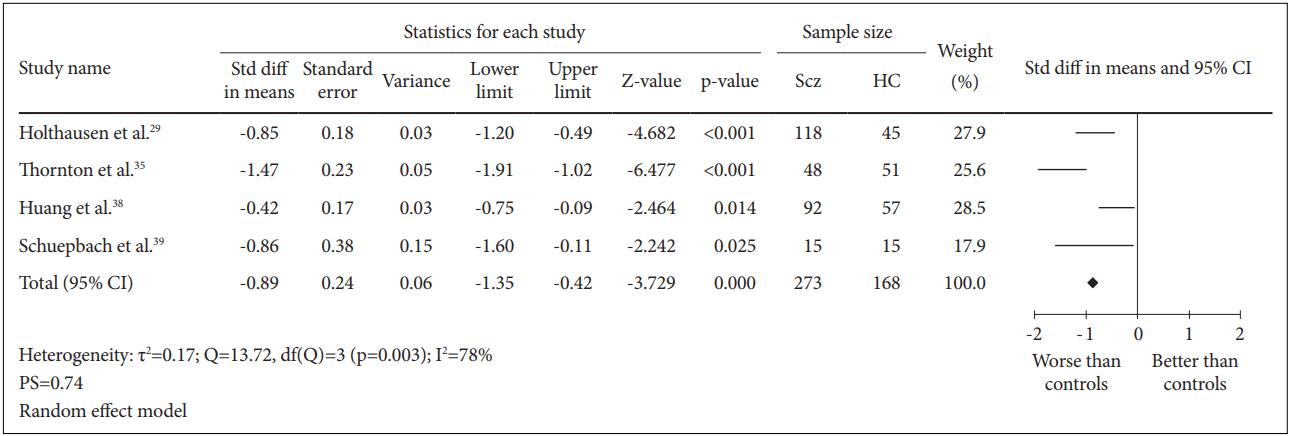
Four case-control studies for a total of 441 subjects were included in this analysis. The comparison between 273 schizophrenia patients and 168 healthy controls generated SMD=-0.89 [random effect, 95% CI (-1.35, -0.42), Z=-3.729, p=0.000] with I2=78% and PS=0.74 (Figure 2). These results demonstrated that there was a significant reduction in psychomotor processing speed among patients with schizophrenia with a high probability (74%) to identify a schizophrenia patient suffering deficit in processing speed compared to healthy controls. However, there was a significantly (p=0.003) high heterogeneity between the studies of which 78% of the observed variance might be caused by the actual difference in the effect size rather than random error.
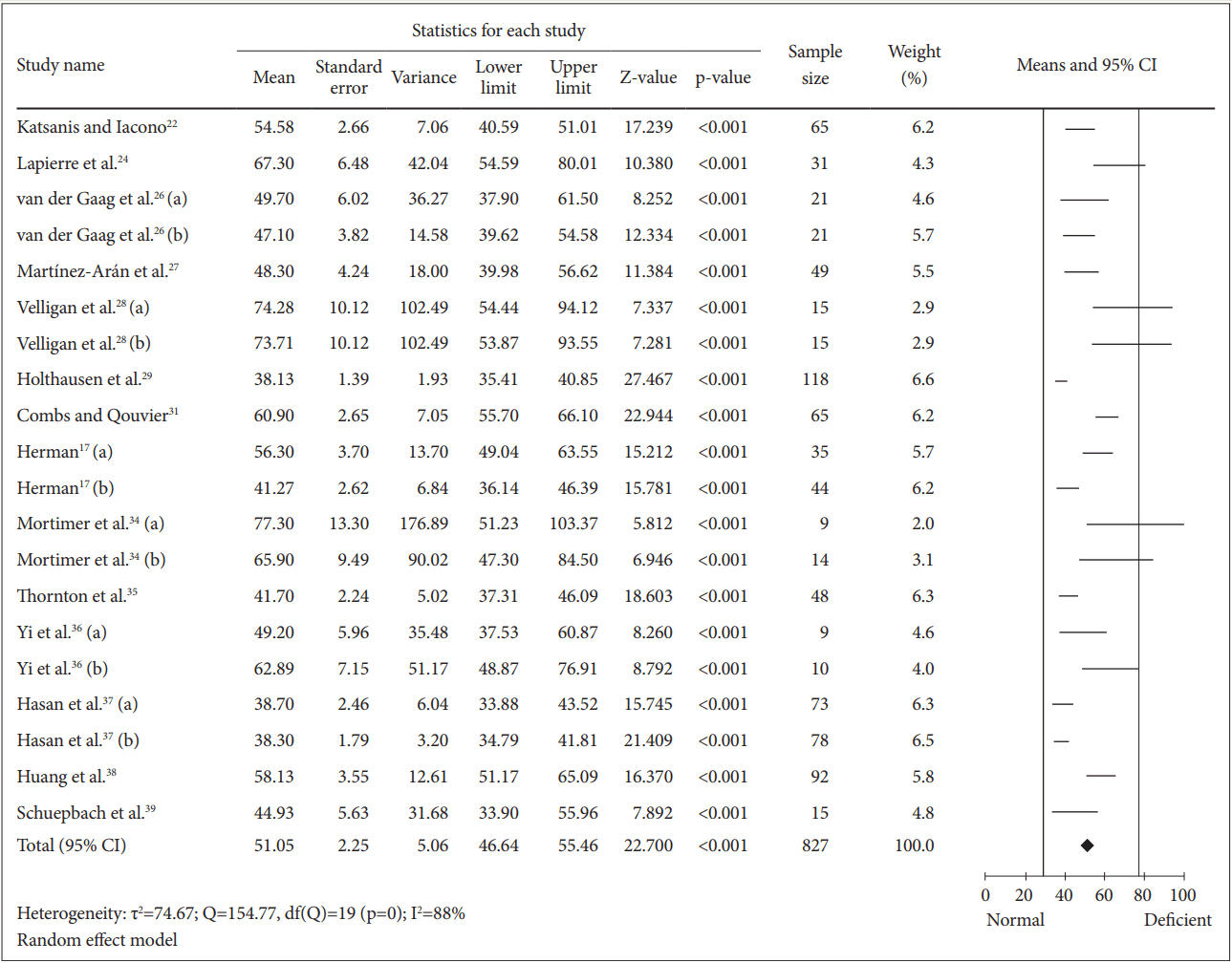
To determine the mean for completion of TMT-A among the schizophrenia patients, 827 patients were included in the analysis (Figure 3). The calculated mean was 51.05 [random effect, 95% CI (46.64, 55.46), Z=22.700, p=0.000] with I2=88%. Nevertheless, the heterogeneity test showed a significant (p=0.000) dispersion across the effect size. Thus, subgroup analyses were performed. All analyses showed that substance abuse, education and clinical status and duration of illness caused insignificant (p>0.050) differences on the mean of TMT-A completion time (Table 2). We also found that the drug naïve patients in the study of Huang et al. [38] spent longer time (7.08 seconds) than overall patients in completing TMT-A test.
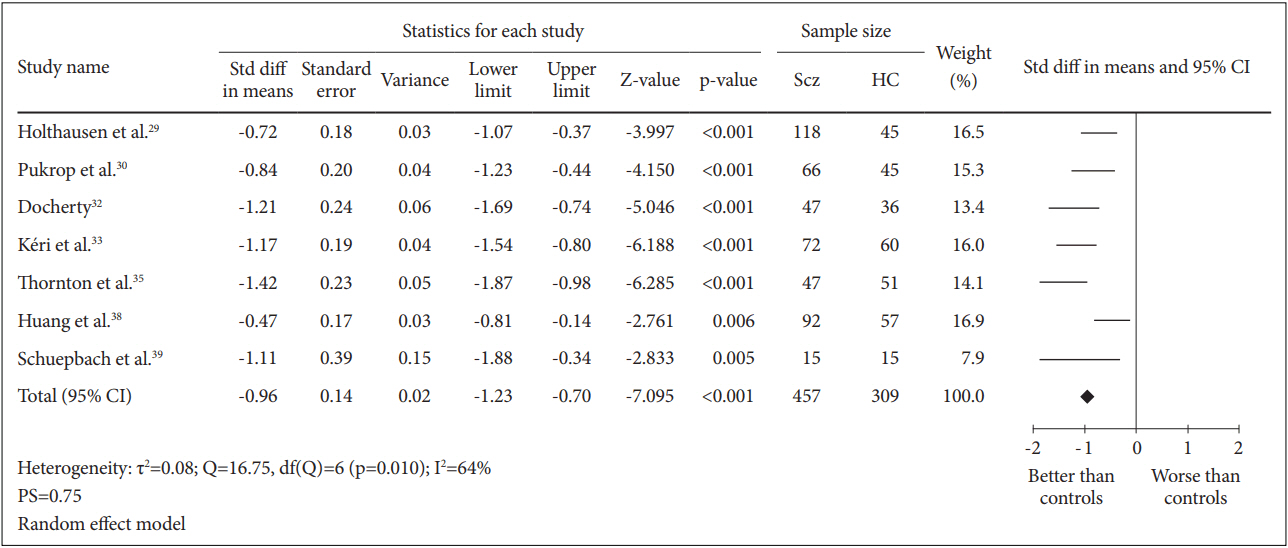
A total of 7 case-control studies were included in this analysis. The SMD for the comparison between 457 schizophrenia patients and 309 healthy controls was -0.96 [95% CI (-1.23, -0.70)] and this value was statistically significant (random effect, Z=-7.095, p=0.000) with I2= 64% and PS= 0.75, indicating that patientsŌĆÖ cognitive flexibility was impaired (Figure 4).
Meanwhile, the mean for overall patientsŌĆÖ TMT-B was 126.28 [random effect, 95% CI (105.69, 146.87), Z=12.021, p=0.000] with I2= 98% (Figure 5). Due to the high magnitude of heterogeneity between studies, subgroup analyses were conducted (Table 3). However, all the differences in the mean completion time obtained from subgroup analyses for TMT-B were insignificant (p>0.050). However, the completion time for drug na├»ve patients [38] was 11.97 seconds faster than the overall patients.
As supported by other studies [43-45], current meta-analysis study demonstrated that psychomotor processing speed and cognitive flexibility of schizophrenia patients were significantly impaired compared to the healthy controls. In addition, meta-analysis of TMT-A and B scores obtained from drug na├»ve schizophrenia patients also demonstrated that they performed worse than the healthy controls [46]. Based on the calculated mean time of completion of TMT-A and B in the current study, we can conclude that patientsŌĆÖ cognitive performances were below average but did not fall in the deficit category. Cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia patients may caused by genetic and socio-demographic factors [47-51].
Cognitive performances in schizophrenia has been associated with the synchronization of neuronal activity in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus [52]. Cognitive flexibility is controlled by dopaminergic, serotonergic and cholinergic systems [53]. Interaction of serotonergic system with other neurotransmitter systems mediates modulatory effects on cognitive performances [54]. Drug abuse can be a risk factor of schizophrenia manifestation or as a consequence of the underlying schizophrenia neuropathology. Drugs abuse and cognitive impairments in schizophrenia might be attributed to the shared mechanisms [55]. Due to the antipsychotic medications, the dopamine (DA) neurotransmission will be interfered as a result of the D2 receptor blockade in nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum, leading to anhedonia [55]. Consequently, in order to compensate the induced anhedonia, patients may seek for drug abuse which leads to the aggravation of negative symptoms and cognitive deficits [55]. In addition, even in individual without schizophrenia manifestation, drug intoxication from the use of cocaine, methamphetamine and marijuana can cause psychotic episodes as a result of excess DA in nucleus accumbens and striatal as well as DA deficit in prefrontal cortex [54]. Contradictory to previous findings [56,57], our study showed that there was no effect of concurrent drug abuse on the patientsŌĆÖ cognitive performances. However, after the subdivision, the I2 and Žä2 values were reduced compared with the overall analysis for each TMT. Nevertheless, the Žä2 values for the substance abuse subgroup remained high, due to the inclusion of mixed group of patients in the subgroup analysis of substance abuse. Approximately 73% of the patients were concurrent substance abuser. Thus, the overall score for both tasks might not fully reflect their cognitive performance.
Years of formal schooling will reflect the pre-morbid functioning, intellectual level and higher level of information-processing skills in patients [13]. It has been demonstrated that longer duration of formal education will give positive impact on several cognitive domains such as vigilance, executive function, memory and constructional ability [13]. Although we did not find significant effect of duration of education on both cognitive domains, our results are suggestive of the idea that education affects executive function more strongly than processing speed.
In addition, hospitalization will also affect the cognitive functions of schizophrenia patients. As shown by the results from analysis of TMT-B, outpatients without concurrent substance abuse performed better than inpatients. This observation complements previous findings [58], which indicated a correlation between hospitalization and cognitive regression development. Additionally, delirium, treatment, anxiety and depression during hospitalization could be potential contributors to the relationship between hospitalization and cognitive decline.
Last but not least, we found that duration of illness had only a small effect on cognitive performances of the patients. Patients with longer duration of illness exhibited only slightly larger means of TMT completion time. Another study also demonstrated that cognitive impairment began at the illness onset and remained stable throughout the illness course [8]. Moreover, Srinivasan and colleagues found that most of the neuropsychological batteries used to measure cognitive functions in schizophrenia were stable over a range periods of illness [13].
Our study has several limitations. We were unable to investigate the correlation between schizophrenia subtypes or spectrums and patientŌĆÖs processing speed as well as cognitive flexibility due to the lack of studies concerning these subjects. In addition, we could not compare the TMT scores between medicated and drug naive patients. We could only compare the mean of overall data for each TMT test with the results for drug na├»ve patients obtained by Huang et al. [38] Our comparison showed that drug na├»ve patients had slower performance to complete TMT-A but better performance in TMT-B. This is because treatment with typical and/or atypical antipsychotics might have an impact on TMT scores. This is because, typical antipsychotics usually antagonize D2 receptors due to their high affinity towards the receptors [59] while most atypical antipsychotics block either only D2 receptors or concurrently antagonize HTR2A and D2 receptors [60]. The blocking of D2 receptors, especially by typical antipsychotics may lead to Parkinsonian side effects and tardive dyskenia, as a result of the drug accumulation in the brain tissue [61]. This in turns may lead to difficulty for the patients to complete the TMT as this test is highly reflected by motor rigidity.
In conclusion, the current meta-analysis study indicated that the cognitive function of schizophrenia patients measured by TMT-A and B were impaired compared to healthy controls. Substance abuse, patientsŌĆÖ clinical status, duration of education as well as illness showed only small effects on the tasksŌĆÖ scores. These findings demonstrated that the studied variables may not affect the patientsŌĆÖ TMT scores greatly.
Figure┬Ā2.
Measures of cognitive processing speed using TMT-A. Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence interval (CI). The diamond represents the point estimate for the effect size. The vertical line represents the reference of no difference in means between the schizophrenia (Scz) group and healthy control (HC) group. df: degree of freedom, PS: probability of superiority, std diff: standardized difference, Žä2 : tausquared. TMT-A: Trail Making Test A.
Figure┬Ā3.
Means of TMT-A completion time for all schizophrenia patients. Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence interval (CI). The diamond represents the point estimate for the mean effect size. The vertical lines represent the standard reference of mean for normal (black line) and deficient (gray line) cognitive performance. df: degree of freedom, Žä2 : tau-squared. TMT-A: Trail Making Test A.
Figure┬Ā4.
Measure of cognitive flexibility using TMT-B. Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence interval (CI). The diamond represents the point estimate for the effect size. The vertical line represents the reference of no difference in means between the schizophrenia (Scz) group and healthy control (HC) group. df: degree of freedom, std diff: standardized difference, Žä2 : tau-squared. TMT-B: Trail Making Test B.
Figure┬Ā5.
Means of TMT-B completion time for schizophrenia patients only. Horizontal lines represent 95% confidence interval (CI). The diamond represents the point estimate for the mean effect size. The vertical lines represent the standard reference of mean for normal (black line) and deficient (gray line) cognitive performance. df: degree of freedom, Žä2 : tau-squared. TMT-B: Trail Making Test B.

Table┬Ā1.
Characteristics of studies included in the present meta-analysis
| Authors | TMT-A(N) | TMT-B(N) | Mean age (years) | % Male | Patients status | Education (years) | Duration of illness (years) | Psychopathological evaluation | Patients medication | Schizophrenia spectrum diagnosis | Substance abused |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Katsanis and Iacono [22] | 65 Scz | 65 Scz | 28.15 | 87 | Inpatients | NA | 9.51 | BPRS: 33.53 | 62 Scz on antipsychotics | 65 Chronic schizophrenia | No |
| GAF: 36.74 | 44 Scz on AP agents | ||||||||||
| NSI: 5.33 | 4 Scz on lithium carbonate | ||||||||||
| PSI: 6.93 | 4 Scz on AD | ||||||||||
| 12 Scz on minor tranquilizers | |||||||||||
| Goldberg et al. [23] | NA | 57 Scz | 34.00 | 53 | Inpatients | NA | 11.1 | BPRS | 13 Scz on antipsychotics | 57 Schizophrenia | No |
| Positive symptoms: 21.1 | 15 Scz on antipsychotics and AD | ||||||||||
| Negative symptoms: 9.2 | 1 Scz on lithium | ||||||||||
| 11 Scz on lithium and antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| 3 Scz on AD | |||||||||||
| 1 Scz on others | |||||||||||
| 3 Scz drug naive | |||||||||||
| Lapierre et al. [24] | 31 Scz | 31 Scz | 36.00 | 100 | Outpatients | 10 | NA | PANSSP: 13 | All Scz on several psychiatric medications | 31 Schizophrenia | Yes (16/31) |
| PANSSN: 14 | |||||||||||
| 15 HC | 15 HC | 33.87 | 67 | 19.17 | None | ||||||
| Docherty et al. [25] | NA | 26 Scz | 32.00 | 80 | Outpatients | 13 | 10 | GAF: 53 | All Scz on antipsychotics | 26 Stable schizophrenia | No |
| 8 Scz on typical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| 18 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| 9 Scz on AP agents | |||||||||||
| 6 Scz on MS | |||||||||||
| 12 Scz on others | |||||||||||
| van der Gaag et al. [26] (a) | 21 Scz | 21 Scz | 30.40 | 62 | Inpatients | Scale: 4.3 | 9.9 | NA | All on stable antipsychotics | 21 Schizophrenia | No |
| 6 Scz on clozapine | |||||||||||
| 36 Scz on typical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| van der Gaag et al. [26] (b) | 21 Scz | 21 Scz | 31.70 | 67 | Inpatients | Scale: 4.7 | 9.6 | NA | 21 Schizophrenia | No | |
| Mart├Łnez-Ar├Īn et al. [27] | 49 Scz | 49 Scz | 30.40 | 78 | Outpatients | 11.3 | NA | GAF: 69.8 | 45 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 49 Schizophrenia | No |
| PANSSP: 11.5 | 4 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | ||||||||||
| PANSSN: 22.5 | 22 Scz on AD | ||||||||||
| 4 Scz on MS | |||||||||||
| Velligan et al. [28] (a) | 15 Scz | 15 Scz | 39.33 | 53 | Outpatients | 11.2 | NA | BPRS positive: 2.62 | 13 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | 11 Schizophrenia/4 Schizoaffective disorder | Yes (2/15) |
| NSA total: 72.47 | |||||||||||
| Velligan et al. [28] (b) | 15 Scz | 15 Scz | 38.93 | 60 | Outpatients | 11.2 | NA | BPRS positive: 3.32 | 10 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | 11 Schizophrenia/4 Schizoaffective disorder | Yes (2/15) |
| NSA total: 70.40 | |||||||||||
| Holthausen et al. [29] | 118 Scz | 118 Scz | 23.30 | 74 | NA | Scale: 4 | NA | PANSSP*: 2.22 | 25 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 84 Schizophrenia/15 Schizoaffective disorder/19 Schizophreniform disorder | Yes (99/118) |
| PANSSN*: 2.33 | 75 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | ||||||||||
| 45 HC | 45 HC | 24.00 | 84 | Scale: 5.4 | None | 18 Scz did not use antipsychotics | |||||
| 10 Scz on AC | |||||||||||
| Pukrop et al. [30] | NA | 66 Scz | 30.10 | 70 | Inpatients | NA | NA | PANSSP: 16.5 | 35 Scz unmedicated | 61 Paranoid/2 Disorganized/3 Undifferentiated schizophrenia | No |
| PANSSN: 20.1 | 4 Scz on typical antipsychotic | ||||||||||
| NA | 45 HC | 29.60 | 31 | NA | None | 27 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||
| Combs and Qouvier [31] | 65 Scz | 65 Scz | 40.7 | 55 | NA | 11.2 | 18.2 | BPRS: 53.8 | 15 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 65 Chronic schizophrenia | No |
| 34 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| 16 Scz on both antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| 36 Scz on AC agents | |||||||||||
| Herman [17] (a) | 35 Scz | 35 Scz | 42.17 | N.a. | Inpatients | 10.9 | NA | BPRS: 55.55 | 12 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 35 Schizophrenia | No |
| 32 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| Herman [17] (b) | 44 Scz | 43 Scz | 30.86 | N.a. | Inpatients | 11.26 | NA | BPRS: 45.60 | 13 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 44 Schizophrenia | Yes (44/44) |
| 33 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||||||||
| Docherty [32] | 47 Scz | 47 Scz | 43.00 | 83 | Inpatients | 13 | NA | BPRS: 49 | NA | 47 Schizophrenia | No |
| GAF: 42 | |||||||||||
| 36 HC | 36 HC | 42.00 | 39 | 14 | None | ||||||
| Keri et al. [33] | NA | 72 Scz | NA | 65 | Outpatients | N.a. | NA | BPRS: 30.4 | 20 Scz on typical antipsychotics | 72 Schizophrenia | No |
| NA | 60 HC | NA | 67 | N.a. | None | 51 Scz on atypical antipsychotics | |||||
| Mortimer et al. [34] (a) | 9 Scz | 8 Scz | N.a. | NA | NA | NA | NA | BPRS: 30.8 (N=ll) | Patients on antipsychotics, AD, AC and/or benzodiazepine medications | (N=NA) Schizophrenia/Schizophreniform disorder | NA |
| Predominant positive symptomatology | |||||||||||
| Mortimer et al. [34] (b) | 14Scz | 14 Scz | N.a. | NA | NA | NA | NA | BPRS score: 35.3 (N=16) | (N=NA) Schizophrenia/S chizophreniform disorder | NA | |
| Predominant positive symptomatology | |||||||||||
| Thornton et al. [35] | 48 Scz | 47 Scz | 35.90 | 64 | Inpatients | 11.4 | 14.5 | NA | 44 Scz on antipsychotic medication | 39 Schizophrenia/11 Schizoaffective disorder | No |
| Yi et al. [36] (a) | 9 Scz | 9 Scz | 41.40 | 78 | Outpatients | 12.3 | NA | PANSSP: 14.4 | Patients on antipsychotics | (N=NA) Schizophrenia/Schizoaffective disorder | No |
| PANSSN: 14.6 | |||||||||||
| Yi et al. [36] (b) | 10 Scz | 10 Scz | 39.70 | 70 | Outpatients | 12.8 | NA | PANSSP: 13.9 | Patients on antipsychotics | (N=NA) Schizophrenia/Schizoaffective disorder | No |
| PANSSN: 17.5 | |||||||||||
| Hasan et al. [37] (a) | 73 Scz | 71 Scz | 36.40 | 86 | Inpatients and outpatients | 11.5 | NA | PANSSP: 14.2 (N=67) | Patients on stable antipsychotics | 73 schizophrenia | No |
| PANSSN: 25.6 (N=68) | |||||||||||
| Hasan et al. [37] (b) | 78 Scz | 76 Scz | 35.50 | 72 | Inpatients and outpatients | 11.2 | NA | PANSSP: 13.0 (N=71) | Patients on stable antipsychotics | 78 schizophrenia | No |
| PANSSN: 25.2 (N=74) | |||||||||||
| Huang et al. [38] | 92 Scz | 92 Scz | 22.86 | 39 | NA | 10.77 | 12.26 | PANSSP: 23.88 | Drug naive | 92 first-episode schizophrenia | NA |
| PANSSN: 19.30 | |||||||||||
| 57 HC | 57 HC | 23.84 | 42 | 11.77 | None | ||||||
| Schuepbach et al. [39] | 15 Scz | 15 Scz | 33.20 | 67 | 10 inpatients and 5 outpatients | 12.77 | 10.43 | BPRS: 36.53 | Patients on antipsychotics | 15 chronic schizophrenia | No |
| 15 HC | 15 HC | 33.87 | 67 | 19.17 | None | 4 Scz on AD and/or MS |
AC: anticholinergic, AD: antidepressant, AP: antiparkinsonian, BPRS: Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, GAF: Global Assessment of Functioning, HC: healthy controls, MS: mood stabilizers, N: total number, NA: not available, NSI: Negative Symptom Index, PANSSN: Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Negative, PANSSP: Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Positive, PSI: Positive Symptom Index, Scz: schizophrenia patients
Table┬Ā2.
Summary of subgroup analyses for TMT-A in schizophrenia patients
| Subgroups | Mean and 95% CI | p-value | Sample size | Žä2 | I2 (%) | Q-value | df (Q) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concurrent substance abuse | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. Absent | 48.02 [43.08, 52.97] | 0.112 | 489 | 59.86 | 86 | 76.24 | 11** |
| ŌĆāb. Present | 58.94 [36.83, 81.05] | 223 | 127.69 | 90 | 41.94 | 4** | |
| Education (without concurrent substance abuse) | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. 12 years and below | 47.14 [39.40, 54.89] | 0.482 | 348 | 85.09 | 92 | 68.27 | 5** |
| ŌĆāb. More than 12 years | 50.87 [43.91, 57.84] | 34 | 38.85 | 50 | 4.02 | 4 | |
| PatientsŌĆÖ clinical status (without concurrent substance abuse) | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. Inpatients | 47.89 [42.38, 52.59] | 0.301 | 190 | 21.21 | 66 | 11.88 | 4* |
| ŌĆāb. Outpatients | 51.31 [45.21, 57.41] | 68 | 20.15 | 38 | 3.25 | 2 | |
| Duration of illness | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. 10 years and below | 50.07 [43.92, 56.22] | 0.872 | 199 | 24.18 | 64 | 8.24 | 2* |
| ŌĆāb. More than 10 years | 49.35 [35.35, 63.35] | 128 | 139.41 | 94 | 31.20 | 2** | |
Table┬Ā3.
Summary of schizophrenia patientsŌĆÖ subgroup analyses for TMT-B
| Subgroups | Mean and 95% CI | p-value | Sample size | Žä2 | I2 (%) | Q-value | df (Q) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concurrent substance abuse | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. Absent | 123.08 [103.99,142.18] | 0.779 | 710 | 492.67 | 90 | 138.76 | 14** |
| ŌĆāb. Present | 127.63 [57.45,197.81] | 222 | 6,114.36 | 97 | 149.64 | 4** | |
| Education (without concurrent substance abuse) | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. 12 years and below | 132.01 [102.47,161.55] | 0.675 | 343 | 1,258.86 | 95 | 101.66 | 5** |
| ŌĆāb. More than 12 years | 121.38 [94.95,147.81] | 107 | 755.77 | 85 | 27.08 | 4** | |
| PatientsŌĆÖ clinical status (without concurrent substance abuse) | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. Inpatients | 140.41 [91.83,188.98] | 0.29 | 317 | 1,101.09 | 93 | 76.49 | 5** |
| ŌĆāb. Outpatients | 116.22 [100.26,132.18] | 166 | 46.34 | 32 | 5.92 | 4 | |
| Duration of illness | |||||||
| ŌĆāa. 10 years and below | 114.22 [104.61,123.82] | 0.686 | 183 | 85.9 | 0 | 0.095 | 2 |
| ŌĆāb. More than 10 years | 118.59 [96.44,140.75] | 184 | 448.41 | 88 | 25.26 | 3** | |
REFERENCES
1. Bora E, Y├╝cel M, Pantelis C. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and affective psychoses: implications for DSM-5 criteria and beyond. Schizophr Bull 2010;36:36-42.



2. Heinrichs RW, Zakzanis KK. Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology 1998;12:426-445.



3. Bowie CR, Harvey PD. Cognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2006;2:531-536.



4. Tombaugh TN. Trail Making Test A and B: normative data stratified by age and education. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2004;19:203-214.



5. Kortte KB, Horner MD, Windham WK. The Trail Making Test, Part B: cognitive Flexibility or Ability to Maintain Set? Appl Neuropsychol 2002;9:106-109.


6. Fucetola R, Seidman LJ, Kremen WS, Faraone SV, Goldstein JM, Tsuang MT. Age and neuropsychologic function in schizophrenia: a decline in executive abilities beyond that observed in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry 2000;48:137-146.


7. Leung A, Chue P. Sex differences in schizophrenia, a review of the literature. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 2000;401:3-38.


8. Velligan DI, Miller AL. Cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia and its importance to outcome: the place of atypical antipsychotics in treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 1999;60:25-28.
9. Berman I, Viegner B, Merson A, Allan E, Pappas D, Green AI. Differential relationships between positive and negative symptoms and neuropsychological deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1997;25:1-10.


10. Cuesta MJ, Peralta V, Zarzuela A. Illness duration and neuropsychological impairments in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1998;33:141-150.


11. Kalwa A, Rzewuska M, Borkowska A. Cognitive dysfunction progression in schizophrenia-Relation to functional and clinical outcome. Arch Psychiatry Psychother 2012;1:5-13.
12. Rajji TK, Ismail Z, Mulsant BH. Age at onset and cognition in schizophrenia: meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry 2009;195:286-293.


13. Srinivasan L, Thara R, Tirupati SN. Cognitive dysfunction and associated factors in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Indian J Psychiatry 2005;47:139-143.



14. Spreen O, Strauss E. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms and Commentary. 2nd Ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998.
15. Mitrushina M, Boone KB, Razani J, DŌĆÖElia LF. Handbook of Normative Data for Neuropsychological Assessment. 2nd Ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2005.
16. Swofford CD, Kasckow JW, Scheller-Gilkey G, Inderbitzin LB. Substance use: a powerful predictor of relapse in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1996;20:145-151.


17. Herman M. Neurocognitive functioning and quality of life among dually diagnosed and non-substance abusing schizophrenia inpatients. Int J Ment Health Nurs 2004;13:282-291.


18. Cooper L, Liberman D, Tucker D, Neuchterlein KH, Tsuang J, Barnett HL. Neurocognitive deficits in the dually diagnosed with schizophrenia and cocaine abuse. Psychiatr Rehabil Skill 1999;3:231-245.

19. Pencer A, Addington J. Substance use and cognition in early psychosis. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2003;28:48-54.


20. Ivleva E, Morris D, Osuji J, Moates A, Carmody TJ, Thaker GK, et al. Cognitive endophenotypes of psychosis within dimension and diagnosis. Psychiatry Res 2012;196:38-44.



21. Burdick KE, Goldberg JF, Harrow M, Faull RN, Malhotra AK. Neurocognition as a stable endophenotype in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. J Nerv Ment Dis 2006;194:255-260.


22. Katsanis J, Iacono WG. Clinical, neuropsychological, and brain structural correlates of smooth-pursuit eye tracking performance in chronic schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 1991;100:526-534.



23. Goldberg TE, Gold JM, Greenberg R, Griffin S, Schulz SC, Pickar D, et al. Contrasts between patients with affective disorders and patients with schizophrenia on a neuropsychological test battery. Am J Psychiatry 1993;150:1355-1362.


24. Lapierre D, Braun CMJ, Hodgins S, Toupin J, L├®veill├®e S, Constantineau C. Neuropsychological correlates of violence in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1995;21:253-262.



25. Docherty NM, Hall MJ, Gordinier SW, Cutting LP. Conceptual sequencing and disordered speech in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2000;26:723-735.



26. van der Gaag M, Kern RS, van den Bosch RJ, Liberman RP. A controlled trial of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2002;28:167-176.



27. Mart├Łnez-Ar├Īn A, Penad├®s R, Vieta E, Colom F, Reinares M, Benabarre A, et al. Executive function in patients with remitted bipolar disorder and schizophrenia and its relationship with functional outcome. Psychother Psychosom 2002;71:39-46.


28. Velligan DI, Prihoda TJ, Ritch JL, Maples N, Bow-Thomas CC, Dassori A. A randomized single-blind pilot study of compensatory strategies in schizophrenia outpatients. Schizophr Bull 2002;28:283-292.



29. Holthausen EAE, Wiersma D, Sitskoorn MM, Dingemans PM, Schene AH, van den Bosch RJ. Long-term memory deficits in schizophrenia: primary or secondary dysfunction? Neuropsychology 2003;17:539-547.



30. Pukrop R, Matuschek E, Ruhrmann S, Brockhaus-Dumke A, Tendolkar I, Bertsch A, et al. Dimensions of working memory dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2003;62:259-268.


31. Combs DR, Qouvier WD. The role of attention in affect perception : an examination of MirskyŌĆÖs four factor model of attention in chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2004;30:727-738.



32. Docherty NM. Cognitive impairments and disordered speech in schizophrenia: thought disorder, disorganization, and communication failure perspectives. J Abnorm Psychol 2005;114:269-278.



33. K├®ri S, Kelemen O, Janka Z, Benedek G. Visual-perceptual dysfunctions are possible endophenotypes of schizophrenia: evidence from the psychophysical investigation of magnocellular and parvocellular pathways. Neuropsychology 2005;19:649-656.



34. Mortimer AM, Joyce E, Balasubramaniam K, Choudhary PC, Saleem PT. Treatment with amisulpride and olanzapine improve neuropsychological function in schizophrenia. Hum Psychopharmacol 2007;22:445-454.


35. Thornton AE, Boudreau VG, Griffiths SY, Woodward TS, Fawkes-Kirby T, Honer WG. The impact of monetary reward on memory in schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Neuropsychology 2007;21:631-645.



36. Yi Z, Fan X, Wang JJ, Liu D, Freudenreich O, Goff D, et al. Rosiglitazone and cognitive function in clozapine-treated patients with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res 2012;200:79-82.


37. Hasan A, Guse B, Cordes J, W├Člwer W, Winterer G, Gaebel W, et al. Cognitive effects of high-frequency rTMS in schizophrenia patients with predominant negative symptoms: results from a multicenter randomized sham-controlled trial. Schizophr Bull 2016;42:608-618.



38. Huang M, Huang Y, Yu L, Hu J, Chen J, Jin P, et al. Relationship between negative symptoms and neurocognitive functions in adolescent and adult patients with first-episode schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2016;16:344




39. Schuepbach D, Egger ST, Boeker H, Duschek S, Vetter S, Seifritz E, et al. Determinants of cerebral hemodynamics during the Trail Making Test in schizophrenia. Brain Cogn 2016;109:96-104.


40. Grissom RJ. Probability of the superior outcome of one treatment over another. J Appl Psychol 1994;79:314-316.

41. Borenstein M, Hedges L, Rothstein H. Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects. Available at: http://www.metaanalysis.com/downloads/Meta-analysis_fixed_effect_vs_random_effects_sv.pdf. Accessed November 5, 2017.
42. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003;327:557-560.



43. Bora E, Pantelis C. Meta-analysis of cognitive impairment in first-episode bipolar disorder: comparison with first-episode schizophrenia and healthy controls. Schizophr Bull 2015;41:1095-1104.




44. Fioravanti M, Bianchi V, Cinti ME. Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: an updated metanalysis of the scientific evidence. BMC Psychiatry 2012;12:1-20.




45. Peri├Ī├▒ez JA, R├Łos-Lago M, Rodr├Łguez-S├Īnchez JM, Adrover-Roig D, S├Īnchez-Cubillo I, Crespo-Facorro B, et al. Trail Making Test in traumatic brain injury, schizophrenia, and normal ageing: sample comparisons and normative data. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2007;22:433-447.



46. Fatouros-Bergman H, Cervenka S, Flyckt L, Edman G, Fard L. Metaanalysis of cognitive performance in drug-naïve patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2014;158:156-162.


47. Kuha A, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Eerola M, Per├żl├ż J, Suvisaari J, Partonen T, et al. Impaired executive performance in healthy siblings of schizophrenia patients in a population-based study. Schizophr Res 2007;92:142-150.


48. Wright B, Peters E, Ettinger U, Kuipers E, Kumari V. Effects of environmental noise on cognitive (dys)functions in schizophrenia: a pilot within-subjects experimental study. Schizophr Res 2016;173:101-108.



49. Talreja BT, Shah S, Kataria L. Cognitive function in schizophrenia and its association with socio-demographics factors. Ind Psychiatry J 2013;22:47-53.



50. Gray JA, Roth BL. Molecular targets for treating cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2007;33:1100-1119.




51. Harvey PD. The genetics of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 2008;5:65-67.


52. Puig MV, Gener T. Serotonin modulation of prefronto-hippocampal rhythms in fealth and disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 2015;6:1017-1025.


53. Logue SF, Gould TJ. The neural and genetic basis of executive function: attention, cognitive flexibility, and response inhibition. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014;123:45-54.


54. ┼Ātrac D┼Ā, Pivac N, M├╝ck-┼Āeler D. The serotonergic system and cognitive function. Transl Neurosci 2016;7:35-49.




55. Volkow ND. Substance use disorders in schizophrenia--clinical implications of comorbidity. Schizophr Bull 2009;35:469-472.




56. Y├╝cel M, Bora E, Lubman DI, Solowij N, Brewer WJ, Cotton SM, et al. The impact of cannabis use on cognitive functioning in patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of existing findings and new data in a first-episode sample. Schizophr Bull 2012;38:316-330.



57. Sevy S, Kay SR, Opler LA, van Praag HM. Significance of cocaine history in schizophrenia. J Nerv Ment Dis 1990;178:642-648.


58. Mathews SB, Arnold SE, Epperson CN. Hospitalization and cognitive decline: can the nature of the relationship be deciphered? Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2014;22:465-840.


59. Dixon LB, Lehman AF, Levine J. Conventional antipsychotic medications for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1995;21:567-577.










