 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 20(8); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Notes
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Kyu-Man Han and Jong-Woo Paik, a contributing editor of the Psychiatry Investigation, were not involved in the editorial evaluation or decision to publish this article. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Kyu-Man Han, Sang Min Lee, Jong-Woo Paik. Data curation: Seok-Joo Kim, Sunju Sohn, Yun-Kyeung Choi, Jinhee Hyun, Heeguk Kim, Jong-Sun Lee, Yu-Ri Lee. Formal analysis: Kyu-Man Han, Sang Min Lee, Minha Hong. Investigation: Seok-Joo Kim, Sunju Sohn, Yun-Kyeung Choi, Jinhee Hyun, Heeguk Kim, Jong-Sun Lee, Yu-Ri Lee. Methodology: Kyu-Man Han, Sang Min Lee, Minha Hong, Jong-Woo Paik. Validation: Kyu-Man Han, Sang Min Lee. Writing—original draft: Kyu-Man Han, Sang Min Lee, Jong-Woo Paik. Writing—review & editing: all authors.
Funding Statement
This research was supported by a grant of Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center (PACEN) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number : HC19C0307). The funding body had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of this report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in this study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figure 1.
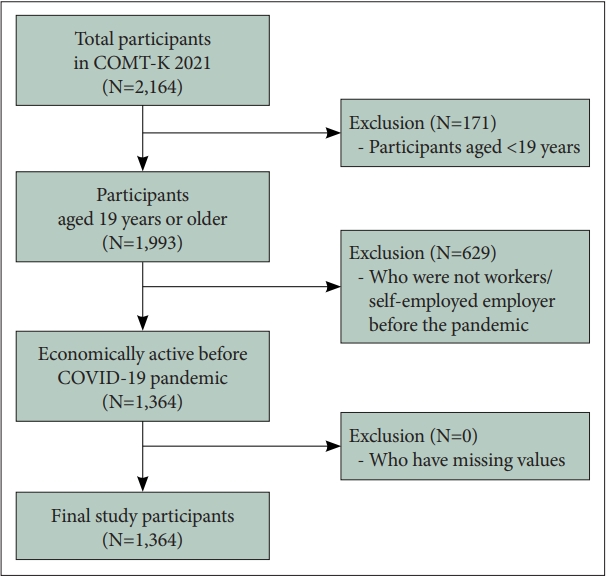
Table 1.
Table 2.
Logistic regression analyses for depressive or anxiety symptoms and suicidality were performed, controlling for age, sex, education level, marital status, religion, monthly household income level, job status, chronic diseases, alcohol consumption, and smoking in the total sample. If OR >1, then they are more likely to have depressive or anxiety symptoms or suicidality compared to the referential variables. COVID-19, coronavirus disease-2019; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval
Table 3.
All estimated effect values, p-values, and confidence intervals were obtained from Hayes and Preacher’s (2014)39 mediation analysis. Only results with significant mediation were represented in the table (p<0.05). COVID-19, coronavirus disease-2019; PHQ-9, Patient Health Questionnaire-9 ; GAD-7, General Anxiety Disorder-7; IV, independent variable; M, mediator; DV, dependent variable; FSSQ, Duke-UNC Functional Social Support Questionnaire; CI, confidence interval
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- Scopus
- 1,532 View
- 55 Download
-
COVID-19 and Risk Factors of Anxiety and Depression in South Korea2021 September;18(9)






