 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 17(9); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
We sought to determine if the links between and within the default mode network (DMN) and dorsal attention network (DAT) exhibited different conditions according to catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene polymorphism in relationship to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms.
Methods
Fifty-seven children with ADHD and 48 healthy controls (HCs) were administered an intelligence test, the ChildrenŌĆÖs Depression Inventory, the Korean ADHD rating scale, and continuous performance test. Resting-state brain functional MRI scans were obtained, and COMT genotyping was performed to distinguish valine carriers and methionine homozygotes.
Results
Compared to controls, children with ADHD showed increased ADHD scale scores, increased visual commission errors, and increased functional connectivity (FC) within the DMN and DAT. Compared to all children with ADHD, children with the methionine homozygote and those who were valine carriers showed increased FC within the DMN and DAT and decreased FC between the DMN and DAT. FC within the DMN was also increased in HC valine carriers compared to HC children with the methionine homozygote, and in children with ADHD who were valine carriers compared to HC valine carriers.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity and has a worldwide prevalence of 5.3% [1,2]. Although several genetic and environmental studies have attempted to understand the pathogenesis of ADHD [3,4], its exact etiology and pathogenesis are unknown and is thought to be a complex, polygenic disorder [5]. Specifically, the heritability of ADHD is estimated to be about 80% according to a meta-analysis. Clinical studies [6,7] have demonstrated abnormalities of the dopaminergic, noradrenergic system and frontal-striatal brain systems [8,9] associated with ADHD.
Many genetic and neuroimaging approaches have been actively studied to clarify the pathogenesis of ADHD mentioned above. Through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies, the core brain regions involved in attention control, and their connectivity and activation levels have been studied. These consist of the dorsal and ventral lateral frontal cortices and the posterior parietal area [10-12]. These regions form an attentional control system consisting of the dorsal and ventral attention networks (DAT and VAT) which operate as an integrated supramodal top-down and bottom-up attentional gating system [10,13]. While traditional accounts of attentional function and dysfunction have focused on task-dependent neural activity within these networks, recent formulations have stressed the importance of a task-independent network [14]. This network, termed the default mode network (DMN), is a large and robustly replicable network of brain regions that are associated with task-irrelevant mental processes. These consist of frontal and posterior midline structures (the medial prefrontal cortex and posterior cingulate cortex with adjacent precuneus) and lateral parietal and medial temporal lobe regions [15]. The DMN shows higher activity and stronger functional connectivity (FC) during rest, and its activity is attenuated following the onset of tasks [15]. Persistence of DMN activity during tasks has been shown to predict errors in task output, and unsuccessful attenuation of the DMN is reportedly associated with momentary lapses in attention denoted by longer reaction times and less accurate performance in an attentional control task [16,17]. When one considers the data from these studies, it seems that effective attentional engagement requires both the ŌĆ£switching onŌĆØ of the task-positive attention networks and the ŌĆ£switching offŌĆØ of the DMN [17-19]. Actually, many recent studies showed evidence of abnormal coordination of the DMN and attention networks, adversely affecting performance in individuals with ADHD [20-24].
Several genetic studies, and brain imaging studies, have been carried out to determine the etiology of ADHD. In particular, imbalance and dysregulation of the dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurotransmitter systems of the central nervous system are key mechanisms related to ADHD [8]. Many genetic studies related to this activation and catabolism have been carried out. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is an important enzyme that plays a major role in the degradation of catecholamine, including dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE), in the synapses [25]. As a result, excessive activation of COMT enzymes lowers the activity of DA and NE in the attention-related brain networks, resulting in clinical impairment of this executive function. These effects are closely related to the symptom expression of ADHD, so the COMT gene is an essential candidate gene for the etiology of ADHD [26,27]. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP, rs4680) in COMT is the most popular SNP in ADHD, leading to valine (Val) to methionine (Met) substitution at codon 158 (Val158-Met) of the COMT. This induces an approximately three- to four-fold decrease in enzyme activity, resulting in increased catecholamine activity [28-30]. There is considerable evidence that the COMT Val/Met SNP is highly related to ADHD, and in a recent Korean study [31], it was revealed that the COMT Val allele of Val158-Met polymorphism is associated with ADHD within the Korean population [32]. Also, children with ADHD with the Val homozygote demonstrated a good response to methylphenidate treatment [33].
We think that it is important to clarify the relationship between the brain imaging findings and the genetic results of ADHD mentioned above and integrate the neuro-genetic and neuroimaging findings together to take a step closer to the pathogenesis of ADHD. However, few studies have mentioned the association between COMT polymorphism and brain FC [34,35], and no study has directly investigated the relation between COMT polymorphism and brain DMN or between COMT polymorphism and the attention network in ADHD.
We hypothesized that, in children with ADHD, the FC within the DMN and DAT was decreased compared to healthy controls (HCs). Additionally, we believed that children with ADHD who were Val carriers would show increased FC within the DMN and DAT, compared to children with ADHD with the Met homozygote.
Initially, 60 children with ADHD and 50 age- and sex-matched HCs were recruited through the psychiatry department at Chung Ang University Hospital. Of the 60 children with ADHD, two had intelligence quotients (IQs) lower than 80. One patient with ADHD and one control participant could not be scanned in an MRI scanner due to claustrophobia. One HC participant showed depressive symptoms. Finally, 57 patients with ADHD and 48 HCs completed the study protocol.
All study procedures and protocols were explained to the patients and controls and their parents. Informed consent was obtained from the patients and controls, and written informed consent was obtained from their parents. The protocol for the current study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chung Ang University Hospital [C2012033 (728)].
All participants in the current study were assessed with the Korean Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime version (K-SADS-PL) [36], and diagnosed by a child and adolescent psychiatric doctor (DHH) following a clinical interview. IQ, depression severity, and ADHD symptoms were assessed using the Korean-Wechsler intelligence scale for children (K-WISC-IV) [37], the ChildrenŌĆÖs Depression Inventory (CDI) [38], and the Korean ADHD rating scale (K-ARS) for parents, respectively [39]. Attention was assessed using a standardized version of continuous performance test (CPT) for Korean children and adolescents, and its reliability and validity as a diagnostic instrument for ADHD has been established [40,41]. The Korean version of the CPT consists of visual and auditory attention tests, each of which takes 15 minutes to complete. The CPT test results included omission errors, commission errors, response time mean, and response time deviation. In this study, we used two major variables: omission errors (a measure of inattention) and commission errors (a measure of impulsivity) in CPT. The exclusion criteria were: 1) a history of another axis I psychiatric disease except for ADHD, 2) IQ <80, and 3) a history of neurological or medical disorders.
The children with ADHD underwent a 7-day medication washout period before their study enrollment and fMRI scans. For the brain connectivity analyses, all children with ADHD and HCs completed a resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) study using an MRI scanner (Philips Achieva 3.0 Tesla TX MRI scanner). The scanning parameters were as follows: TR=3 s, 12-minute scan, 240 volumes, 128├Ś128 matrix, 40 slices at 4.0 mm slice thickness. Preprocessing included despiking (AFNI: 3dDespike), motion correction, coregistration to MPRAGE image, normalization to MNI space in SPM 12b, temporal detrend (Matlab: detrend.m), bandpass filtering (Matlab: idealfilter.m), and voxelwise regression of identically bandpass filtered time series of six head motion parameters.
Children with ADHD and HCs were asked to remain awake with their eyes closed. To avoid head movements, the childrenŌĆÖs heads were stabilized with cushions. To avoid microhead movements, we applied realignment steps using six rigidbody parameters with each participantŌĆÖs estimated motion [42-44], but no regression of the global signal was performed.
We extracted eight regions of two brain networks (four DMNs: the middle prefrontal cortex, right/left lateral parietal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex; four dorsal attention networks: right/left frontal eye field, right/left inferior parietal sulcus) from the Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL) atlas of the brain (AAL ver 2) [45], which were found in group independent component analysis (ICA) analysis of all participants [46]. Fisher-transformed correlation coefficients were measured for each pair of ROIs in each participant. We calculated the FC between regions of interest (ROIs) using the CONN-fMRI Functional Connectivity Toolbox (ver.15; www. Nitrc.org/projects/conn). Between-group effects were considered significant with a cluster-level false discovery rate (FDR) and p values less than 0.05.
Genotyping was performed at the Laboratory of Labgenomics, Korea. According to the manufacturerŌĆÖs protocol, genetic DNA was extracted from blood (stored frozen) using a G-DEXTM II Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Intron Biotechnology, Seoul, Korea). The SNPs were analyzed using the polymerase chain reaction-ligase detection reaction (PCR-LDR) method. First, the PCR reaction was performed in a volume of 20 ┬ĄL containing PCR master mix (Nanohelix, Korea), 500 nM of each primer of Table 1, and about 50 ng genomic DNA. The reaction consisted of denaturation at 95┬░C for 15 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95┬░C for 20 s, 55┬░C for 40 s, and 72┬░C for 1 min, with a final extension at 72┬░C for 5 min. Following PCR, unincorporated primers and dNTPs were removed by adding 1/10 volume of Exo-Sap (ExoProStar 1, GE Healthcare) and incubating for 15 min at 37┬░C, followed by 15 min at 85┬░C for enzyme inactivation. Then, the LDR reaction was carried out in a buffer containing 4 ┬ĄL of PCR product, 10X ligase buffer (NEB), 12.5 nM each allele-specific probe (left probe, Bioneer, Korea) and 25 nM each common probe (right probe, Bioneer, Korea) of Table 1, and 1.25 units of 9┬░ NTM ligase (NEB). The reaction volume was 20 ┬ĄL, and the LDR consisted of 25 cycles of 94┬░C for 60 seconds and 65 ┬░C for 150 seconds. The LDR products were then analyzed by ABI 3730 Gene Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
There was a significant difference in K-ARS scores and visual commission errors between children with ADHD and HCs. However, there were no significant between-group differences in age, education year, CDI scores, and COMT gene distribution (Table 2).
Of the 57 children with ADHD, 23 children were of the inattentive type, 21 were combined type, and 13 were hyperactive type. All children with ADHD took methylphenidate 27.9┬▒13.2 mg/day.
During the group ICA analysis of the 105 participants, five brain circuits including the DMN, sensory-motor (SM), visual (VS), DAT, and cerebellar network were best-matched (Figure 1). Of the five regions, we selected two networks (DMN and DAT), which were already reportedly associated with children with ADHD in previous studies (Figure 1).
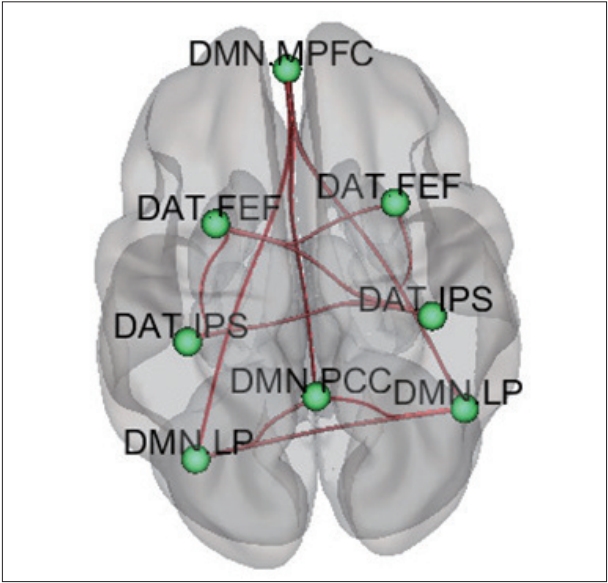
Compared to HCs, children with ADHD showed increased FC within the DMN (left lateral parietal-right lateral parietal, left lateral parietal-posterior cingulate gyrus, right lateral parietal-posterior cingulate gyrus, middle prefrontal gyrus-posterior cingulate gyrus, middle prefrontal gyrus-right lateral parietal, middle prefrontal gyrus-left lateral parietal) and DAT (left inferior parietal sulcus-right inferior parietal sulcus, right frontal eye field-right inferior parietal sulcus, left frontal eye field-right frontal eye field, left frontal eye field-left inferior parietal sulcus, left frontal eye field-right inferior parietal sulcus) (Figure 2, Table 3).
Visual commission errors in children with ADHD were associated with FC within the DMN (left lateral parietal-right lateral parietal). There were no significant differences in visual commission errors between children with ADHD with Val carriers and children with ADHD with Met homozygote.
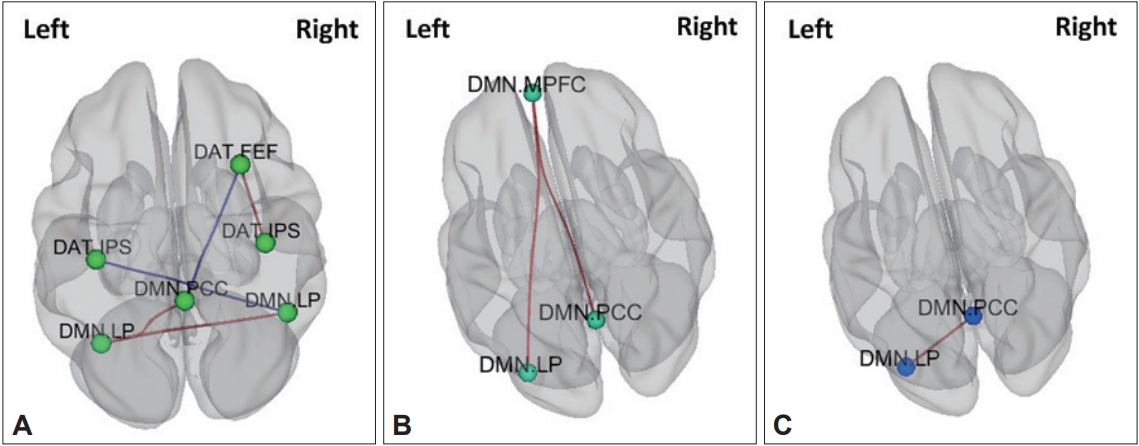
Compared to children with ADHD with the Met homozygote (n=24), children with ADHD who were Val carriers (n=33) showed increased FC within the DMN (left lateral parietal-posterior cingulate, left lateral parietal-right lateral parietal) and DAT (right frontal eye filed-right inferior parietal sulcus).
We analyzed the FC within the DMN and DAT networks and between the DMN and DAT networks according to genetic COMT subtype (Val carriers vs. Met homozygotes) in children with ADHD and HCs. In this way, the relationship between brain attentional control (the DMN and DAT) and one of the core candidate genes associated with ADHD (COMT Val158-Met polymorphism) could be examined.
We found hyperconnectivity within the DMN as well as within the DAT in children with ADHD compared to HCs in the resting-state. These findings were similar to the results of other ADHD studies [47-49]. Sidlauskaite et al. [48] reported that the connectivity within DMN regionsŌĆörepresenting the task-independent brain activity state like resting statusŌĆöwas more imbalanced in individuals with ADHD compared to HCs. Moreover, high FC within the DMN in the resting-state is considered ineffective for rapid switching of the brain to the concentration state when a sudden stimulus or goal-related task is given [47]. It becomes difficult to exert effective quality attention, resulting in the clinical symptoms that characterize ADHD [19,23,48].
We also found hyperconnectivity within DAT in children with ADHD, which was consistent with another recent study [48]. Usually, the DAT and VAT systems are differentiated by their specific functions in attentional control [13]. Also, the interplay between these systems during attentional processing is important for sustained elaborate attention [50]. However, the increased connectivity within the DAT may lead to dysfunction of the integrated attention [50]. This means that there might be a problem with efficient information exchange and complementary function between the DAT and VAT, potentially leading to incomplete cognitive and attentional functions when a task is given.
However, other studies of ADHD produced controversial results. Differences in fMRI analytic method techniques among previous studies could explain the inconsistent DMN connectivity findings. In the same participants, the one seed-based analytic study and the other network homogeneity analytic study appeared to show decreased connectivity within DMN regions [51,52]. Readers should consider controversial results with various analytic methods when interpreting the findings.
Interestingly, CPT test visual commission errors in the current study were significantly higher in the ADHD group than in the HCs, and visual commission errors showed a significant positive correlation with DMN connectivity. Among the CPT test variables, commission errors, which are false responses, represent impulsivity and are well established neurocognitive endophenotypes of ADHD [53]. Several studies have suggested that the difficulties in impulse control were associated with increased FC within the DMN [54,55].
The availability of DA and NE in the prefrontal cortex is mainly affected by COMT enzymes [56]. Recent research showed that altered dopaminergic and noradrenergic tone, affected by COMT genotypes including the Val158-Met polymorphism, resulted in neuroadaptive changes in several task-positive and negative network basal FC. This could, in turn, contribute to its effects on behavior [57-62]. Endogenous DA and NE have a large role in working memory performance, and both systems are inseparable for normal executive function [63].
In the current study, increased FC within the DMN and DAT might provide preliminary evidence of lowered DA and NE levels in these networks in the Val polymorphism compared to the Met. This finding appears to demonstrate a more severe attentional crisis in children with ADHD and the Val polymorphism, consistent with our findings comparing FC in children with ADHD to HCs. This is also supported by the fact that FC within the DMN was higher in the Val group than in the Met HC group. Interestingly, even with the same Val type, the ADHD Val group had a higher FC within the DMN than the HC Val group.
DA and NE levels may be decreased in those with the Val allele compared to those with the Met allele [28-30]. Also, the availability of DA and NE in the prefrontal cortex is mainly affected by COMT enzymes [56]. Recent research shows the altered DA and NE tone, affected by COMT genotypes, including the Val158-Met polymorphism, resulting in neuroadaptive changes in several task-positive and negative network basal FC. This could contribute to its effects on behavior [57-62]. Endogenous DA and NE have a large role in working memory performance, and both systems are inseparable for normal executive function [63].
The decreased FC finding ŌĆ£betweenŌĆØ the DMN and DAT in children with the Val polymorphismŌĆöcompared to the MetŌĆöwas consistent with another research report on ADHD [64]. This finding was also mentioned as a distinct intrinsic network connective feature of the ADHD group compared to the HCs, suggesting a diminished antagonistic connection between the DMN and attention networks. This may result in excess task-related DMN connectivity [51,65,66].
Taking these findings together, ADHD symptoms may be associated with the polygenic etiologies of genetic and brain development. Also, these substantial findings in ADHD were more characteristic to the Val polymorphism than to the Met. Val carriers may exhibit more evident ADHD traits, suggesting that it is one of the candidate genes involved in the etiology of ADHD.
Our research findings elucidate brain FC in children with ADHD and the relationship to DA-related gene effects. However, our study has some limitations. Due to the small number of participants, it would be insufficient to say that our findings were due to genetic differences, so future studies should analyze additional participants to boost study reliability. We are hopeful that future research efforts will continue to clarify default and attention-related network connectivity, considering ADHD subtypes as well as the effects of medication (methylphenidate). Second, the heterogeneity of the ADHD group in this study should be considered.
ADHD is a complex disorder, and its subtypes can be further sub-divided into three categories: inattentive, hyperactive, and combined [67]. We did not distinguish among the ADHD group subtypes, so future studies should clarify and account for these differences. Thirdly, we did not perform other neuropsychiatric tests that could assess executive function and attention, opting instead to only administer the CPT. Therefore, we were limited in our ability to evaluate various symptoms of ADHD and link these symptoms to neurophysiologic and genetic factors. Lastly, although the participants with ADHD had a sufficient medication washout period before their study enrollment and fMRI scan, we did not consider individual histories and durations of stimulant and other psychoactive medication use, such as antidepressants. Such medications may exert different effects on functional brain organization and should be considered by future studies.
In conclusions, we found increased brain connectivity within the DMN and DAT in children with ADHD. The COMT Val158-Met polymorphism was related to altered brain connectivity between the DMN and DAT due to its effect on DA and NE. These findings suggest that, in individuals with ADHD, there is disrupted connectivity between brain networks, particularly attention-related shifting networks, including the DMN. Moreover, these are a neurophysiological phenomenon of ADHD and dopaminergic and noradrenergic actions may affect the FC of these networks. These factors might be related to the pathophysiology of ADHD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by grants from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A120013) and Korea Creative Content Agency (R2014040055).
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Doug Hyun Han. Data curation: Jeong Ha Park. Formal analysis: Young Don Son. Funding acquisition: Doug Hyun Han, Yeni Kim. Investigation: Jeong Ha Park. Methodology: Young Don Son. Project administration: Doug Hyun Han. Resource: Doug Hyun Han. Software: Young Don Son. Supervision: Doug Hyun Han. Validation: Yeni Kim. Visualization: Jeong Ha Park. WritingŌĆöoriginal draft: Jeong Ha Park. WritingŌĆöreview & editing: Doug Hyun Han.
Figure┬Ā1.
Brain networks in all subjects. In group ICA analysis of 105 subjects, five brain circuits including default mode network, sensory motor, visual, dorsal attention network, and cerebellar network were best matched. ICA: independent component analysis.

Figure┬Ā2.
Comparison of functional connectivity between ADHD children and healthy children. DMN: Default mode network, DAT: Dorsal attention network, MPFC: middle prefrontal cortex, FEF: frontal eye field, IPS: inferior parietal sulcus, LP: lateral parietal lobe, PCC: posterior cingulate cortexDMN: Default mode network, DAT: Dorsal attention network, MPFC: middle prefrontal cortex, FEF: frontal eye field, IPS: inferior parietal sulcus, LP: lateral parietal lobe, PCC: posterior cingulate cortex.
Figure┬Ā3.
Genetic neuroimaging results in patients with ADHD and healthy comparison children. A: Comparison of functional connectivity between ADHD children with Val carriers and ADHD children with Met homozygote, B: Comparison of functional connectivity between healthy comparison (HC) children with Val carriers and HC children with Met homozygote, C: Comparison of functional connectivity between ADHD children with Val carriers and HC children with Val carriers. DMN: Default mode network, DAT: Dorsal attention network, MPFC: middle prefrontal cortex, FEF: frontal eye field, IPS: inferior parietal sulcus, LP: lateral parietal lobe, PCC: posterior cingulate cortex.
Table┬Ā1.
Polymerase chain reaction primers and ligase detection reaction probes
Table┬Ā2.
Demographic characteristics
| ADHD (57) | Control (48) | Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 11.7┬▒2.8 | 10.8┬▒3.2 | t=1.5, p=0.13 | |
| Sex (male/female) | 44/13 | 30/18 | Žć2=2.70, p=0.13 | |
| Educations | 5.6┬▒2.7 | 4.8┬▒3.2 | t=1.3, p=0.18 | |
| K-ARS | 24.0┬▒8.9 | 5.3┬▒4.4 | t=13.3, p<0.01* | |
| CDI | 6.7┬▒3.2 | 6.0┬▒3.9 | t=1.0, p=0.30 | |
| Medications | n | Dose (mg/day) | ||
| ŌĆāMethylphenidate | 57 | 27.9┬▒13.2 | - | |
| CPT test (normal/abnormal) Visual omission | 39/18 | 39/9 | Žć2=2.25, p=0.18 | |
| ŌĆāAuditory omission | 46/11 | 41/7 | Žć2=0.41, p=0.61 | |
| ŌĆāVisual commission | 40/17 | 42/6 | Žć2=4.57, p=0.03* | |
| ŌĆāAuditory commission | 41/16 | 40/8 | Žć2=1.92, p=0.24 | |
| COMT gene | ||||
| ŌĆāGG | 24 | 25 | ||
| ŌĆāGA | 25 | 21 | Žć2=2.39, p=0.12 | |
| ŌĆāAA | 8 | 2 |
Table┬Ā3.
Functional connectivity in brain networks
REFERENCES
1. Moffitt TE, Houts R, Asherson P, Belsky DW, Corcoran DL, Hammerle M, et al. Is adult ADHD a childhood-onset neurodevelopmental disorder? Evidence from a four-decade longitudinal cohort study. Am J Psychiatry 2015;172:967-977.



2. Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry 2007;164:942-948.


3. Lionel AC, Crosbie J, Barbosa N, Goodale T, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Rickaby R, et al. Rare copy number variation discovery and cross-disorder comparisons identify risk genes for ADHD. Sci Transl Med 2011;95:95ra75

4. Pingault JB, Viding E, Galera C, Greven CU, Zheng Y, Plomin R, et al. Genetic and environmental influences on the developmental course of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms from childhood to adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry 2015;72:651-658.



5. Franke B, Neale BM, Faraone SV. Genome-wide association studies in ADHD. Hum Genet 2009;126:13-50.




6. Brikell I, Kuja-Halkola R, Larsson H. Heritability of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2015;168:406-413.


7. Larsson H, Chang Z, DŌĆÖOnofrio BM, Lichtenstein P. The heritability of clinically diagnosed attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Psychol Med 2014;44:2223-2229.


8. Del Campo N, Chamberlain SR, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW. The roles of dopamine and noradrenaline in the pathophysiology and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2011;69:145-157.

9. Sharp SI, McQuillin A, Gurling HM. Genetics of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Neuropharmacology 2009;57:590-600.


10. Corbetta M, Shulman GL. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002;3:201-215.



11. Hopfinger JB, Buonocore MH, Mangun GR. The neural mechanisms of top-down attentional control. Nat Neurosci 2000;3:284-291.



12. Woldorff MG, Hazlett CJ, Fichtenholtz HM, Weissman DH, Dale AM, Song AW. Functional parcellation of attentional control regions of the brain. J Cogn Neurosci 2004;16:149-165.


13. Vossel S, Geng JJ, Fink GR. Dorsal and ventral attention systems: distinct neural circuits but collaborative roles. Neuroscientist 2014;20:150-159.



14. Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL. The brainŌĆÖs default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2008;1124:1-38.


15. Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL. A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001;98:676-682.



16. Eichele T, Debener S, Calhoun VD, Specht K, Engel AK, Hugdahl K, et al. Prediction of human errors by maladaptive changes in event-related brain networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:6173-6178.



17. Weissman DH, Roberts KC, Visscher KM, Woldorff MG. The neural bases of momentary lapses in attention. Nat Neurosci 2006;9:971-978.



18. Lawrence NS, Ross TJ, Hoffmann R, Garavan H, Stein EA. Multiple neuronal networks mediate sustained attention. J Cogn Neurosci 2003;15:1028-1038.


19. Sonuga-Barke EJ, Castellanos FX. Spontaneous attentional fluctuations in impaired states and pathological conditions: a neurobiological hypothesis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2007;31:977-986.


20. Helps SK, Broyd SJ, James CJ, Karl A, Chen W, Sonuga-Barke EJ. Altered spontaneous low frequency brain activity in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Brain Res 2010;1322:134-143.


21. Liddle EB, Hollis C, Batty MJ, Groom MJ, Totman JJ, Liotti M, et al. Task-related default mode network modulation and inhibitory control in ADHD: effects of motivation and methylphenidate. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 2011;52:761-771.


22. Menon V. Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends Cogn Sci 2011;15:483-506.


23. Peterson BS, Potenza MN, Wang Z, Zhu H, Martin A, Marsh R, et al. An FMRI study of the effects of psychostimulants on default-mode processing during Stroop task performance in youths with ADHD. Am J Psychiatry 2009;166:1286-1294.



24. Supekar K, Menon V. Developmental maturation of dynamic causal control signals in higher-order cognition: a neurocognitive network model. PLoS Comput Biol 2012;8:e1002374



25. Napolitano A, Cesura AM, Da Prada M. The role of monoamine oxidase and catechol O-methyltransferase in dopaminergic neurotransmission. J Neural Transm Suppl 1995;45:35-45.

26. Choudhry Z, Sengupta S, Thakur G, Page V, Schmitz N, Grizenko N, et al. Catechol-o-methyltransferase gene and executive function in children with ADHD. J Atten Disord 2014;18:202-211.


27. Levy F. What do dopamine transporter and catechol-o-methyltransferase tell us about attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder? Pharmacogenomic implications. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2007;41:10-16.


28. Zhang L, Chang S, Li Z, Zhang K, Du Y, Ott J, et al. ADHDgene: a genetic database for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nucleic Acids Res 2012;40:D1003-D1009.


29. Mannisto PT, Kaakkola S. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): biochemistry, molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical efficacy of the new selective COMT inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 1999;51:593-628.

30. Tunbridge EM, Bannerman DM, Sharp T, Harrison PJ. Catechol-omethyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 2004;24:5331-5335.



31. Sun H, Yuan F, Shen X, Xiong G, Wu J. Role of COMT in ADHD: a systematic meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol 2014;49:251-261.



32. Park S, Park JE, Yoo HJ, Kim JW, Cheong JH, Han DH, et al. Association of the Catechol O-Methyltransferase Val158-Met Polymorphism and reduced interference control in Korean children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Investig 2015;12:563-565.



33. Kereszturi E, Tarnok Z, Bognar E, Lakatos K, Farkas L, Gadoros J, et al. Catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met Polymorphism is associated with methylphenidate response in ADHD children. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008;147B:1431-1435.


34. Kabukcu Basay B, Buber A, Basay O, Alacam H, Ozturk O, Suren S, et al. White matter alterations related to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and COMT val(158)met polymorphism: children with valine homozygote attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder have altered white matter connectivity in the right cingulum (cingulate gyrus). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2016;12:969-981.


35. Mizuno Y, Jung M, Fujisawa TX, Takiquchi S, Shimada K, Saito DN, et al. Catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism is associated with the cortico-cerebellar functional connectivity of executive function in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Sci Rep 2017;7:4850



36. Kim YS, Cheon KA, Kim BN, Chang SA, Yoo HJ, Kim JW, et al. The reliability and validity of Kiddie-Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime Version- Korean version (K-SADS-PL-K). Yonsei Med J 2004;45:81-89.



37. Kwak G, Oh S, Kim C. K-WISC-IV Manual for Professionals. Seoul: Hakjisa Publisher; 2011.
39. Jang SJ, Suh DS, Byun HJ. Normative study of the K-ARS (Korean ADHD Rating Scale) for parents. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2007;18:38-48.
40. Greenberg LM, Waldman ID. Developmental normative data on the test of variables of attention (TOVA). J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1993;34:1019-1030.


41. Cho SZ, Chun SY, Hong KE, Shin MS. A study of the development and standardization of ADHD diagnostic system. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000;11:91-99.
42. Anderson JS, Druzgal TJ, Lopez-Larson M, Jeong EK, Desai K, Yurgelun-Todd D. Network anticorrelations, global regression, and phaseshifted soft tissue correction. Hum Brain Mapp 2011;32:919-934.


43. Murphy K, Birn RM, Handwerker DA, Jones TB, Bandettini PA. The impact of global signal regression on resting state correlations: are anti-correlated networks introduced? NeuroImage 2009;44:893-905.


44. Saad ZS, Gotts SJ, Murphy K, Chen G, Jo HJ, Martin A, et al. Trouble at rest: how correlation patterns and group differences become distorted after global signal regression. Brain Connect 2012;2:25-32.



45. Rolls ET, Joliot M, Tzourio-Mazoyer N. Implementation of a new parcellation of the orbitofrontal cortex in the automated anatomical labeling atlas. Neuroimage 2015;122:1-5.


46. Calhoun VD, Liu J, Adali T. A review of group ICA for fMRI data and ICA for joint inference of imaging, genetic, and ERP data. Neuroimage 2009;45(1 Suppl):S163-S172.


47. McCarthy H, Skokauskas N, Mulligan A, Donohoe G, Mullins D, Kelly J, et al. Attention network hypoconnectivity with default and affective network hyperconnectivity in adults diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in childhood. JAMA Psychiatry 2013;70:1329-1337.


48. Sidlauskaite J, Sonuga-Barke E, Roeyers H, Wiersema JR. Altered intrinsic organisation of brain networks implicated in attentional processes in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state study of attention, default mode and salience network connectivity. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2016;266:349-357.



49. Tian L, Jiang T, Wang Y, Zang Y, He Y, Liand M, et al. Altered restingstate functional connectivity patterns of anterior cingulate cortex in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurosci Lett 2006;400:39-43.


50. Corbetta M, Patel G, Shulman GL. The reorienting system of the human brain: from environment to theory of mind. Neuron 2008;58:306-324.



51. Castellanos FX, Margulies DS, Kelly C, Uddin LQ, Ghaffari M, Kirsch A, et al. Cingulate-precuneus interactions: a new locus of dysfunction in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2008;63:332-337.


52. Uddin LQ, Kelly AM, Biswal BB, Marqulies DS, Shehzad Z, Shaw D, et al. Network homogeneity reveals decreased integrity of default-mode network in ADHD. J Neurosci Methods 2008;169:249-254.


53. Kebir O, Joober R. Neuropsychological endophenotypes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review of genetic association studies. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2011;261:583-594.



54. Vogt BA. Cingulate impairments in ADHD: comorbidities, connections, and treatment. Handb Clin Neurol 2019;166:297-314.


55. Han DH, Kim SM, Bae S, Renshaw PF, Anderson JS. A failure of suppression within the default mode network in depressed adolescents with compulsive internet game play. J Affect Disord 2016;194:57-64.


56. Yavich L, Forsberg MM, Karayiorgou M, Gogos JA, Mannisto PT. Site-specific role of catechol-O-methyltransferase in dopamine overflow within prefrontal cortex and dorsal striatum. J Neurosci 2007;27:10196-10209.



57. Arnsten AF. Catecholamine influences on dorsolateral prefrontal cortical networks. Biol Psychiatry 2011;69:e89-e99.



58. Beckmann CF, DeLuca M, Devlin JT, Smith SM. Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2005;360:1001-1013.



59. Cole DM, Oei NY, Soeter RP, Both S, van Gerven JM, Rombouts SA, et al. Dopamine-dependent architecture of cortico-subcortical network connectivity. Cereb Cortex 2013;23:1509-1516.



60. Dang LC, OŌĆÖNeil JP, Jagust WJ. Dopamine supports coupling of attention-related networks. J Neurosci 2012;32:9582-9587.



61. Liu B, Song M, Li J, Liu Y, Li K, Yu C, et al. Prefrontal-related functional connectivities within the default network are modulated by COMT val158met in healthy young adults. J Neurosci 2010;30:64-69.



62. Tunbridge EM, Farrell SM, Harrison PJ, Mackay CE. Catechol-Omethyltransferase (COMT) influences the connectivity of the prefrontal cortex at rest. NeuroImage 2013;68:49-54.



63. Xing B, Li YC, Gao WJ. Norepinephrine versus dopamine and their interaction in modulating synaptic function in the prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 2016;1641(Pt B):217-233.



64. Meyer BM, Huemer J, Rabl U, Boubela RN, Kalcher K, Berger A, et al. Oppositional COMT Val158Met effects on resting state functional connectivity in adolescents and adults. Brain Struct Funct 2016;221:103-114.



65. Sripada C, Kessler D, Fang Y, Welsh RC, Prem Kumar K, Angstadt M. Disrupted network architecture of the resting brain in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 2014;35:4693-4705.










