 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 16(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Schizophrenia is a disabling disorder of unknown aetiology, lacking definite diagnostic method and cure. A reliable biological marker of schizophrenia is highly demanded, for which traceable immune mediators in blood could be promising candidates. We aimed to gather the best findings of neuroinflammatory markers for first-episode psychosis (FEP).
Methods
We performed an extensive narrative review of online literature on inflammation-related markers found in human FEP patients only.
Results
Changes to cytokine levels have been increasingly reported in schizophrenia. The peripheral levels of IL-1 (or its receptor antagonist), soluble IL-2 receptor, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-╬▒ have been frequently reported as increased in FEP, in a suggestive continuum from high-risk stages for psychosis. Microglia and astrocytes establish the link between this immune signalling and the synthesis of noxious tryptophan catabolism products, that cause structural damage and directly hamper normal neurotransmission. Amongst these, only 3-hydroxykynurenine has been consistently described in the blood of FEP patients.
Schizophrenia is a severe disorder that impairs the personŌĆÖs entire behaviour and psychosocial functioning. It affects almost 1% of the population worldwide [1], and has a serious socioeconomic impact [2]. Thus far, there is no definite biological explanation for its intriguing symptoms nor its fateful progression. This lack of knowledge in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia makes its diagnosis rely solely on psychopathological descriptions, creating uncertainties and delaying treatment. Furthermore, the compelling need for anticipatory diagnostic strategies was emphasized by studies on high-risk states for schizophrenia that support a significant prognostic impact of early interventions [3-5].
Several techniques have been explored in the search for biological signatures of schizophrenia, comprising genetic, proteomic and metabolomics [6-13], histopathological [14,15], imagiological [16,17], and neurophysiological studies [6,18]. Unfortunately, they could not yet provide a reliable and feasible biomarker for usage in current clinical practice, nor could they support a definite pathophysiological explanation for the disorder and its clinical manifestations.
Interestingly, a growing body of evidence has unveiled a lifelong, insidious immune dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia [19-24] and brought the possibility of tracing its mediators in blood. Therefore, cost-effective diagnostic markers of early-onset schizophrenia, that may even help predict treatment response, are on the horizon [25,26]. However, the increasing literature on inflammation in schizophrenia presents multiple designations and often lays on heterogeneous patient populations, regardless of the disease clinical stage, making it difficult to draw clear-cut conclusions. We, therefore, critically reviewed relevant discoveries on blood markers related to inflammation specifically found in patients at first-episode psychosis (FEP), aiming at seizing promising biomarker candidates for early schizophrenia.
We performed an extensive narrative review of literature published in English-language until May 2018. We retrieved references from Pubmed/MEDLINE combining the terms ŌĆ£first-episodeŌĆØ, ŌĆ£schizophreniaŌĆØ, ŌĆ£inflammat*ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£(bio) marker.ŌĆØ Other relevant articles and printed books were added from cross-referencing. Studies addressing other biomarkers, patients not at FEP or animal models were excluded.
Among 804 references, 18 complied with our scope, reporting three main kinds of markers stemming from inflammation in FEP patients: cytokines, microglial activity markers and tryptophan catabolism products. These with be detailed below and schematized in Table 1.
Only a few biomarker studies adopted prospective assessments and selected drug-na├»ve acutely ill patients. Before acute illness, asymptomatic first-degree relatives of schizophrenia patients and people experiencing brief or attenuated symptoms (classically described as a prodromal stage) are considered to be at clinical high risk (CHR) for the disease [27]. In relatives at risk, higher levels of serum soluble IL-2 receptor (sILŌĆÉ2r) [28] and IL-10 [29] with lower IFN-╬│ [29] have been reported. In prodromal individuals, increased blood levels of the IL-6 [30], IL-8 [9] and IL-1-receptor antagonist (IL-1-RA) [9], with decreased IL-17 [30], support the hypothesis of a pre-clinically deregulated immune state. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of CHR subjects showed decreased receptors for IL-2 and TNF and elevated IL-8 as well [31]. Also a recent review suggests IL-1╬▓, IL-7, IL-8 and matrix metalloproteinase-8 are predictors of conversion to acute psychosis, with IL-6 failing to prove statistical significance [32].
For FEP, significant increases in serum ILŌĆÉ1╬▓, sILŌĆÉ2r, IL-6, IL-12, TNF-╬▒, TGFŌĆÉ╬▓, and IFN-╬│ have been reported by Miller et al. [33], together with reduced IL-10 in acute relapse. In this metaŌĆÉanalysis, the authors suggested that ILŌĆÉ1╬▓, ILŌĆÉ6, and TGFŌĆÉ╬▓ could be ŌĆ£stateŌĆØ markers, given their raised levels in acute episodes followed by normalization under antipsychotic treatment, while ILŌĆÉ12, IFN-╬│, TNF-╬▒, and sILŌĆÉ2R were proposed to be ŌĆ£trait markersŌĆØ, as their levels were maintained after treatment. Recently, other authors reported increased serum levels of IL-1-RA [9,34,35], ILŌĆÉ1╬▓ [29,36,37], sILŌĆÉ2r [35,36,38], IL-4 [38-40], IL-6 [29,35-38,41,42], IL-8 [38], IL-10 [9,34,41,42], IL-12 [29], IL-13 [9], IL-15 [34], IFN-╬│ [40], and TNF-╬▒ [35-38,40-42], and decreased levels of IL-17 [39] in drug-na├»ve FEP patients. Increased serum levels of IL-23, a key modulator of the inflammatory response, were also found in FEP patients and acute relapses [43].
Some studies consistently found increased plasmatic concentrations of S100B, a protein marker of glial activity, in patients with schizophrenia [44,45], including in early-stage unmedicated patients [46]. Osteopontin has also been suggested as a marker of microglial activation in blood under experimental exposure to hypoxia and lipopolysaccharide, but to the best of our knowledge, it has not been related to psychosis [47].
Tryptophan obtained from our diet is the precursor for serotonin synthesis, hence being largely researched in neuroscience. Some of its metabolites have been found in altered levels in patients with schizophrenia, raising interest about their role [48,49]. Both plasma tryptophan and kynurenine showed decreased in FEP patients [50]. The serum levels of 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-OHKY) showed increased, as well as positively correlated to psychopathology and treatment response [51]. A product of a competing branch in the TRYCAT cascade, Kynurenic acid (KA), did show an increase in the CSF of FEP patients, but not in plasma [48,52,53].
The findings in this review bring consistency to the neuroinflammatory hypothesis of schizophrenia, while relying on an explicable theoretical model. We present a schema of this model in Figure 1 to help following our discussion. Extensive data on the potential contribution of inflammation for schizophrenia has been published since SmithŌĆÖs first immune model [54]. The link between infection and psychosis has been suspected since the 1920s [55], and has found support in epidemiological studies relating schizophrenia either to prenatal [56-59], childhood or adulthood infections [60], irrespective of the infectious agent. Other early environmental determinants, such as low maternal vitamin D, iron or zinc levels, obstetric complications and exposure to certain aromatics, have been implicated in the dysregulation of the immune response [22], following a vulnerability-stress model [61]. These insults could be critical for priming the immune system, making it respond excessively in face of later stimuli, postulated by Keshavan as ŌĆ£second-hitsŌĆØ [62]. The neurodevelopmental hypothesis for schizophrenia [63] hence came to challenge earlier perspectives of neurodegeneration and dementia praecox, postulating it is a multifactorial disease beginning in early life, triggered by successive environmental stimuli to the developing brain of vulnerable subjects. A similar hypothesis is under research for autism spectrum disorders, which share some clinical and immunological features with schizophrenia despite emerging at an earlier age [64].
Critical immune dysregulation affecting the central nervous system (CNS) involves both T-helper-1 lymphocyte (Th1) and T-helper-2 lymphocyte (Th2) pathways and autoimmune mechanisms [23,24,65-69]. The finding of anti-NMDA-receptor IgG-antibodies in encephalitis with psychotic symptoms emphasized this hypothesis [70], although only IgA and IgM autoantibodies in a minority of patients with schizophrenia has been found so far [71,72]. Genetic research has pointed to various susceptibility genes and defective regulatory microRNA in schizophrenia which are related to immune response [73-76] and family history of the disease was shown to convey a higher risk after prenatal infection [77]. Several contributors to neuroinflammation fit the concept of KeshavanŌĆÖs second-hits. A defective antioxidant defence system, that prevents neural damage and inflammation in the brain, was found in schizophrenia patients [78,79]. Stress, either in earlylife [80], in the proximity of full-blown psychosis [81] or in later chronic phases [82] has been reported to contribute to the disease through the effects of cortisol on glial activation and cytokine release [83]. Cannabis consumption which has also been widely reported to increase the risk of psychosis [84,85], might also act on cortisol-mediated stress pathways [86]. Finally, the immune involvement in schizophrenia has led to therapeutic trials with anti-inflammatory drugs [87-89] with some promising results already. It should be reminded, however, that neuroinflammation likely underlies other neurological and psychiatric conditions, in which cytokine imbalance and microglial activation are reported, and may be subject to some degree of unspecificity due to confounding factors like obesity, glucose intolerance and tobacco use [35,90-94].
Concerning the biomarker value of cytokines, we should remind they play pleiotropic roles, from immune signalling to regulating early neurogenesis, maturation and neuroplasticity [95]. Increased TNF-╬▒ has been implicated in reduced hippocampal neurogenesis [96], as increased IL-6 [97,98] and IL-8 [99] have in reductions of brain volume in schizophrenia. Increased IL-6 levels in children [100] and premorbid risk individuals [101] were later associated to schizophrenia in adult life. Since maternal cytokines can invade fetal CNS [102], we can understand how an immune challenge affecting the motherŌĆÖs cytokine balance could tamper fetal neurodevelopment [67]. Accordingly, elevated maternal TNF-╬▒ [103] and IL-8 [99,104] levels were associated to schizophrenia in the offspring. In this context, inflammation could account for the premorbid impairments in fine motor coordination, memory and social behaviours, which are evident around adolescence in schizophrenia patients [22]. Numerous studies, with cross-sectional design and including patients irrespective of chronicity stage or type of treatment, have reported cytokine alterations in schizophrenia [35,105-107] while others report none [108]. Our findings of elevated IL-1-RA, sIL-2r, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10, along with lower IFN-╬│ and IL-17 levels in CHR individuals, support the hypothesis of a pre-clinically deregulated immune state, transitioning to that found in medication-na├»ve FEP patients, who consistently show increased levels of IL-1-RA, ILŌĆÉ1╬▓, sILŌĆÉ2r, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-13, IL-15, TNF-╬▒, TGFŌĆÉ╬▓, and IFN-╬│ and decreased levels of IL-17. A few discordant reports of lowered IL-4 [42], IL-10 [109], and IFN-╬│ [29] levels in FEP could reflect some timing differences in sample selection, since an immunological challenge is apparent between T-helper-1 type, proinflammatory cytokines (TNF, IFN-╬│, and IL-2) and Thelper-2 type, anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10), starting from the early high-risk phase.
Cytokine level normalisation after antipsychotic treatment is in accordance with the hypothesis of their immune modulating action [110], but particular cytokine changes could depend on the drugs used [23], which can be misleading when differentiating chronic ŌĆ£traitŌĆØ from acute ŌĆ£state markers.ŌĆØ Besides, Song et al. [37], observed normalised cytokine levels rising again after the first weeks of antipsychotic treatment. We therefore defend that such distinction of acute psychosis markers should be based on clinically evaluated symptomatic remission. Correlations with clinical status were found for IL-6 in the metaanalysis by Miller et al. [33], for IL-10 in the meta-analyses by de Witte et al. [34], and for no biomarker at all in the study by Noto et al. [41] Specifically, negative symptoms of schizophrenia (like flattened affect and low volition) were correlated with increased serum IL-4 and decreased IL-10 levels [109], while both positive (delusions and hallucinations) and negative symptoms were correlated to increased IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-╬▒ [111].
The role of cytokines in schizophrenia becomes even more relevant if we consider their effects on microglia, the brainresident macrophages. Microglia become activated by proinflammatory cytokines in response to immune challenges [82], releasing cell-damaging reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and other cytokines. They also enhance TRYCAT towards detrimental end-products [23]. Early-life microglial activation, triggered by infection or other insults, could initiate priming of the immune system, maintaining low-level inflammation and making it prone to exaggerated response to later challenges, thus increasing the risk for schizophrenia [83,112]. In accordance, microglial activity has been found increased in the brains of patients with schizophrenia in imagiological studies, namely in the anterior cingulate cortex, mediodorsal thalamus [113] and hippocampus [16]. Microglial overactivation can be associated with excessive synaptic pruning and at least sub-lethal apoptotic activity [114], relating to regional brain atrophy in first-episode psychosis and acute relapses [115]. Not surprisingly, elevated plasmatic S100B levels are found in FEP patients, making the protein suitable for psychosis biomarker. Further plasmatic molecules reflecting microglial activity should be sought to increase diagnostic accuracy.
Finally, tryptophan catabolism byproducts mediate the aforementioned immune changes in schizophrenia, through direct interference with neurotransmission. IL-1╬▓, IL-6, TNF-╬▒, IFN-╬│, and ILŌĆÉ18 induce microglial enzyme indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO), whereas IL-1╬▓ and stress-driven cortisol induce astrocytic enzyme tryptophan-2,3-deoxygenase (TDO) [116]. TRYCAT cascade under IDO releases excitotoxic NMDA-receptor agonists quinolinic acid (QUIN) [117] and 3-OHKY, while under TDO it releases KA. KA is an antagonist to NMDA and ╬▒7nACh receptors, impairing inhibitory activity of subcortical GABA-ergic interneurons [118]. This ultimately leads to unbalanced mesolimbic dopamine neurotransmission that can elicit psychotic symptoms [49,119]. Likewise, while the dopaminergic hypothesis for schizophrenia has prevailed for decades, attention to the hyperglutamatergic activity in the frontal cortex, secondary to decreased subcortical inhibition, has raised [120]. This perspective is more in accordance with the hypothesis of functional dysconnectivity in schizophrenia [121]. The value of KA as a feasible biomarker for psychosis is still questionable, however. Its levels were found elevated in their CSF but not in peripheral blood [48,122]. Besides, considerable part of brain kynurenine is produced systemically and KA cannot normally traverse the blood-brain barrier. On the other hand, TRYCAT cascade showed tendency to lean to the 3-OHKY branch, this metabolite being reported elevated in peripheral blood of FEP patients more consistently. As a matter of fact, excitotoxic and neurotoxic TRYCAT end-products such as 3-OHKY, QUIN and glutamate can cause neuronal loss and explain neuroprogression in schizophrenia [51].
In conclusion, this is the first study, of our knowledge, addressing serum biomarker candidates in relation to the whole natural history of the disease. Cytokine level changes are the most widely reported so far in FEP and appear in a continuum from high-risk stages, in accordance with the hypothesis of a progressive inflammatory process, which also allows an anticipated diagnosis. To help surpass their possible limitation of specificity for the disease, other molecules (such as inflammation-related microRNA) should be part of a comprehensive biomarker panel, in order to assist the diagnostic rationale in clinical practice. The present review is subject to selection and publication bias itself. In the future, prospective studies, monitoring these molecules in parallel to clinical presentation, with longer follow-up periods, are warranted for validation. This represents a crucial initial step for early and reliable diagnosis of schizophrenia and prognostic enhancement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been conducted with the support of the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology.
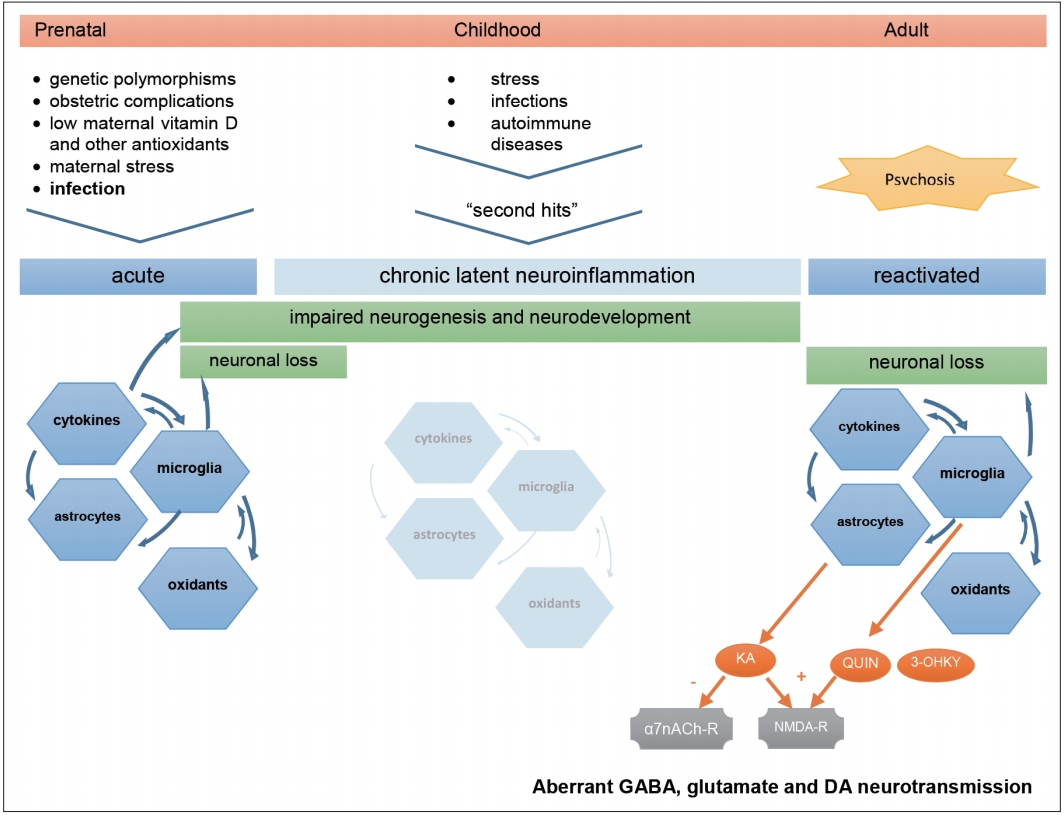
Figure┬Ā1.
Hypothetical aetiology and pathogenesis of Schizophrenia. Prenatal infection in context of other environmental factors can prime the immune system of already genetically vulnerable offspring. This first insult starts a neuroinflammatory cascade that compromises normal neurodevelopment and is maintained subclinically throughout life, waiting for the next triggers to restart an inflammatory process that, in turn, can lead to neuron damage, aberrant neurotransmission, and clinical symptoms. KA: kynurenic acid, QUIN: quinolinic acid, 3-OHKY: 3-hydroxykynurenine, ╬▒7nACh-r: alpha7-nicotinic-acetylcholine receptor, NMDA-r: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, DA: dopamine.
Table┬Ā1.
Temporal perspective of peripheral immune biomarkers in Schizophrenia
| Marker | Prenatal | Pre-morbid | High-risk | First-episode | Chronic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-╬▒ | Ōåæ [103] | - | Normal [40] | Ōåæ [33,35-38,40-42] | Ōåæ [33,37] |
| NAAP [110] | |||||
| IL-1╬▓ | - | - | Ōåæ [32] | Ōåæ [29,33,36-38] | Ōåæ [33,35,37] |
| IL-1- RA | - | - | Ōåæ [9] | Ōåæ [9,34,35,105] | NAAP [34] |
| sIL-2r | - | Ōåæ [28] | - | Ōåæ [33,35,36,105] | Ōåæ [33,35] |
| IL-4 | - | - | Ōåæ [40] | Ōåæ [38-40,109] | Ōåō [41] |
| Ōåō [42] | |||||
| IL-6 | - | Ōåæ [69] | Ōåō [40] | Ōåæ [29,33,35-38,41,42,105] | NAAP [33,35] |
| Ōåæ [30,32] | Ōåæ [37] | ||||
| IFN-╬│ | - | - | Normal [30] | Ōåæ [33,40] | Ōåæ [33] |
| Ōåō [29] | Ōåō [29] | NAAP [110] | |||
| IL-7 | - | - | Ōåæ [32] | - | - |
| IL-8 | Ōåæ [99] | - | Ōåæ [9,40,32] | Ōåæ [29] | - |
| IL-10 | - | - | Ōåæ [28,29] | Ōåæ [9,41,42] | NAAP [34,41] |
| Ōåō [109] | |||||
| IL-12 | - | - | - | Ōåæ [29,33] | Ōåæ [33] |
| IL-15 | - | - | - | Ōåæ [34] | Ōåæ [34] |
| IL-17 | - | - | Ōåō [30] | Ōåō [39] | - |
| IL-23 | - | - | - | Ōåæ [43] | Ōåæ [43] |
| TGF-╬▓ | - | - | - | Ōåæ [33,39] | NAAP [33] |
| 3-OHKY | - | - | - | Ōåæ [51,53] | NAAP [51,53] |
| KA | - | - | - | Ōåō [53] | NAAP [53] |
| S100B | - | - | - | Ōåæ [46] | Ōåæ [44] |
REFERENCES
1. McGrath J, Saha S, Chant D, Welham J. Schizophrenia: a concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiol Rev 2008;30:67-76.



2. Nordstroem AL, Talbot D, Bernasconi C, Berardo CG, Lalonde J. Burden of illness of people with persistent symptoms of schizophrenia: a multinational cross-sectional study. Int J Soc Psychiatry 2017;63:139-150.


3. Fusar-Poli P, Borgwardt S, Bechdolf A, Addington J, Riecher-Rossler A, Schultze-Lutter F, et al. The psychosis high-risk state: a comprehensive state-of-the-art review. JAMA Psychiatry 2013;70:107-120.



4. Henry LP, Amminger GP, Harris MG, Yuen HP, Harrigan SM, Prosser AL, et al. The EPPIC follow-up study of first-episode psychosis: longerterm clinical and functional outcome 7 years after index admission. J Clin Psychiatry 2010;71:716-728.


5. Schultze-Lutter F, Michel C, Schmidt SJ, Schimmelmann BG, Maric NP, Salokangas RK, et al. EPA guidance on the early detection of clinical high risk states of psychoses. Eur Psychiatry 2015;30:405-416.


6. Schmitt A, Rujescu D, Gawlik M, Hasan A, Hashimoto K, Iceta S, et al. Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on Biological Markers: Criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia part II: Cognition, neuroimaging and genetics. World J Biol Psychiatry 2016;17:406-428.


7. Sun XY, Lu J, Zhang L, Song HT, Zhao L, Fan HM, et al. Aberrant microRNA expression in peripheral plasma and mononuclear cells as specific blood-based biomarkers in schizophrenia patients. J Clin Neurosci 2015;22:570-574.


8. Schmitt A, Martins-de-Souza D, Akbarian S, Cassoli JS, Ehrenreich H, Fischer A, et al. Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on Biological Markers: Criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia, part III: Molecular mechanisms. World J Biol Psychiatry 2017;18:330-356.


9. Chan MK, Krebs MO, Cox D, Guest PC, Yolken RH, Rahmoune H, et al. Development of a blood-based molecular biomarker test for identification of schizophrenia before disease onset. Transl Psychiatry 2015;5:e601.




10. Schwarz E, Guest PC, Rahmoune H, Harris LW, Wang L, Leweke FM, et al. Identification of a biological signature for schizophrenia in serum. Mol Psychiatry 2012;17:494-502.



11. Sabherwal S, English JA, Focking M, Cagney G, Cotter DR. Blood biomarker discovery in drug-free schizophrenia: the contributionof proteomics and multiplex immunoassays. Expert Rev Proteomics 2016;13:1141-1155.


12. Rodrigues-Amorim D, Rivera-Baltanas T, Lopez M, Spuch C, Olivares JM, Agis-Balboa RC. Schizophrenia: a review of potential biomarkers. J Psychiatr Res 2017;93:37-49.


13. Martins-de-Souza D. Proteomics and Metabolomics in Psychiatry. Basel, New York: Karger; 2014.
14. Harrison PJ. The hippocampus in schizophrenia: a review of the neuropathological evidence and its pathophysiological implications. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004;174:151-162.



15. Chana G, Bousman CA, Money TT, Gibbons A, Gillett P, Dean B, et al. Biomarker investigations related to pathophysiological pathways in schizophrenia and psychosis. Front Cell Neurosci 2013;7:95



16. Doorduin J, de Vries EF, Willemsen AT, de Groot JC, Dierckx RA, Klein HC. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia-related psychosis: a PET study. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1801-1807.


17. Koutsouleris N, Meisenzahl EM, Borgwardt S, Riecher-Rossler A, Frodl T, Kambeitz J, et al. Individualized differential diagnosis of schizophrenia and mood disorders using neuroanatomical biomarkers. Brain 2015;138:2059-2073.




18. Thibaut F, Boutros NN, Jarema M, Oranje B, Hasan A, Daskalakis ZJ, et al. Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on Biological Markers: criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia part I: Neurophysiology. World J Biol Psychiatry 2015;16:280-290.


19. Watkins CC, Andrews SR. Clinical studies of neuroinflammatory mechanisms in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2016;176:14-22.


20. Muller N, Weidinger E, Leitner B, Schwarz MJ. The role of inflammation in schizophrenia. Front Neurosci 2015;9:372



21. Khandaker GM, Cousins L, Deakin J, Lennox BR, Yolken R, Jones PB. Inflammation and immunity in schizophrenia: implications for pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015;2:258-270.



22. Meyer U. Developmental neuroinflammation and schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;42:20-34.


23. Anderson G, Maes M. Schizophrenia: linking prenatal infection to cytokines, the tryptophan catabolite (TRYCAT) pathway, NMDA receptor hypofunction, neurodevelopment and neuroprogression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;42:5-19.


24. Tomasik J, Rahmoune H, Guest PC, Bahn S. Neuroimmune biomarkers in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2016;176:3-13.


25. Fond G, d'Albis MA, Jamain S, Tamouza R, Arango C, Fleischhacker WW, et al. The promise of biological markers for treatment response in first-episode psychosis: a systematic review. Schizophr Bull 2015;41:559-573.




26. Mondelli V, Ciufolini S, Belvederi Murri M, Bonaccorso S, Di Forti M, Giordano A, et al. Cortisol and inflammatory biomarkers predict poor treatment response in first episode psychosis. Schizophr Bull 2015;41:1162-1170.




27. Yung AR, Yuen HP, McGorry PD, Phillips LJ, Kelly D, Dell'Olio M, et al. Mapping the onset of psychosis: the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2005;39:964-971.


28. Gaughran F, O'Neill E, Sham P, Daly RJ, Shanahan F. Soluble interleukin 2 receptor levels in families of people with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2002;56:235-239.


29. Lizano PL, Keshavan MS, Tandon N, Mathew IT, Mothi SS, Montrose DM, et al. Angiogenic and immune signatures in plasma of young relatives at familial high-risk for psychosis and first-episode patients: a preliminary study. Schizophr Res 2016;170:115-122.


30. Zeni-Graiff M, Rizzo LB, Mansur RB, Maurya PK, Sethi S, Cunha GR, et al. Peripheral immuno-inflammatory abnormalities in ultra-high risk of developing psychosis. Schizophr Res 2016;176:191-195.


31. Hayes LN, Severance EG, Leek JT, Gressitt KL, Rohleder C, Coughlin JM, et al. Inflammatory molecular signature associated with infectious agents in psychosis. Schizophr Bull 2014;40:963-972.



32. Khoury R, Nasrallah HA. Inflammatory biomarkers in individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis (CHR-P): State or trait? Schizophr Res 2018;199:31-38.


33. Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B. Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 2011;70:663-671.



34. de Witte L, Tomasik J, Schwarz E, Guest PC, Rahmoune H, Kahn RS, et al. Cytokine alterations in first-episode schizophrenia patients before and after antipsychotic treatment. Schizophr Res 2014;154:23-29.


35. Goldsmith DR, Rapaport MH, Miller BJ. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol Psychiatry 2016;21:1696-1709.




36. Upthegrove R, Manzanares-Teson N, Barnes NM. Cytokine function in medication-naive first episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 2014;155:101-108.


37. Song X, Fan X, Li X, Zhang W, Gao J, Zhao J, et al. Changes in pro-inflammatory cytokines and body weight during 6-month risperidone treatment in drug naive, first-episode schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2014;231:319-325.



38. Di Nicola M, Cattaneo A, Hepgul N, Di Forti M, Aitchison KJ, Janiri L, et al. Serum and gene expression profile of cytokines in first-episode psychosis. Brain Behav Immun 2013;31:90-95.



39. Borovcanin M, Jovanovic I, Radosavljevic G, Djukic Dejanovic S, Bankovic D, Arsenijevic N, et al. Elevated serum level of type-2 cytokine and low IL-17 in first episode psychosis and schizophrenia in relapse. J Psychiatr Res 2012;46:1421-1426.


40. Karanikas E, Manganaris S, Ntouros E, Floros G, Antoniadis D, Garyfallos G. Cytokines, cortisol and IGF-1 in first episode psychosis and ultra high risk males. Evidence for TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, TauNFbeta, IL-4 deviation. Asian J Psychiatr 2017;26:99-103.


41. Noto C, Ota VK, Santoro ML, Ortiz BB, Rizzo LB, Higuchi CH, et al. Effects of depression on the cytokine profile in drug naive first-episode psychosis. Schizophr Res 2015;164:53-58.


42. Noto C, Ota VK, Gouvea ES, Rizzo LB, Spindola LM, Honda PH, et al. Effects of risperidone on cytokine profile in drug-naive first-episode psychosis. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2014;18.


43. Borovcanin M, Jovanovic I, Dejanovic SD, Radosavljevic G, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML. Increase systemic levels of IL-23 as a possible constitutive marker in schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015;56:143-147.


44. Hong W, Zhao M, Li H, Peng F, Wang F, Li N, et al. Higher plasma S100B concentrations in schizophrenia patients, and dependently associated with inflammatory markers. Sci Rep 2016;6:27584




45. Deng H, Kahlon RS, Mohite S, Amin PA, Zunta-Soares G, Colpo GD, et al. Elevated plasma S100B, psychotic symptoms, and cognition in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Q 2018;89:53-60.



46. Zhang XY, Xiu MH, Song C, Chen DC, Wu GY, Haile CN, et al. Increased serum S100B in never-medicated and medicated schizophrenic patients. J Psychiatr Res 2010;44:1236-1240.


47. Li Y, Dammer EB, Zhang-Brotzge X, Chen S, Duong DM, Seyfried NT, et al. Osteopontin is a blood biomarker for microglial activation and brain injury in experimental hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. eNeuro 2017;4.

48. Erhardt S, Blennow K, Nordin C, Skogh E, Lindstrom LH, Engberg G. Kynurenic acid levels are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 2001;313:96-98.


49. Erhardt S, Engberg G. Increased phasic activity of dopaminergic neurones in the rat ventral tegmental area following pharmacologically elevated levels of endogenous kynurenic acid. Acta Physiol Scand 2002;175:45-53.


50. Joaquim HPG, Costa AC, Gattaz WF, Talib LL. Kynurenine is correlated with IL-1beta in plasma of schizophrenia patients. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2018;125:869-873.



51. Condray R, Dougherty GG Jr, Keshavan MS, Reddy RD, Haas GL, Montrose DM, et al. 3-Hydroxykynurenine and clinical symptoms in first-episode neuroleptic-naive patients with schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2011;14:756-767.




52. Plitman E, Iwata Y, Caravaggio F, Nakajima S, Chung JK, Gerretsen P, et al. Kynurenic Acid in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull 2017;43:764-777.




53. Myint AM, Schwarz MJ, Verkerk R, Mueller HH, Zach J, Scharpe S, et al. Reversal of imbalance between kynurenic acid and 3-hydroxykynurenine by antipsychotics in medication-naive and medication-free schizophrenic patients. Brain Behav Immun 2011;25:1576-1581.


54. Smith RS. A comprehensive macrophage-T-lymphocyte theory of schizophrenia. Med Hypotheses 1992;39:248-257.


55. Tsay CJ. Julius Wagner-Jauregg and the legacy of malarial therapy for the treatment of general paresis of the insane. Yale J Biol Med 2013;86:245-254.


56. Buka SL, Tsuang MT, Torrey EF, Klebanoff MA, Bernstein D, Yolken RH. Maternal infections and subsequent psychosis among offspring. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001;58:1032-1037.


57. Brown AS, Begg MD, Gravenstein S, Schaefer CA, Wyatt RJ, Bresnahan M, et al. Serologic evidence of prenatal influenza in the etiology of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004;61:774-780.


58. Brown AS. Prenatal infection as a risk factor for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2006;32:200-202.




59. Brown AS, Derkits EJ. Prenatal infection and schizophrenia: a review of epidemiologic and translational studies. Am J Psychiatry 2010;167:261-280.



60. Brown AS. The risk for schizophrenia from childhood and adult infections. Am J Psychiatry 2008;165:7-10.


61. Zubin J, Spring B. Vulnerability--a new view of schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 1977;86:103-126.


62. Keshavan MS. Development, disease and degeneration in schizophrenia: a unitary pathophysiological model. J Psychiatr Res 1999;33:513-521.


63. Murray RM, Lewis SW. Is schizophrenia a neurodevelopmental disorder? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987;295:681-682.



64. Prata J, Santos SG, Almeida MI, Coelho R, Barbosa MA. Bridging Autism Spectrum Disorders and Schizophrenia through inflammation and biomarkers - pre-clinical and clinical investigations. J Neuroinflammation 2017;14:179




65. Drexhage RC, Hoogenboezem TA, Cohen D, Versnel MA, Nolen WA, van Beveren NJ, et al. An activated set point of T-cell and monocyte inflammatory networks in recent-onset schizophrenia patients involves both pro- and anti-inflammatory forces. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2011;14:746-755.



66. Altamura AC, Pozzoli S, Fiorentini A, Dell'osso B. Neurodevelopment and inflammatory patterns in schizophrenia in relation to pathophysiology. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;42:63-70.


67. Na KS, Jung HY, Kim YK. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2014;48:277-286.


68. Eaton WW, Byrne M, Ewald H, Mors O, Chen CY, Agerbo E, et al. Association of schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases: linkage of Danish national registers. Am J Psychiatry 2006;163:521-528.


69. Khandaker GM, Zammit S, Lewis G, Jones PB. A population-based study of atopic disorders and inflammatory markers in childhood before psychotic experiences in adolescence. Schizophr Res 2014;152:139-145.



70. Kayser MS, Dalmau J. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis, autoimmunity, and psychosis. Schizophr Res 2016;176:36-40.


71. Pollak TA, McCormack R, Peakman M, Nicholson TR, David AS. Prevalence of anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor [corrected] antibodies in patients with schizophrenia and related psychoses: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol Med 2014;44:2475-2487.


72. Lennox BR, Palmer-Cooper EC, Pollak T, Hainsworth J, Marks J, Jacobson L, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of serum neuronal cell surface antibodies in first-episode psychosis: a case-control study. Lancet Psychiatry 2017;4:42-48.


73. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 2014;511:421-427.




74. Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D, et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009;460:744-747.




75. Jeffries CD, Perkins DO, Chandler SD, Stark T, Yeo E, Addington J, et al. Insights into psychosis risk from leukocyte microRNA expression. Transl Psychiatry 2016;6:e981.




76. Liu S, Zhang F, Wang X, Shugart YY, Zhao Y, Li X, et al. Diagnostic value of blood-derived microRNAs for schizophrenia: results of a meta-analysis and validation. Sci Rep 2017;7:15328




77. Clarke MC, Tanskanen A, Huttunen M, Whittaker JC, Cannon M. Evidence for an interaction between familial liability and prenatal exposure to infection in the causation of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2009;166:1025-1030.


78. Yao JK, Keshavan MS. Antioxidants, redox signaling, and pathophysiology in schizophrenia: an integrative view. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011;15:2011-2035.



79. Sawa A, Sedlak TW. Oxidative stress and inflammation in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2016;176:1-2.


80. Shovestul BJ, Glassman M, Rowland LM, McMahon RP, Liu F, Kelly DL. Pilot study examining the relationship of childhood trauma, perceived stress, and medication use to serum kynurenic acid and kynurenine levels in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2017;185:200-201.



81. Phillips LJ, McGorry PD, Garner B, Thompson KN, Pantelis C, Wood SJ, et al. Stress, the hippocampus and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: implications for the development of psychotic disorders. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2006;40:725-741.


82. Garcia-Bueno B, Caso JR, Leza JC. Stress as a neuroinflammatory condition in brain: damaging and protective mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2008;32:1136-1151.


83. Frank MG, Baratta MV, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Microglia serve as a neuroimmune substrate for stress-induced potentiation of CNS pro-inflammatory cytokine responses. Brain Behav Immun 2007;21:47-59.


84. Di Forti M, Marconi A, Carra E, Fraietta S, Trotta A, Bonomo M, et al. Proportion of patients in south London with first-episode psychosis attributable to use of high potency cannabis: a case-control study. Lancet Psychiatry 2015;2:233-238.


85. Niemi-Pynttari JA, Sund R, Putkonen H, Vorma H, Wahlbeck K, Pirkola SP. Substance-induced psychoses converting into schizophrenia: a register-based study of 18,478 Finnish inpatient cases. J Clin Psychiatry 2013;74:e94-e99.


86. Hill MN, McLaughlin RJ, Morrish AC, Viau V, Floresco SB, Hillard CJ, et al. Suppression of amygdalar endocannabinoid signaling by stress contributes to activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009;34:2733-2745.




87. Muller N, Myint AM, Krause D, Weidinger E, Schwarz MJ. Anti-inflammatory treatment in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;42:146-153.


88. Koola MM, Raines JK, Hamilton RG, McMahon RP. Can anti-inflammatory medications improve symptoms and reduce mortality in schizophrenia? Curr Psychiatr 2016;15:52-57.


89. Marini S, De Berardis D, Vellante F, Santacroce R, Orsolini L, Valchera A, et al. Celecoxib adjunctive treatment to antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a review of randomized clinical add-on trials. Mediators Inflamm 2016;2016:3476240




90. Fillman SG, Sinclair D, Fung SJ, Webster MJ, Shannon Weickert C. Markers of inflammation and stress distinguish subsets of individuals with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry 2014;4:e365.




91. Altamura AC, Buoli M, Pozzoli S. Role of immunological factors in the pathophysiology and diagnosis of bipolar disorder: comparison with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2014;68:21-36.


92. Regen F, Hellmann-Regen J, Costantini E, Reale M. Neuroinflammation and alzheimer's disease: implications for microglial activation. Curr Alzheimer Res 2017;14:1140-1148.


93. Careaga M, Murai T, Bauman MD. Maternal immune activation and autism spectrum disorder: from rodents to nonhuman and human primates. Biol Psychiatry 2017;81:391-401.


94. Haroon E, Miller AH, Sanacora G. Inflammation, glutamate, and glia: a trio of trouble in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017;42:193-215.



96. Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD. Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 2003;302:1760-1765.


97. Garver DL, Tamas RL, Holcomb JA. Elevated interleukin-6 in the cerebrospinal fluid of a previously delineated schizophrenia subtype. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;28:1515-1520.



98. Prasad KM, Upton CH, Nimgaonkar VL, Keshavan MS. Differential susceptibility of white matter tracts to inflammatory mediators in schizophrenia: an integrated DTI study. Schizophr Res 2015;161:119-125.


99. Ellman LM, Deicken RF, Vinogradov S, Kremen WS, Poole JH, Kern DM, et al. Structural brain alterations in schizophrenia following fetal exposure to the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-8. Schizophr Res 2010;121:46-54.



100. Khandaker GM, Pearson RM, Zammit S, Lewis G, Jones PB. Association of serum interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein in childhood with depression and psychosis in young adult life: a population-based longitudinal study. JAMA Psychiatry 2014;71:1121-1128.



101. Stojanovic A, Martorell L, Montalvo I, Ortega L, Monseny R, Vilella E, et al. Increased serum interleukin-6 levels in early stages of psychosis: associations with at-risk mental states and the severity of psychotic symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014;41:23-32.


103. Buka SL, Tsuang MT, Torrey EF, Klebanoff MA, Wagner RL, Yolken RH. Maternal cytokine levels during pregnancy and adult psychosis. Brain Behav Immun 2001;15:411-420.


104. Brown AS, Hooton J, Schaefer CA, Zhang H, Petkova E, Babulas V, et al. Elevated maternal interleukin-8 levels and risk of schizophrenia in adult offspring. Am J Psychiatry 2004;161:889-895.


105. Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E. Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry 2008;63:801-808.



106. Al-Hakeim HK, Al-Rammahi DA, Al-Dujaili AH. IL-6, IL-18, sIL-2R, and TNFalpha proinflammatory markers in depression and schizophrenia patients who are free of overt inflammation. J Affect Disord 2015;182:106-114.



107. Al-Asmari AK, Khan MW. Inflammation and schizophrenia: alterations in cytokine levels and perturbation in antioxidative defense systems. Hum Exp Toxicol 2014;33:115-122.


108. Baker I, Masserano J, Wyatt RJ. Serum cytokine concentrations in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1996;20:199-203.


109. Simsek S, Yildirim V, Cim A, Kaya S. Serum IL-4 and IL-10 Levels correlate with the symptoms of the drug-naive adolescents with first episode, early onset schizophrenia. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2016;26:721-726.


110. Monji A, Kato TA, Mizoguchi Y, Horikawa H, Seki Y, Kasai M, et al. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia especially focused on the role of microglia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;42:115-121.


111. Garcia-Alvarez L, Garcia-Portilla MP, Gonzalez-Blanco L, Saiz Martinez PA, de la Fuente-Tomas L, Menendez-Miranda I, et al. Differential blood-based biomarkers of psychopathological dimensions of schizophrenia. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment 2016;9:219-227.


112. Sparkman NL, Johnson RW. Neuroinflammation associated with aging sensitizes the brain to the effects of infection or stress. Neuroimmunomodulation 2008;15:323-330.



113. Steiner J, Bielau H, Brisch R, Danos P, Ullrich O, Mawrin C, et al. Immunological aspects in the neurobiology of suicide: elevated microglial density in schizophrenia and depression is associated with suicide. J Psychiatr Res 2008;42:151-157.


114. Howes OD, McCutcheon R. Inflammation and the neural diathesisstress hypothesis of schizophrenia: a reconceptualization. Transl Psychiatry 2017;7:e1024.




115. Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007;8:57-69.



116. Giriko CA, Andreoli CA, Mennitti LV, Hosoume LF, Souto Tdos S, Silva AV, et al. Delayed physical and neurobehavioral development and increased aggressive and depression-like behaviors in the rat offspring of dams fed a high-fat diet. Int J Dev Neurosci 2013;31:731-739.


117. Baldwin P, Browne D, Scully PJ, Quinn JF, Morgan MG, Kinsella A, et al. Epidemiology of first-episode psychosis: illustrating the challenges across diagnostic boundaries through the Cavan-Monaghan study at 8 years. Schizophr Bull 2005;31:624-638.



118. Banerjee J, Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Albuquerque EX. Regulation of GABAergic inputs to CA1 pyramidal neurons by nicotinic receptors and kynurenic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2012;341:500-509.



119. Kegel ME, Bhat M, Skogh E, Samuelsson M, Lundberg K, Dahl ML, et al. Imbalanced kynurenine pathway in schizophrenia. Int J Tryptophan Res 2014;7:15-22.



120. de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Reyes-Madrigal F, Mao X, Leon-Ortiz P, Rodriguez-Mayoral O, Solis-Vivanco R, et al. Cortico-striatal GABAergic and glutamatergic dysregulations in subjects at ultra-high risk for psychosis investigated with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2015;19:pyv105









