 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 15(10); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
A radial arm maze (RAM) is an essential tool for assessing spatial learning and memory. Although this tool is widely used to study deficits in spatial memory in animal models, it has several restrictions that prevent its adaptation to human research and training. Therefore, we developed a head-mounted-display RAM (HMD-RAM) program for humans and verified its validity by comparing it to the results obtained by previous RAM studies. We also compared the HMD and a flat monitor as experimental devices.
Methods
Forty participants were recruited for the current study (Study 1: 20 participants with the HMD device; Study 2: 20 participants with the flat monitor). They navigated a virtual room as a first-person viewer and used environmental landmarks to remember their spatial position and orientation. The main dependent measures were working memory error, reference memory error, detection time, travel distance, and participant’s head movements. To validate the program, participants also conducted neuropsychological assessments and self-reported measures.
Results
The results for HMD-RAM tasks were consistent with the results of previous research conducted on animals, and the HMD elicited a higher sense of presence, immersion, and simulator sickness than the flat monitor. According to post-experiment questions on navigation strategy, creating landmarks was important when people were discovering locations in their environment, and an HMD was beneficial for better navigation strategy.
Rodents and other mammals have survival habits, including instinctively locating and retrieving food [1]. Spatial learning and memory are necessary for recording information regarding spatial orientation and the environment. Spatial memory, including episodic memory, is important in habits, and the hippocampus is implicated as an essential region for creating and maintaining spatial and cognitive maps [2]. The prefrontal cortex, which is crucial for studying complex, goaldirected human behavior, is involved in working memory according to neuroimaging and neurobehavioral studies [3]. Neurobehavioral studies commonly show that hippocampal damage disrupts spatial learning and memory processing in mammals [4], including humans [5]. Patients with hippocampal damage also show impairments in spatial navigation [6], spatial orientation [7], and visuospatial memory [8]. These impairments are highly related with mental disorders, including amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [9].
According to previous studies, the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of rodents and humans are involved in spatial learning and memory [10,11]. Spatial working and reference memory associated with spatial learning and memory are connected to different neuronal networks [12]. The prefrontal cortex and premotor cortex are involved in spatial working memory, whereas the hippocampal region and posterior parietal cortex are involved in spatial reference memory [13].
The radial arm maze (RAM) was pioneered by Olton & Samuelson [1]. RAMs has been commonly used by researchers for measuring spatial learning and memory in rodents; it allows for the evaluation of spatial working and reference memory. A RAM typically has a center area with eight arms radiating outward. Each arm has food sites at the end that are not visible from the central area; four arms have food at the distal end, and the other four arms do not have any. During a trial of the RAM, an animal must acquire food from all four areas of the maze. For each trial, the same configuration is used so that rodents can learn to acquire food from all areas without entering the arms that do not have food at the end. Two types of memories, i.e., working and reference, are assessed during the maze task. Assessment of working memory (WM) involves rodents re-entering previously entered arms during the same trial, whereas that of reference memory (RM) involves rodents entering the nonrewarding arms in each trial. Previous studies using RAMs observed that working and reference memory decreased as the trials progressed in animal studies [1,14].
Although a RAM is extensively used to evaluate spatial ability, including working and reference memory, it has several restrictions on its adaptation to humans [1]. Tools intended for rats are small so that rats can walk around them, whereas tools for experiments with people must be proportionally larger. A RAM tool for humans must be large, making it difficult to manufacture and manipulate. Therefore, memory in humans is commonly measured by simple neuropsychological assessments using paper-and-pencil tasks. These tasks require participants to carry out imaginary manipulations of geometric objects or figures or otherwise accomplish a visual transformation of the stimuli shown on paper [15-18]. Animal RAMs assess spatial learning and memory by quantifying the performances of the animals as they navigate and remember paths in the real world. Tools for spatial memory for humans and animals differ from traditional psychometric measures and navigational route-finding measures of spatial ability. In particular, animal tasks require physically moving through the environment, whereas neuropsychological assessments require no such translocations by humans.
To adapt RAM tasks to humans, researchers developed a monitor-based radial arm maze (M-RAM) with a flat monitor [13,18-23]. Participants used the monitor to conduct the RAM tasks. These tools led to evaluations of behavioral spatial learning and memory in humans, which found that humans use spatial strategies similar to those of rodents to manipulate RAM tasks. Dependent measures including WM error and RM error decreased as the trials proceeded. However, previous RAM studies for humans used only a flat monitor and did not have sufficient ecological validity related physical movements, including head/body coordination.
In this study, to assess spatial learning and memory in humans to overcome the limitations of neuropsychological assessments and M-RAM programs, we designed a head-mounted display-radial arm maze (HMD-RAM) program in which a RAM tool was operated in virtual reality (VR) with a head-mounted display (HMD), which is a video display device. VR platforms provide immersive experiences for humans in three-dimensional (3D) worlds using computer-generated environments [24], and there are numerous research studies on the advantages of VR technologies for spatial ability [25-29]. To experience the simulated space, participants put on the HMD. When participants move their heads, computer-generated images are translated or rotated as they move in the virtual world. Previous studies suggested that participants experienced significantly more presence, immersion, and simulator sickness using an HMD device, which provides depth perception by employing a stereoscopic view, than when using a flat monitor display [30-32].
Consequently, we designed an HMD-RAM program with a RAM tool operated in VR with an HMD. The RAM program created in a virtual world had eight arms and four rewards, similar to a standard RAM. The behavioral-dependent measures in this study were WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, and participant’s head movements and included traditional RAM and new VR-dependent measures. Our specific hypotheses were as follows:
1) The behavioral-dependent measures of humans would decrease as the blocks progressed, similar to the results of previous animal RAM studies [1,14].
2) Neuropsychological assessments would be associated with current measures of spatial learning and memory.
3) HMDs and flat monitors would have common points in behavioral- and subjective-dependent measures.
The protocol was approved by the university’s Institutional Review Board (IRB) before beginning the recruitment (HYI-14-100-1). Twenty participants (30% female, n=6) were recruited through advertisements placed on the Hanyang University campus. All participants provided their consent (age: M=23.0 years, SD= 2.1) (Table 1). No participants reported currently being prescribed any psychiatric medications.
We created a RAM program in a virtual world using a 3D development platform (Vizard 5.2; WorldViz, Santa Barbara, CA, USA). We used a desktop workstation running Microsoft Windows 7 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and equipped with a high-end graphics card (nVidia GeForce, nVidia, CA, USA). In the HMD-RAM task, the program was implemented with an HMD (Oculus DK2, Oculus VR, Irvine, CA, USA) that collected head movement data with three degrees of freedom (yaw, pitch, and roll) with a 100° field-of-view system and high resolution (960×1,080 pixels per eye). For comfort, adjustable headbands were used to fit the HMD during the experiments. A one-handed joystick (PlayStation navigation controller, Sony, Tokyo, Japan) was also used to navigate the virtual world. A stereo speaker was connected to a computer for auditory feedback in conjunction with the visual stimuli when participants found treasures. All tasks were observed by an experimenter through a 24-inch LED flat monitor that showed the progress of the program.
For this study, we developed a RAM program for humans. The participants navigated a virtual room as a first-person viewer using an HMD and a joystick. For landmark cues, the virtual room had different colored wallpapers, and pieces of furniture (e.g., sofa, table, chair, etc.) were located between paths (Figure 1). Participants could use those landmarks to remember their spatial position and orientation, and their viewpoint was changed according to their head movements.
The RAM had eight paths extending out of a middle area with a reward or nonreward chest at the end of each path. Participants were required to discover the four treasures as quickly as possible. Upon finding a treasure, they received positive auditory feedback. The task had five blocks, and each block was allocated a time of up to 5 min. When the participants found the four treasures or 5 min had elapsed, the block was terminated. The same configuration of the environment of the virtual room and rewarded paths was used for all blocks so that the participants could remember the locations of the treasures as the blocks progressed.
The main dependent measures in the HMD-RAM task were WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, and participant’s head movements. WM error was defined as the number of times a participant discovered a path that he/she had previously entered in the same block, regardless of whether that path was rewarded. RM error was defined as the number of times a participant reentered paths that were not rewarded. Detection time and travel distance were recorded every 1/60 s during each block. To measure the travel distance in the virtual room, we used a virtual distance (quant) [33], which is a distance measure in the virtual world. We also analyzed head movements every 1/60 s, which were collected as head movement data with the HMD during the tasks. All measures were recorded for each block separately.
To validate the program, we conducted memory-related neuropsychological assessments. Participants took the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (ROCFT; copying, immediate, and 20-min delayed recall), which measures visuospatial construction and memory [15,17]. This test assesses immediate and delayed memory by copying a complex picture and then drawing it from memory. ROCFT immediate was conducted to assess the performance of WM. ROCFT delayed was conducted to assess the performance of RM. Participants also did the Seoul Verbal Learning Test (SVLT; three immediate trials of 12 words and 20-min delayed recall trial for the words) of the Samsung Neuropsychological Screening Battery [34], which tests verbal learning and memory. SVLT immediate was conducted to assess the performance of WM. SVLT delayed was conducted to assess RM performance.
To assess presence, the degree to which the participant feels immersed in the virtual environment, we used the Presence Questionnaire (PQ) [35]. The PQ has 33 items and uses a 7-point Likert scale (1=not at all, 7=completely). To assess the degree of simulator sickness, we used the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ) [36]. The SSQ is a 16-item symptom checklist that uses a 4-point Likert scale (0=not at all, 3=severe). To assess the immersion of the RAM program, we modified the Immersive Experience Questionnaire [37] and the Flow State Scale [38]. Our Immersive Questionnaire (IMQ) had three questions and used an 11-point Likert scale. The questions we modified were as follows: “Did you feel that you and the things were in the same place?” “Did you feel that you got around in the room?” and “My attention was focused entirely on what I was doing.” Because humans can explain their navigation strategies, we asked the participants about their navigation strategy for the RAM task after the completion of all blocks. To verify the navigation strategies, we used the following post-experiment instruction on navigation strategy: “Please describe how you remembered the position of the treasure chest.”
This research was conducted in accordance with the appropriate university IRB protocol. Written consent and assent were obtained from the participants upon arrival at the research area. The participants were asked to complete a brief questionnaire to gather data on age, gender, average time of gaming per week, prior virtual world experience, and prior joystick experience. They were given neuropsychological assessments (ROCFT and SVLT). The experimenters described the progress of the task to the participants and assisted them with the HMD head placement. The participants completed a practice block of the RAM task for approximately 5 min, during which they practiced manipulating their viewpoint, using the joystick, and performing head rotations, and understand how they would conduct the task. After the practice block, the participants carried out five main blocks that required finding the four treasures as soon as possible. They rested for approximately 1 min after each block to prevent fatigue effects. Immediately after the completion of all blocks, the participants filled in the PQ, SSQ, IMQ, and Navigation Strategy Questionnaire. They were debriefed regarding the purpose of the study and received a class credit for participation.
We conducted a repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) to test for differences in dependent measures in block progress (Figure 2). WM error showed a significant main effect as the blocks increased [F(4, 76)=2.521, p<0.05, η2=0.117). We also found a significant main effect in RM error as the blocks progressed [F(4, 76)=7.107, p<.001, η2= 0.272). The participants committed fewer WM and RM errors as the blocks proceeded. We observed a significant main effect as the blocks increased, indicating that the participants manipulated for shorter detection time [F(4, 76)=9.100, p<0.001, η2=0.324) and shorter travel distance [F(4, 76)=7.586, p<0.001, η2=0.285) to discover the treasures. We also found a significant main effect as the blocks increased, indicating that the participants used fewer head movements [F(4, 76)=7.588, p<0.001, η2=0.285) to see their viewpoint as the blocks proceeded.
Correlation analysis determined whether the previous neuropsychological assessments were related to HMD-RAM performance (Table 2). We compared four neuropsychological assessment measures (i.e., ROCFT immediate, ROCFT delayed, SVLT immediate, and SVLT delayed) and five behavior-dependent measures for HMD-RAM (i.e., RM error, WM error, detection time, travel distance, and head movement). Several significant relationships between task performance and neuropsychological measures were discovered.
In the correlation analysis, ROCFT immediate was significantly negatively correlated with RM errors [r(20)=-0.498, p<0.05), WM errors [r(20)=-0.513, p<0.05], detection time [r(20)=-0.456, p<0.05], and travel distance [r(20)=-0.499, p<0.05]. However, no significant correlations were observed with head movements (p>0.521). The performance on ROCFT delayed was significantly positively correlated with RM errors [r(20)=-0.526, p<0.05], WM errors [r(20)=-0.515, p<0.05], detection time [r(20)=-0.447, p<0.05], and travel distance [r(20)=-0.508, p<0.05]. However, no significant correlation was observed between ROCFT delayed and head movements (p>0.454).
In the correlation analysis, the performance on SVLT immediate was not significantly correlated with WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, or head movement (all ps>0.092). SVLT delayed also showed no significant correlation with WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, or head movement (all ps>0.065).
To evaluate the potential compounding effects of age, average time of gaming per week, PQ, SSQ, and IMQ, we conducted a correlation analysis with WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, and head movement. The SSQ was significantly positively correlated with travel distance [r(20)=0.451, p<0.05). However, no significant differences by age, average time of gaming per week, PQ, or IMQ were observed (all ps>0.521). We conducted independent samples t-tests according to prior virtual world experience, and prior joystick experience with five behavioral measures (i.e., WM error, RM error, detection time, travel distance, and head movements). No significant differences were observed for the following components: prior virtual world experience (all ps>0.479) and prior joystick experience (all ps>0.261).
The results of Study 1 were consistent with the hypothesis that behavioral measures in a RAM decrease as the blocks progress. We also found that visuospatial memory was associated with behavioral measures, whereas verbal memory was not. These results were consistent with previous results in rats [1,14] and meaningful because they indicated that a maze tool for humans had been developed and increased ecological validities. The results suggested that the HMD-RAM could be used to measure visuospatial memory in humans. However, there was another option to employ the RAM for humans. We could, for example, conduct a RAM experiment with a flat monitor instead of an HMD. Therefore, we conducted a second study to compare the HMD and a flat monitor, hypothesizing that HMD and flat monitor devices would have common and different points in behavioral- and subjective-dependent measures.
To address the need for control data for the M-RAM, we modified the display and control devices used in Study 1. In Study 1, the participants conducted the experiments with an HMD and a joystick. In Study 2, they conducted the experiments with a 24-inch flat monitor, a keyboard, and a mouse. The participants rotated their viewpoint using the mouse and translated their position using the arrow keys of the keyboard. To match the tasks between Study 1 and Study 2, we kept the location of treasures, arrival distance/time from the center position to each chest, and number of blocks the same. We also created an equal number of paths that the participants could see at once to match the visual field ranges between the HMD-RAM and M-RAM.
A new sample of 20 participants (20% female; n=4; age: M=23.2 years, SD=2.4) was recruited for Study 2. All consented to participate (Table 1). No participants reported currently being prescribed any psychiatric medications. The design and procedure for Study 2 were identical to those of Study 1 except for the different display and control devices.
A series of 2×5 ANOVA tests were conducted to test for differences in the main dependent measures (WM errors, RM errors, detection time, and travel distance) between the two groups (HMD-RAM and M-RAM) as the five blocks progressed. Participant head movement was not analyzed because the interaction methods were different between the HMD and the flat monitor. We found significant differences in WM error as the blocks proceeded [F(4, 152)=5.085, p<0.001, η2=0.118] and in RM error [F(4, 152)=14.608, p<0.001, η2=0.278]. The participants committed fewer WM and RM errors as the blocks proceeded. There were significant main effects as the blocks proceeded, indicating a shorter detection time [F(4, 152)=14.976, p<0.001, η2=0.283] and a shorter travel distance [F(4, 152)=13.622, p<0.001, η2=0.264]. However, no significant differences were observed between the two groups (all ps>0.204), and no significant interaction effects were observed for behavioral measures (all ps>0.649).
We compared the HMD-RAM and the M-RAM groups for level of presence, simulator sickness, and immersion after the experiments. Independent samples t-tests analyzed the differences in these factors for the two task environments (Table 3). The results of the PQ were significantly different [t(38)=2.130, p<0.05], and the HMD-RAM group (M=138.3, SD=23.6) showed a significantly higher sense of presence than the M-RAM group (M=122.4, SD=23.8). The SSQ also significantly differed between the two groups [t(38)=2.027, p<0.05]. The HMD-RAM group (M=12.2, SD=12.9) showed more simulator sickness than the M-RAM group (M=5.4, SD=7.7). The results of the IMQ were also significantly different [t(38)=2.992, p<0.005].
Because humans can report their navigation strategies, we collected data on participants’ navigation strategies. The participants reported the following: “I realized that the treasure was located next to the sofa, table, chair, and bed”; “I remembered the classification of the furniture and reward chest because the shape of the road was the same”; “I just discovered the paths by going clockwise”; “I walked along the path in one direction”; etc. In the HMD-RAM group, 15 participants reported that they remembered the environments (Remen), and five participants reported that they did not remember the environments (No-Remen). In the M-RAM group, 10 participants reported that they remembered the environments (Remen), and 10 participants reported that they did not (No-Remen). We also conducted a series of 2 (Remen vs. No-Remen) ×2 (HMD-RAM vs. M-RAM) ANOVA tests to compare the differences according to navigation strategies for dependent measures (WM error, RM error, detection time, and travel distance). The quantitative differences on how the four groups differed in five consecutive blocks are shown in Figure 3. Significant differences in RM error were found for navigation strategy [F(4, 76)=15.646, p<0.001, η2=0.303]. The No-Remen group showed more RM errors than the Remen group. The No-Remen group traveled significantly longer distances than the other group [F(4, 76)=10.071, p<0.005, η2=0.219). The No-Remen group spent a significantly more time than the Remen group [F(4, 76)=4.546, p<0.05, η2=0.112). However, significant differences in WM error were not observed (p>0.420). Additionally, significant interaction effects were not seen for any dependent measures (all ps>0.355).
To compare the potential differences between the HMD-RAM and M-RAM groups, we conducted independent samples t-tests for age and average time of gaming per week. No significant differences were found for any measures (all ps>0.108). Chi-square tests were performed to compare the differences in gender, prior virtual world experience, and prior joystick experience. No significant differences were seen for any of these measures (all ps>0.716).
We had three initial hypotheses. First, WM and RM error would decrease as the blocks progressed for the HMD-RAM as for an animal RAM, which is consistent with the findings of past research on rats [1,14]. Second, the neuropsychological assessments would be related to the five dependent measures for the HMD-RAM, and a visuospatial test would be associated with the measures, but a verbal test would not be. Lastly, the measures of the HMD-RAM would have common points behaviorally and subjectively compared to the measures of the M-RAM and behavioral measures, which showed similar characteristics, whereas subjective measures did not.
This research is meaningful because its findings indicate that a maze tool for humans had been developed and increased the ecological validity, which was the limitation of previous studies [13,18-23]. We developed a virtual maze task that used head movements and a joystick. In ecological conditions, self-generated movements provide corresponding movements in the optical environment. This information of visual field produces dependent measures, including travel distance and head movement [39]. A kinesthetic connection between the muscles and the vestibular system of the inner ear gives crucial cues about the direction of distance and heading information [40]. The results of this study suggested that the HMD-RAM would be appropriate for measuring spatial learning and memory in humans. It may be a useful tool for early detection of deficits in spatial memory, including aging-related disorders.
Even in animal RAM experiments, assessing the precise value of rat performances in the real world is difficult. Several studies could not measure the exact detection time and travel distance of tasks [1,14]. However, the VR that is controlled by a computer system can solve this issue. We also could measure the head movements, detection time, and travel distance of humans every 1/60 s during the whole maze task. According to animal-based RAM studies, spatial memory abilities can affect animals differently in the real world [41,42]. However, previous studies could not verify whether rodents really remembered the environments or not. Our study carried out experiments on humans rather than on animals so that we could measure the participants’ strategies. We found that people with better navigation strategies showed smaller RM errors and shorter moving distances and detection time. These results and methods could be extended to spatial learning and memory performances according to individual navigation strategies.
Although the ROCFT and SVLT tests assess WM and RM [15,17,34], only the former test showed a significant correlation with our measures, including RM error, WM error, detection time, and travel distance. Previous studies found that ROCFT measures are linked to visuospatial and organizational skills [15,17,43]. Our results showed that the HMD-RAM program was more closely associated with visuospatial conceptualization than with verbal abilities. This observation was supported by a previous study [20] that observed that only the ROCFT had a significant linear correlation with a monitor-based maze task. These results suggest that the HMD-RAM performance for assessing spatial learning and memory may correspond to previous neuropsychological assessments that are related only to visuospatial skills.
An observation of the differences between the HMD-RAM and the M-RAM groups showed that tools for experiencing a virtual world were not important for behavioral measures. Possibly, the finding of no significant behavioral differences might be caused by the very close matching between the HMD-RAM and the M-RAM devices in the current study. We extensively tried to match the view size and time to find treasures. However, the experiments with the HMD evoked greater presence and immersion according to the participants’ self-reports than the experiments with the flat monitor. Like in previous VR studies [30-32], we saw increases in presence and immersion as the virtual environment technology progressed from the flat monitor to the HMD. VR technologies have been developed over time to enhance the sense of presence or immersion, and our results are in line with those previous VR studies. The simulator sickness score was also higher with the HMD than with the flat monitor, in accordance with previous studies [30-32]. Simulator sickness may be caused by various elements, including image quality, frame rate, and field-of-view limitations. The travel distance of the current study was positively correlated with simulator sickness, allowing for the assumption that, when increasing the manipulation in a virtual world, nausea, oculomotor inconvenience, and disorientation can increase. A previous study also suggested that more rigorous head and body tracking technologies [44], like VR motion capture and treadmills, can reduce simulator sickness. We may need to consider those technologies to reduce simulator sickness and increase the ecological validity of the HMD-RAM.
This study had several limitations. First, the power of analysis was restricted because of the small number of participants. The correlation data were not strong (Table 2), and a larger sample size would have resulted in better statistical data. A second limitation was the gender ratio, as fewer females than males participated in the study. The gender effects of spatial learning and memory should be considered [18,23] and need to be evaluated in subsequent studies. Third, we conducted only two neuropsychological batteries (ROCFT and SVLT), and, therefore, additional tests are needed on spatial learning and memory. Finally, we need to experimentally investigate elderly participants or patients with hippocampal diseases, including aMCI and AD. This work would be valuable for assessing the spatial learning and memory of patients.
In this study, we suggested a new HMD-RAM program for spatial learning and memory, and measured human subjects’ patterns using that measure. The results suggested that the HMD-RAM program may be capable of human measurements of spatial working and reference memory. We hope that these results will contribute to new methods and raise new questions, and to renewed enthusiasm for human spatial learning and memory research. We believe that this work is an important foundation for the early diagnosis of deficits in spatial learning and memory, and we hope that it will help people who have spatial memory handicaps, including aMCI and AD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2017R1E1 A2A02022966) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning for convergent research in Development program for convergence R&D over Science and Technology Liberal Arts (NRF-2017M3C1B6071069).
Figure 1.
Head-mounted display-radial arm maze (HMD-RAM). A: HMD-RAM with eight arms in a virtual environment. B: A view of the HMD-RAM.
Figure 2.
Mean results for the HMD-RAM test for humans. (A) Number of RM errors. (B) Number of WM errors. (C) Average time. (D) Distance. (E) Sum of head movement. RM: reference memory, WM: working memory, HMD-RAM: head mounted display-radial arm maze.

Figure 3.
Results of the differences in strategies between the HMD-RAM and the M-RAM. (A) Number of RM errors. (B) Number of WM errors. (C) Average detection time. (D) Travel distance. RM: reference memory, WM: working memory, HMD: head-mounted display, M: monitor.
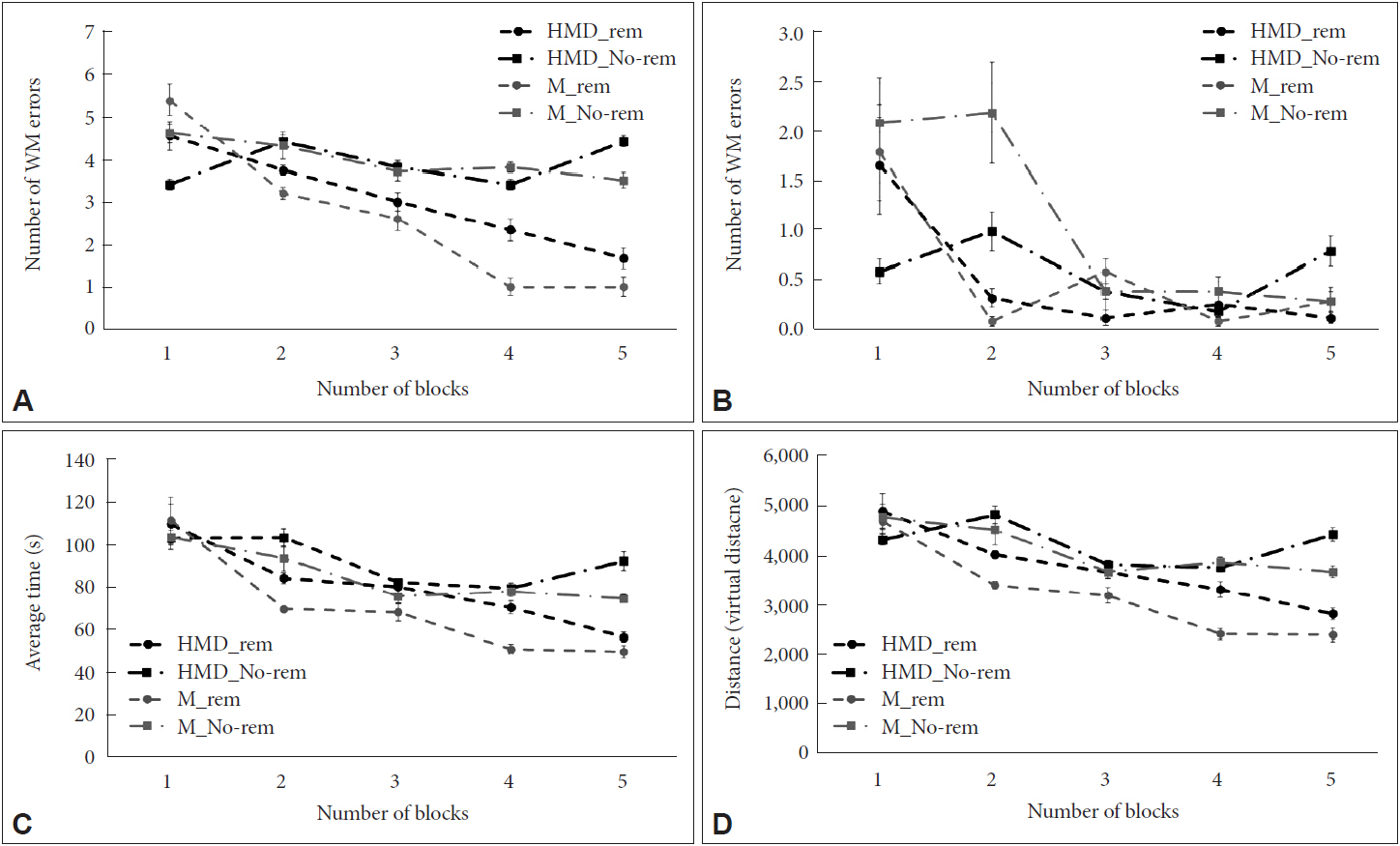
Table 1.
Participants’ demographic data
Table 2.
Correlations between dependent measures and neuropsychological measures
| Detection time | RM error | WM error | Travel distance | Head movement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROCFT | |||||
| Immediate | -0.456* | -0.498* | -0.513* | -0.499* | -0.188 |
| 0.043 | 0.025 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.428 | |
| Delayed | -0.447* | -0.526* | -0.515* | -0.508* | -0.204 |
| 0.048 | 0.017 | 0.020 | 0.022 | 0.389 | |
| SVLT | |||||
| Immediate | -0.161 | -0.349 | -0.205 | -0.387 | -0.047 |
| 0.497 | 0.131 | 0.386 | 0.092 | 0.845 | |
| Delayed | -0.051 | -0.073 | -0.420 | -0.131 | -0.266 |
| 0.832 | 0.761 | 0.065 | 0.583 | 0.258 |
REFERENCES
1. Olton DS, Samuelson RJ. Remembrance of places passed: spatial memory in rats. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 1976;2:97-116.

2. Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron 2002;35:625-641.


3. Jonides J, Smith EE, Koeppe RA, Awh E, Minoshima S, Mintun MA. Spatial working memory in humans as revealed by PET. Nature 1993;363:623-625.



4. Hodges H. Maze procedures: the radial-arm and water maze compared. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 1996;3:167-181.


5. Astur RS, Taylor LB, Mamelak AN, Philpott L, Sutherland RJ. Humans with hippocampus damage display severe spatial memory impairments in a virtual Morris water task. Behav Brain Res 2012;132:77-84.

6. Pearce JM, Roberts AD, Good M. Hippocampal lesions disrupt navigation based on cognitive maps but not heading vectors. Nature 1998;396:75-77.



7. Pai MC, Jacobs WJ. Topographical disorientation in community‐residing patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatr 2004;19:250-255.

8. Mendez MF. Visuospatial deficits with preserved reading ability in a patient with posterior cortical atrophy. Cortex 2001;37:535-543.


9. Hort J, Laczó J, Vyhnálek M, Bojar M, Bureš J, Vlček K. Spatial navigation deficit in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:4042-4047.



10. Astur RS, St Germain SA, Baker EK, Calhoun V, Pearlson GD, Constable RT. fMRI hippocampal activity during a virtualradial arm maze. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 2005;30:307-317.



11. Floresco SB, Seamans JK, Phillips AG. Selective roles for hippocampal, prefrontal cortical, and ventral striatal circuits in radial-arm maze tasks with or without a delay. J Neurosci 1997;17:1880-1890.



12. Madl T, Chen K, Montaldi D, Trappl R. Computational cognitive models of spatial memory in navigation space: a review. Neural Netw 2015;65:18-43.


13. Spieker EA, Astur RS, West JT, Griego JA, Rowland LM. Spatial memory deficits in a virtual reality eight-arm radial maze in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2012;135:84-89.


14. Mizuno M, Yamada K, Olariu A, Nawa H, Nabeshima T. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats. J Neurosci 2000;20:7116-7121.



15. Rey A. L’examen psychologique dans les cas d’encéphalopathie traumatique. (Les problems.). Arch Pediatr 1941;28:215-285.
16. Sheslow D, Adams W. Wide Range Assessment of Memory and Learning--Revised (WRAML-2), Administration and Technical Manual. Wilmington, DE: Wide Range. Inc.; 2003.
17. Osterrieth PA. Le test de copie d’une figure complexe. Arch Psychol 1944;30:206-356.
18. Moffat SD, Hampson E, Hatzipantelis M. Navigation in a “virtual” maze: sex differences and correlation with psychometric measures of spatial ability in humans. Evol Hum Behav 1998;19:73-87.

19. Xu D, Hao X, Wang Z, Duan Y, Liu F, Marsh R, et al. A virtual radial arm maze for the study of multiple memory systems in a functional magnetic resonance imaging environment. Int J Virtual Real 2012;11:63-76.



20. Lee JY, Kho S, Yoo HB, Park S, Choi JS, Kwon JS, et al. Spatial memory impairments in amnestic mild cognitive impairment in a virtual radial arm maze. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2014;10:653-660.



21. Levy LJ, Astur RS, Frick KM. Men and women differ in object memory but not performance of a virtual radial maze. Behav Neurosci 2005;119:853-862.



22. Goodrich-Hunsaker NJ, Hopkins RO. Spatial memory deficits in a virtual radial arm maze in amnesic participants with hippocampal damage. Behav Neurosci 2010;124:405-413.



23. Astur RS, Tropp J, Sava S, Constable RT, Markus EJ. Sex differences and correlations in a virtual Morris water task, a virtual radial arm maze, and mental rotation. Behav Brain Res 2004;151:103-115.


24. Majoros AE, Boyle E. Maintainability. In: Salvendy G, editor. Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1997, p. 1587-1590.
25. León I, Cimadevilla JM, Tascón L. Developmental gender differences in children in a virtual spatial memory task. Neuropsychology 2014;28:485-495.



26. Kim K, Mundy P. Joint attention, social-cognition, and recognition memory in adults. Front Hum Neurosci 2012;6:1-11.



27. Cánovas R, León I, Roldán MD, Astur R, Cimadevilla JM. Virtual reality tasks disclose spatial memory alterations in fibromyalgia. Rheumatology 2009;48:1273-1278.



28. Jang W, Shin JH, Kim M, Kim KK. Human field of regard, field of view, and attention bias. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2016;135:115-123.


29. Chai XJ, Jacobs LF. Effects of cue types on sex differences in human spatial memory. Behav Brain Res 2010;208:336-342.


30. Kim K, Rosenthal MZ, Zielinski DJ, Brady R. Effects of virtual environment platforms on emotional responses. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2014;113:882-893.


31. Slater M, Linakis V, Usoh M, Kooper R, Street G. Immersion, presence, and performance in virtual environments: An experiment with tri-dimensional chess. In ACM virtual reality software and technology (VRST). New York, NY: ACM Press; 1996, p. 163-172.
32. Ruddle RA, Payne SJ, Jones DM. Navigating large-scale virtual environments: what differences occur between helmet-mounted and desktop displays? Presence 1999;8:157-168.

33. Kim K, Kim SI, Cha KR, Park J, Rosenthal MZ, Kim JJ, et al. Development of a computer-based behavioral assessment of checking behavior in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Compr Psychiatry 2010;51:86-93.


34. Kang Y, Na D. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery. Incheon: Human Brain Research & Consulting co.; 2003.
35. Witmer BG, Jerome CJ, Singer MJ. The factor structure of the presence questionnaire. Presence 2005;14:298-312.

36. Kennedy RS, Lane NE, Berbaum KS, Lilienthal MG. Simulator sickness questionnaire: an enhanced method for quantifying simulator sickness. Int J Aviat Psychol 1993;3:203-220.

37. Jennett C, Cox AL, Cairns P, Dhoparee S, Epps A, Tijs T, et al. Measuring and defining the experience of immersion in games. Int J Hum Comput Stud 2008;66:641-661.

38. Jackson SA, Marsh HW. Development and validation of a scale to measure optimal experience: The Flow State Scale. J Sport Exerc Psychol 1996;18:17-35.

39. Goodale MA, Ellard CG, Booth L. The role of image size and retinal motion in the computation of absolute distance by the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Vision Res 1990;30:399-413.


40. Etienne AS, Teroni E, Maurer R, Portenier V, Saucy F. Short-distance homing in a small mammal: the role of exteroceptive cues and path integration. Cell Mol Life Sci 1985;41:122-125.


41. Brown MF, Farley RF, Lorek EJ. Remembrance of places you passed: social spatial working memory in rats. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 2007;33:213-224.



42. Timberlake W. Niche-related learning in laboratory paradigms: the case of maze behavior in Norway rats. Behav Brain Res 2002;134:355-374.








