 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 15(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Conventional methods for organotypic hippocampal tissue slice culture (OHSC) have shown several disadvantages or limitations regarding age of animals used, duration of culture and difficulty using neurodegenerative models. Therefore, we tried to establish OHSC from old 3xTg-Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice for longer period (over 4 weeks) and to validate utility of this system as a valid platform for translational neuroscience of AD.
Methods
OHSC was performed with old 3xTg-AD mice (12-14 months), old wild type mice (12-14 months) and young 3xTg-AD mice (2-4 months) using serum-free medium for 4 weeks. Hippocampal structure was evaluated by 4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) intensity and neuronal metabolism was measured by Alamarblue assay. Pathologic characteristics of AD were also investigated; β-amyloid levels by ELISA, amyloid plaque deposition by Thioflavin-S staining, and glial activation by immunohistochemistry.
Results
Following 4-week culture in serum-free media, hippocampal cells and layers were well preserved in cultured slices from old AD mice as was in those from young AD and old wild type mice. On the contrary, excessive regression of total visible cells was observed in conventional serum-containing medium regardless of genotype of mice. In parallel with this well preserved structure, major pathologic characteristics of AD were also well manifested in hippocampal slices from old AD mice.
Organotypic hippocampal tissue slice culture (OHSC) is a unique platform used in various fields of neuroscience. In this ‘ex vivo’ system, hippocampal slices are cultured as a still integrated tissue maintaining its typical features as it would in the in vivo brain [1,2]. Thus, in contrast to the primary neuronal culture where only neurons are selected and cultured, OHSC enables investigation of specific characteristics of in vivo brain such as synaptogenesis, interregional connectivity, neurovascular coupling, and neuro-glial dynamics [3-6]. In addition, dozens of slices are generally obtained from a single mouse brain. So they can serve as homogenous platforms which would be particularly useful for studies to compare effects of various external conditions (i.e., drugs) while minimizing both inter-individual variability and the sacrifice of experimental animals.
However, despite these obvious advantages, ‘conventional’ OHSC system has held several limitations towards broader usage. First, owing to the vulnerability of neurons to insufficient supply of oxygen inevitably accompanied during experimental procedures, it has been made mostly of neonatal brains, which may be inappropriate for studies on brain ageing and many age-related neuropsychiatric disorders [7-9]. Second, it has been cultured only for a limited time duration (several days to a week), which is unsuitable for the translational researches since most of psychotropic drugs generally manifest their proper actions in 3-4 weeks [10,11]. More importantly, long-term OHSC from various transgenic disease model mice still remains to be established. This would be obviously a challenge in that mutually exclusive two conditions should be achieved simultaneously; on the one hand, the specific pathogenic properties should be well preserved for the OHSC to be a valid ex vivo disease model [2,11]. On the other hand, despite its own pathogenesis, overall viability of neuronal tissue should be well maintained over a sufficient period. However, if well established, such ex vivo disease model system would be of value in terms of reducing expense and sacrifice of model animals in addition to the general advantages of OHSC.
Therefore, we attempted to establish OHSC from 3xTg-AD mouse, a model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and examined its validity as a putative ex vivo model of AD. Although cellular as well as animal models of AD have been widely used, little has been known about the availability of ‘tissue’ models of AD. So we assumed that several aspects are required for this tissue model system to be practically useful. First, the hippocampal tissue should be obtained from old mouse; old enough to develop obvious AD-related pathologies. Second, the tissue should stably remain organotypic over a period, long enough to provide sufficient time to examine chronic effects of drug administration. Third, it should maintain disease-related characteristics over the period to be a valid disease-model. Fourth, as a prominent advantage of OHSC, not only neurons but also glial cells should be well preserved in the sliced tissues, which would be useful for the studies on neuro-glial interactions in the context of AD-related neuroinflammation [12].
We report here that using serum-free (SF) culture media13 is an effective approach to establish OHSC from old (12-14 months) 3xTg-AD mice over 4 weeks. When compared to OHSC from young (2-4 months) 3xTg-AD or old (12-14 months) wild type (WT) C57BL/6J mice, OHSC from the old 3xTg-AD mice showed obvious pathological features yet comparable cellular structure. This approach could serve to facilitate the development of a new ex vivo model of other neurodegenerative disorders as well.
WT (C57BL/6J, Joongang, Seoul, Korea) and 3xTg-AD mice (AD mice) harboring APPSwe, tauP301L and PS1M148V transgenes (The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) were used in this study. There were 3 groups; young AD (2-4 months), old AD (12-14 months) and, old WT mice (12-14 months). All mice were female, and housed in groups of 2-4 per cage. Food and water were provided ad libitum under 12/12 hr light-dark cycles. All animal studies were approved by the Committee for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals at Yonsei University Health System (YUHS-IACUC 2013-0082) and performed according to the National Institute of Health guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
OHSC was performed based on the method described by Stoppini et al. [14] with slight modifications [13,15,16]. Following decapitation of mice, hippocampi were rapidly dissected, refined and then placed into a chilled dissection medium (DM) composed of hibernate A (BrainBits, Springfield, IL, USA), 2% B27 supplement, 2 mM L-glutamine by GlutamMax and antibiotic-antimycotics (all from Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Isolated hippocampi were sliced coronally at 300 μm thickness using a manual tissue slice chopper (#390610, Vibratome company, Saint Louis, MO, USA). The slices were gently separated from each other in fresh chilled DM and transferred onto membrane inserts (PICM0RG50; Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) in 6-well plates containing growth medium. 4-6 slices were placed in one insert and incubated in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. The medium was entirely changed at day 1 and changed by half 3 times a week thereafter for 3-4 weeks.
To confirm effectiveness of SF medium, slices were cultured in two types of medium, which is serum-containing (SC) and SF (Table 1). SC medium consisted of Neurobasal A with 20% horse serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, and antibiotics-antimycotics. SF medium contained Neurobasal A with 2% B27, 2 mM L-glutamine, and antibiotic-antimycotics. After 4 days in vitro (DIV), antibiotic-antimycotics was removed from both media.
To investigate cellular distribution, slices were stained with 4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; 10 μg/mL, Sigma-Aldrich Co., Saint Louis, MO, USA) for 30 min and imaged using an inverted fluorescence microscope with a camera (Olympus, Central Valley, PA, USA) at 1, 4, 7, 14, 21, and 28 DIV. The fluorescent intensity of the slices was quantified by ImageJ in the public domain (1.47v, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) in a 4X field containing the whole hippocampal area. Measured intensity was corrected by background and selected field area. Four slices per group were measured for statistical analysis.
Neuronal metabolism was analyzed by AlamarBlue cell health indicator assay (Invitrogen) as previously described [17,18]. At 1 DIV and 28 DIV, a 1:10 dilution of the AlamarBlue in the fresh culture medium was incubated with the slice cultures for 24 hr. After incubation, colorimetric readings were evaluated with the UV spectrophotometer at 570 nm. Blank standard was AlamarBlue-mixed media incubated without slices. 6 slices per well were used for 1 assay. 4 assays were used in each group for statistics.
In each well, 5 slices were placed on the membrane and cultured for 4 weeks. At 28 DIV, both the slices and culture media were harvested 48 hr after the last renewal of media. To measure Aβ in the tissue, slices were homogenized in RIPA lysing buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, 0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Sodium deoxycholate, 2 mM EDTA and protease inhibitor for 15 minute. The homogenized samples were centrifuged and used for ELISA procedure. For measuring Aβ in the media, we concentrated it using Amicon Ultra-0.5 mL centrifugal filters (Millipore), because absolute quantity of Aβ in the media was too little to measure. Aβ was measured by Human Aβ (1-42) ELISA kit (EZHS42, Millipore). Aβ level from slices (tissue) and media (secreted) were normalized by protein level measured with Pierce BCA protein assay kit (PJ209596A, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and compared across groups. Slices and media from 3 wells in each group were used for statistical analysis.
For histological staining, slice cultures were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and then fixed with 4% paraformaldahyde for 30 min. After fixing, pieces of membrane with slices were cut individually and placed in storing buffer consisting of PBS with 0.3% ethylene glycol and 0.3% glycerin before staining. Through staining process, slices were handled in a floating condition. Slices were permeabilized by incubation in PBS with 0.3% Tx-100 for 3 hr in room temperature.
For amyloid plaque staining, pretreated-slices were incubated with 0.05% thioflavin-S (Sigma-Aldrich Co.) dissolved in 50% ethanol for 4 hr. Then, slices were washed twice with 50% ethanol briefly and then washed with distilled water (DW) three times.
To observe immunoreactivity for activated astrocytes, fixing and permeabilization steps were proceeded as above. After pretreatment, slices were blocked using 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS with 0.3% Tx-100 for overnight and then incubated with anti-GFAP-antibody (1:100, RRID: AB_641021, sc-6170, Santa Cruz) in 2% BSA in PBS with 0.3% Tx-100 for 2 days. After washing with PBS three times, slices were labeled with secondary antibodies targeting donkey anti-goat IgG conjugated to Alexaflour 488 (1:100, RRID: AB_2340430 705-546-147, Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA, USA) for 1 day. Slices were washed three times with PBS again. All slices for astrocyte staining were already stained with DAPI during culture.
Stained slices were mounted on 1-hole slide glasses with DW (plaque staining) or PBS (astrocyte staining) containing Vectashield-mounting solution. Stained plaques were imaged with a confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM700, Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY, USA) and counted by an experimenter who was blind to age and genotype conditions. The fluorescence intensity was analyzed by Zen2011 (Carl Zeiss).
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Changes in DAPI intensity according to DIV were analyzed by the repeated measures Analysis of Variance (RM ANOVA). If sphericity was not assumed in RM ANOVA, the value after Greenhouse-Geisser correction was accepted. To compare 2 independent groups, the 2-tailed t-test was used. The 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc test was performed for multiple groups. Significance level was set at p<0.05.
To verify that SF medium is effective for long-term OHSC of AD mice, we compared differences in retention rates of hippocampal principal neurons (DAPI intensity) between conventional SC versus SF medium using both young AD and WT mice (5 months). In RM ANOVA with independent factors as genotype (AD vs. WT), time (DIV), and medium (SC vs. SF), we found a significant main effect of time (F1.9, 22.2=69.62, p< 0.001) and medium by time interaction (F1.9, 22.2=58.89, p< 0.001), which indicate that DAPI intensity was maintained only in SF but not in SC condition as DIV increased (Figure 1). However, there was no main effect of genotype (F1, 12=0.81, p= 0.39) or genotype by time interaction (F1.9, 22.2=1.57, p=0.23), which means that SF medium was effective for cell survival in long term OHSC regardless of genotypes. At 21 DIV, DAPI intensity of slices from both types of mice was maintained at about 90-100% of the initial value in SF medium (Figure 1B). However, the intensity significantly decreased to less than 1% in the SC medium (Figure 1B). In accordance with previous study [13], pyramidal neurons in cornus ammonis region 3 (CA3) already started to disappear at 4 DIV, and few granular cells were DAPI-positive in the dentate gyrus (DG) at 21 DIV in SC medium (Figure 1A).
As we simply identified the utility of SF medium for OHSC from young 3xTg-AD mice (Figure 1), next we attempted to this method is still effective for long-term OHSC from ‘aged’ AD mice. To this aim, we serially examined cellular distribution of OHSC in SF medium using old AD mice compared to young AD and old WT mice over 4 weeks. We found that DAPI fluorescence intensity was maintained around 100% of the initial value throughout 4 weeks in all groups (Figure 2), indicated by insignificant main effect of time for DAPI intensity across the groups (old AD, F4, 12=0.18, p=0.95; young AD, F4, 12= 0.20, p=0.94; old WT, F4, 12=0.67, p=0.62) (Figure 2B). These results confirmed that use of SF medium is an effective approach for long-term OHSC from old AD mice.
To identify whether cellular metabolism as well as cell viability is maintained in the long-term OHSC of old AD mice within SF medium, we performed AlamarBlue assay and found that metabolic activity was well maintained at 28 DIV compared to the basal metabolic level measured at 1 DIV (Figure 3) (t=-0.33, df=6, p=0.75).
To be a practically useful ex vivo platform of disease-model, not only cellular viability but also pathologic characteristics should be maintained throughout the culture period. Thus, we investigated the level of Aβ production, deposition of amyloid plaques and morphology of astrocytes in the 4-week-cultured slices from old AD mice.
We measured intracellular and secreted levels of Aβ in sliced tissues and media, respectively. There were statistically significant increases in Aβ levels in both tissues and media from old AD (Figure 4) (1-way ANOVA effect of group: tissue, F2, 6= 181.77, p<0.001; media, F2, 6=38.01, p<0.001). Post-hoc test also identified that Aβ levels in old AD condition were significantly higher than those in other two conditions (young AD: tissue, p<0.001; media, p=0.001, old WT mice: tissue, p<0.001; media, p=0.002). These results suggest that OHSC from old AD mice could provide an ex vivo system which is useful to see changes in intracellular production and secretion of Aβ in response to various environmental conditions including drugs and toxins.
Given that another key neuropathologic feature associated with AD is an accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain [19], we attempted to visualize plaques in OHSC with thioflavin-S staining [20]. We found that plaques were almost exclusively observed only in the slices from old AD mice (Figure 5A) compared to young AD (p=0.001) or old WT mice (p=0.001) (Figure 5). Most plaques in old AD mice were deposited around cornus ammonis region 1 (CA1) (Figure 5A), which was consistent with previous studies showing that Aβ accumulation starts from CA1 and spreads to other regions in the hippocampus [21].
Different from primary neuronal cultures, OHSC could preserve structure of glial cells within sliced tissues. Because both quantitative and qualitative expansion of glial cells are another critical features of AD brain [22], we imaged astrocytes with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) antibody. One-way ANOVA showed that GFAP signal intensity were significantly different between groups in all hippocampal subregions (Figure 6) (CA1, F2, 14=9.44, p=0.003; CA3, F2, 13=4.41, p=0.03; DG, F2, 12=8.34, p=0.005). Post-hoc analysis revealed that signal intensity of old AD mice was significantly higher than that of young AD (CA1, p=0.007; DG, p=0.01) and old WT mice (CA1, p=0.009; DG, p=0.01) in CA1 and DG (Figure 6B and D). In CA3, old AD mice showed higher signal than young AD did (p=0.04) but not than old WT mice (p=0.16) (Figure 6C). Moreover, in old AD mice we observed morphologic features of activated astrocytes, such as hypertrophic processes and swollen soma, which were not the case in young AD or old WT mice (Figure 7).
In this study, we examined the potential of long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mouse to be used as an ex-vivo platform for translational research of AD. Consistent with our previous study [13], SF medium was found to be effective to maintain hippocampal structure and cellular distribution over 4 weeks, even with the sliced tissues from the disease model mouse which was old enough (12-14 months old) to develop AD-related pathologies. Not only the structure and metabolic activity of neurons, but also various pathological features, such as production of Aβ, deposition of amyloid plaque, and glial cell activation, were all well identified in the long-term cultured hippocampal slices from the old AD mouse.
We confirmed that OHSC from old AD mice still have capacity to generate and secrete Aβ, suggesting that this system is readily used to screen candidate drugs by examining if they suppress production or enhance clearance of Aβ or both. We also found that glial cell morphology in the OHSC is well maintained as an active form, which suggests that this system may be suitable for the study of neuroinflammation in the context of AD pathogenesis. In addition, we can obtain decades of slices from a single AD mouse. This would be of great help to reduce the expense and sacrifice of the model mice. However, one of the most important advantages of using many sliced tissues from one single mouse might be that we can manipulate a number of experimental conditions (such as drugs, toxins, or their doses) between virtually identical platforms. This would minimize the statistical noise resulting from inter-individual variability, to which in vivo studies are often liable, particularly when the number of animals used is not sufficient.
Additionally, our model of OHSC with 3xTg-AD mouse made a step forward from OHSC using other kinds of AD models, which has recently been proposed [23,24], in terms of animal age and duration of culture. First, our study used 12-14 month-old AD mice for the first time. We believe that this is of translational importance. At the age of 12-14 months, 3xTg-AD mice begin to generate amyloid plaques [21]. We may also be able to apply the same method to younger 3xTg-AD mice within any range of age before plaque formation to investigate any preventive measure at earlier stage of AD pathogenesis (e.g., mild cognitive impairment) as well as mechanisms underlying plaque formation. Second, we established OHSC over 4 weeks, which may be a minimum period enabling studies to reveal genuine actions of psychotropic drugs.
Several limitations of our study remain to be explored in the future. First, we did not identify the molecular basis underlying the effectiveness of serum-withdrawal method on long-term survival of neurons in OHSC. Second, we only observed morphology of activated glial cells, but not neuro-glial dynamics directly, which would provide some clues for contributions of inflammation to AD pathogenesis. Third, we did not explore the morphology or function of specific circuit for AD pathology, such as cholinergic or dopaminergic neurons [2,24]. Finally, we omitted to examine tau-related pathology in OHSC from AD mice. In our 3xTg-AD mice, tau pathology as well as Aβ deposition occurs around 8-12 months of age. So we believe that OHSC from 3xTg-AD mice could also be a good platform to study tau-related AD pathogenesis such as hyperphosphorylation of tau or neurofibrillary tangle formation. We intended to only focus on Aβ pathologies for there are many different kinds of tau-phosphorylation sites, which would be a valuable subject of a separate study using this OHSC.
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that long-term OHSC could be successfully settled from old 3xTg-AD mouse using SF medium, as a promising ex vivo system for AD research. As well as cellular distribution, pathologic characteristics of AD, such as Aβ overproduction, amyloid plaque formation, and glial cell activation, were well preserved in the ex vivo hippocampal tissues throughout 4 weeks of culture. This system could serve as a translational platform for drug candidate screening or in-depth study of AD pathogenesis while truly conforming to one of the 3R principles, the reduction of animal sacrifice [25].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as the Environmental Health Action Program (Grant Number 2014001360002).
Figure 1.
Effects of culture media and genotype on maintenance of hippocampal structure in long-term OHSC. A: DAPI-positive nuclei (blue) according to DIV in cultured hippocampal slices of adult WT and 3xTg-AD mouse. Yellow arrows indicate DAPI positive regions. B: Quantification of the DAPI-positive fluorescent intensity according to media and genotype by time. Each point, mean±SE. Scale bars, 1 mm. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 indicate significance when compared to SF-WT condition in Bonferroni post hoc analysis. DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, WT: wild type, AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), DIV: days in vitro, SF: serum-free, SC: serum-containing.

Figure 2.
Effects of age and genotype on maintenance of hippocampal structure in long-term OHSC. A: Time-dependent changes on intensity of DAPI-positive nuclei (blue) in cultured hippocampal slices from young AD, old WT, and old AD mouse with serum-free medium. Yellow arrows indicate DAPI positive regions. B: Quantification of the DAPI-positive fluorescent intensity according to DIV in the images. No significant difference among 3 groups. Each point, mean±SE. Scale bars, 1 mm. DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, WT: wild type, AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), DIV: days in vitro, SF: serum-free, SC: serum-containing.

Figure 3.
Neuronal metabolism in long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mice. Cellular metabolism and viability were measured by AlamarBlue assay in hippocampal slices from old AD mice at 1 DIV and 28 DIV. Each bar, mean±SE. AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), DIV: days in vitro.
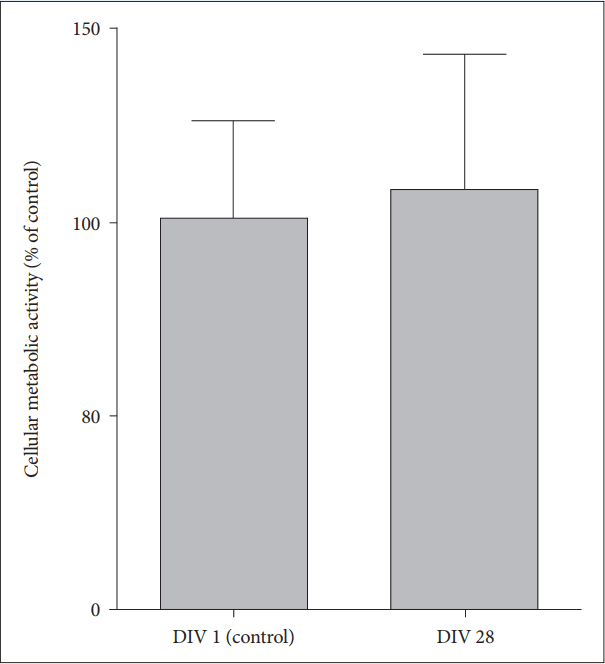
Figure 4.
Aβ levels in tissues and culture media in long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mice. Following 4-week culture, levels of Aβ42 from (A) lysed hippocampal slices and (B) culture media collected for 48 hr were measured by ELISA in young 3xTg-AD, old WT C57BL/6J and old 3xTg-AD mice. Each bar, mean±SE. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Bonferroni post-hoc analysis. Aβ: β-amyloid, AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), WT: wild type.

Figure 5.
Amyloid plaques in long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mouse. A: Amyloid plaques (bright green), stained with thioflavin-S, were exclusively shown in the 4-week-cultured hippocampal slices from old 3xTg-AD mouse. Photos were taken in the CA1. B: The number of amyloid plaques were counted bya blind experimenter in the whole hippocampus. Each bar, mean±SE. Scale bars, 100 μm. **p<0.01 by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), WT: wild type, CA: cornus ammonis, DG: dentate gyrus.
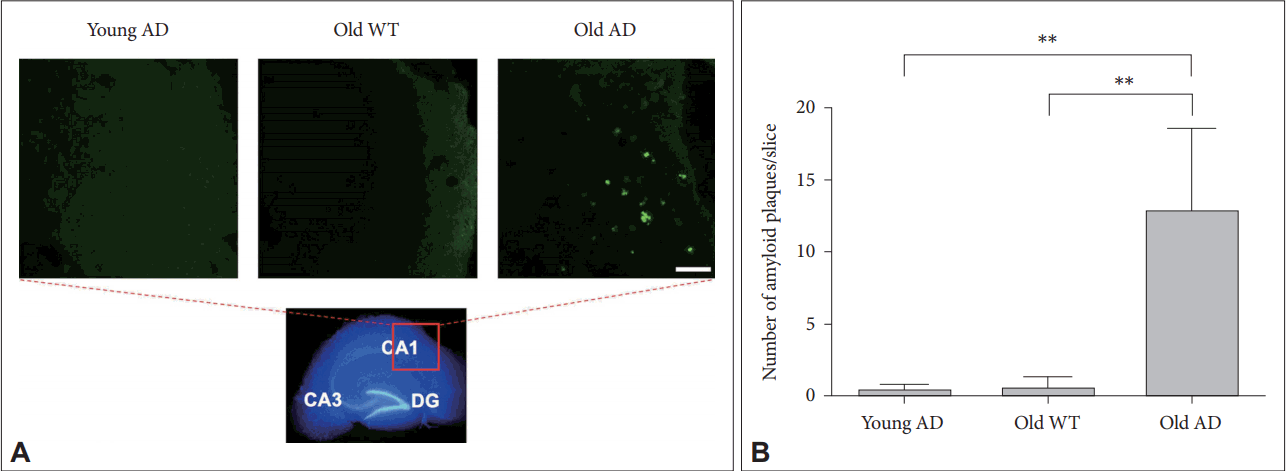
Figure 6.
Activated astrocytes in long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mouse. A: Representative confocal images show astrocytes stained with anti-GFAP-antibody (green) and DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) in the 4-week-cultured hippocampal slices from young 3xTg-AD, old WT C57BL/6J and old 3xTg-AD mice. GFAP signal intensity was quantitatively measured in (B) CA1, (C) CA3, and (D) DG regions. Each point, mean±SE. Scale bars, 100 μm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model), GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein, DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, WT: wild type, CA: cornus ammonis, DG: dentate gyrus.
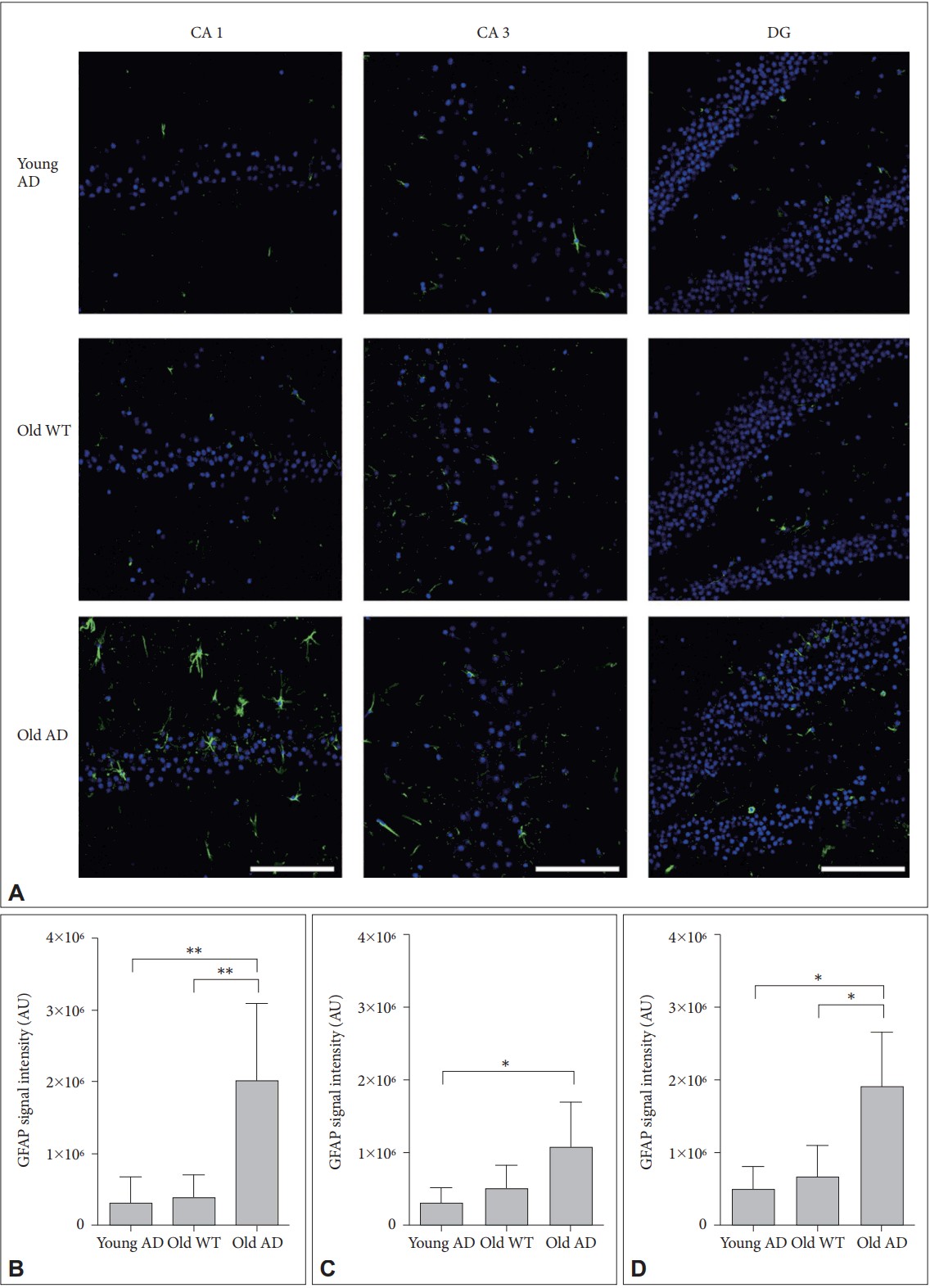
Figure 7.
Morphology of activated astrocyte in long-term OHSC from old 3xTg-AD mice. Morphological difference of astrocytes according to age and genotype. In the hippocampal slices from old 3xTg-AD mice, morphologic characteristics of activated astrocytes, such as hypertrophic process or swollen soma, were observed. Scale bars, 20 μm. WT: wild type, AD: Alzheimer’s disease (model).
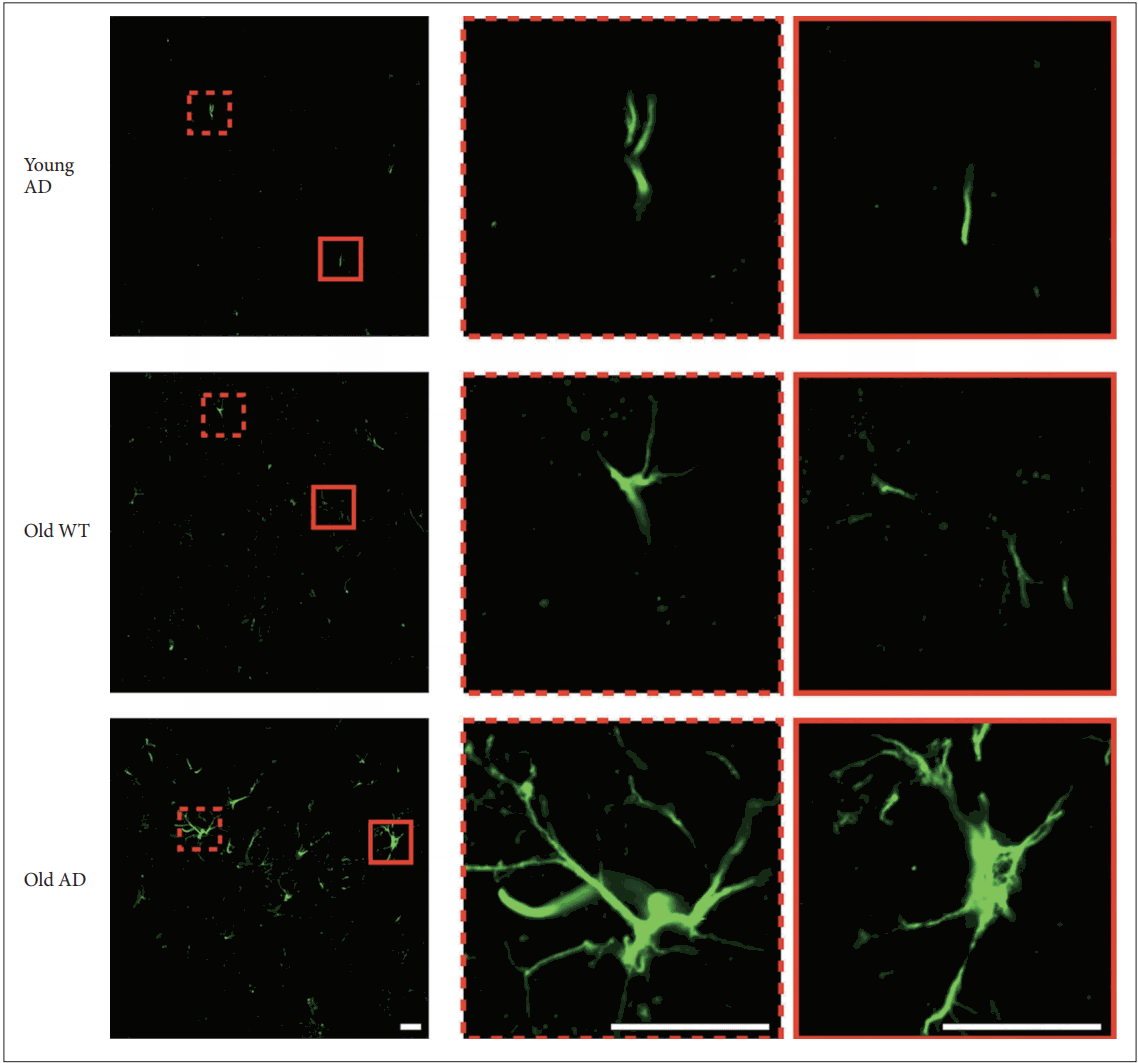
Table 1.
Composition of media
REFERENCES
1. Gähwiler B, Capogna M, Debanne D, McKinney R, Thompson S. Organotypic slice cultures: a technique has come of age. Trends Neurosci 1997;20:471-477.


3. Camenzind RS, Chip S, Gutmann H, Kapfhammer J, Nitsch C, Bendfeldt K. Preservation of transendothelial glucose transporter 1 and P-glycoprotein transporters in a cortical slice culture model of the blood-brain barrier. Neuroscience 2010;170:361-371.


4. Holopainen IE. Organotypic hippocampal slice cultures: a model system to study basic cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuronal cell death, neuroprotection, and synaptic plasticity. Neurochem Res 2005;30:1521-1528.


5. Kovács R, Papageorgiou I, Heinemann U. Slice cultures as a model to study neurovascular coupling and blood brain barrier in vitro. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol 2011;2011:646958




6. Noraberg J, Poulsen FR, Blaabjerg M, Kristensen BW, Bonde C, Montero M, et al. Organotypic hippocampal slice cultures for studies of brain damage, neuroprotection and neurorepair. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2005;4:435-452.


7. Daviaud N, Garbayo E, Lautram N, Franconi F, Lemaire L, Perez-Pinzon M, et al. Modeling nigrostriatal degeneration in organotypic cultures, a new ex vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2014;256:10-22.


8. Kearns SM, Scheffler B, Goetz AK, Lin DD, Baker HD, Roper SN, et al. A method for a more complete in vitro Parkinson’s model: slice culture bioassay for modeling maintenance and repair of the nigrostriatal circuit. J Neurosci Methods 2006;157:1-9.


9. Towfighi J, Mauger D, Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ. Influence of age on the cerebral lesions in an immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia: a light microscopic study. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 1997;100:149-160.


10. Pena F. Organotypic cultures as tool to test long-term effects of chemicals on the nervous system. Curr Med Chem 2010;17:987-1001.


11. Sundstrom L, Morrison B, Bradley M, Pringle A. Organotypic cultures as tools for functional screening in the CNS. Drug Discov Today 2005;10:993-1000.


12. Zorec R, Parpura V, Vardjan N, Verkhratsky A. Astrocytic face of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res 2017;322:250-257.


13. Kim H, Kim E, Park M, Lee E, Namkoong K. Organotypic hippocampal slice culture from the adult mouse brain: a versatile tool for translational neuropsychopharmacology. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013;41:36-43.


14. Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 1991;37:173-182.


15. Finley M, Fairman D, Liu D, Li P, Wood A, Cho S. Functional validation of adult hippocampal organotypic cultures as an in vitro model of brain injury. Brain Res 2004;1001:125-132.


16. Schrag M, Sharma S, Brown-Borg H, Ghribi O. Hippocampus of Ames dwarf mice is resistant to β-amyloid-induced tau hyperphosphorylation and changes in apoptosis-regulatory protein levels. Hippocampus 2008;18:239-244.


17. Nakayama GR, Caton MC, Nova MP, Parandoosh Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth and viability in vitro. J Immunol Methods 1997;204:205-208.


18. Staal JA, Alexander SR, Liu Y, Dickson TD, Vickers JC. Characterization of cortical neuronal and glial alterations during culture of organotypic whole brain slices from neonatal and mature mice. PLoS One 2011;6:e22040.



20. Wang J, Ho L, Chen L, Zhao Z, Zhao W, Qian X, et al. Valsartan lowers brain β-amyloid protein levels and improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 2007;117:3393-3402.



21. Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Kayed R, et al. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Aβ and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003;39:409-421.


22. Griffin W, Sheng J, Royston M, Gentleman S, McKenzie J, Graham D, et al. Glial-neuronal interactions in Alzheimer’s disease: the potential role of a ‘cytokine cycle’ in disease progression. Brain Pathol 1998;8:65-72.


23. Harwell CS, Coleman MP. Synaptophysin depletion and intraneuronal Aβ in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures from huAPP transgenic mice. Mol Neurodegener 2016;11:44









