 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 16(12); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The most existing research has predominantly focused on city rather than township hospitals. This study aimed to explore depressive symptoms and its associated factors among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals.
Methods
This cross-sectional study was carried out in Liaoning, China in 2016. 2,000 general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals were recruited and 1,736 of them became final subjects (effective response rate: 86.8%). Data on depressive symptoms, workplace violence (WPV), psychological capital (PsyCap), and demographic factors were collected through questionnaires. Hierarchical multiple regression was used to explore the factors related to depressive symptoms. Asymptotic and resampling strategies were applied to examine the potential mediating effect of PsyCap.
Results
The prevalence of depressive symptoms among the participants was 49.9%. Workplace violence was positively associated with depressive symptoms, whereas psychological capital and its components of hope, optimism and resilience were negatively associated with depressive symptoms. Psychological capital and its components of hope, optimism and resilience all played partial mediating roles between workplace violence and depressive symptoms.
Workplace violence (WPV) was defined as physical assaults and threats of assault directed towards persons at work [1]. Furthermore, WPV-related depressive symptoms have been in the limelight around the world. Depression can be regarded as one of common disorders of psychological distress and it mainly manifests as depressed emotion, slow thinking, poor sleep, reduced initiative, pessimism, and even suicidal thoughts [2]. According to a study, this showed that 36.3% of WPV victims presented intermediate depressive symptoms and 16% probably had major depression [3]. Depressive symptoms can develop into depression causing the affected person to function poorly at school, at work, and in the family, or even worse, leading to suicide [4].
Doctors and nurses, as particular occupational population, undertake the responsibilities of curing diseases and promoting health, which can predispose them to high occupational stress inevitably leading to distressed emotion [5]. Due to this special occupational environment, there is high prevalence of depressive symptoms among doctors and nurses. A study by Saijo et al. [6] found that about 46.7% of nurses had depressive symptoms in Japan. In China, Gong et al. [7] reported that 38% of nurses had depressive symptoms. Shen et al. [8] also revealed that the prevalence of depressive symptoms among Chinese physicians was 31.7%. Medical staff with depressive symptoms could seriously influence their own quality of life and medical services [9]. Noticeably, depressive symptoms among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals should be highlighted. On one hand, China is still a big agricultural country with huge rural population [10]. Rural patients may bring about serious economic burden of the society if their health problems are not cured effectively due to reduced medical service [11]. On the other hand, it is township hospitals that provide primary medical service to rural residents [12]. However, understaffed general practitioner and nurses are faced with less advanced medical devices and equipment [13], high workload but low income [14], few promotion opportunities [15], and more challenges in WPV [16], all of which may lead to their depressive symptoms.
WPV has been identified as risk factors for depressive symptoms [17,18]. WPV can be defined as abuse, threats and attacks, which pose a major threat to employeesŌĆÖ safety or health in their work environment [1]. WPV occurs commonly in hospitals. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) reports, 8% to 38% of medical staff suffered physical violence at work, with a large proportion suffered verbal abuse or threat [19]. In China, most existing research has focused on city rather than township hospitals [20], approximately 50% of medical staff in city were reported to experience a form of violence at work in a year [15]. Hospital violence not only has an impact on organizational commitment, job satisfaction and turnover of health workers, but also affects their physical and mental health such as depressive symptoms [17,21,22]. However, research in other countries has determined there is higher risk to rural general practitioners and nurses compared to city hospitals [23,24]. In China, township hospitals are characterized by relatively outdated medical devices and equipment, along with the shortage of health human resources, and accordingly, medical staff there often cannot provide high quality medical services [12], which may lead to more conflicts with patients, including hospital violence. Thus, we will explore the association and hypothesize WPV may be an important contributing factor of depressive symptoms in the study.
Psychological capital (PsyCap), as a positive psychological resource which can be measured, plays a vital role in both work performance and physical and mental health of employees [25,26]. Based on positive psychology, PsyCap is defined as ŌĆ£a positive state of mind exhibited during the growth and development of an individualŌĆØ [27]. PsyCap consists of four core elements: hope, optimism, resilience and self-efficacy [28]. Hope is defined as ŌĆ£a positive motivational state that is based on an interactively derived sense of successful agency (goal-directed energy) and pathways (planning to meet goals).ŌĆØ Optimism is an attributional mode which explains positive events as results of internal, permanent and general causes whereas negative events as results of external and temporary causes. Resilience is usually considered as the developable abilities to rebound or bounce back from tragedy, frustration and failure or even positive events. Self-efficacy refers to individualŌĆÖs belief about their capability to motivate the intention, cognitive resources and the necessary action to finish a specific task within established environment [28]. Prior research suggested that PsyCap had significant negative effects on depressive symptoms. For example, Liu et al. [29] reported that PsyCap and its components (hope, optimism, resilience and self-efficacy) were all negatively related to depressive symptoms among Chinese male correctional officers.
On the other hand, in the studies on the relationship between depressive symptoms and its associated factors, PsyCap and its components often worked as mediators combating depressive symptoms. For instance, Hao et al. [30] reported that PsyCap, hope and optimism were identified as mediators on the associations between work-family conflict and depressive symptoms among Chinese nurses. A previous study also found that resilience partially mediated the relationship between psychological stress and depressive symptoms among Chinese bladder and renal cancer patients [31]. In addition, another study indicated that self-efficacy could play a mediating role on the association between big five personality and depressive symptoms among Chinese unemployed population [32]. However, the potential effects of PsyCap on the association between WPV and depressive symptoms have not been examined among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals. Thus, we hypothesize that the PsyCap will work as a mediator in the relationship between WPV and depressive symptoms in the present study.
In light of the above concerns, the aim of the present study was to examine the relationship between WPV and depressive symptoms among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals. More importantly, we aimed to confirm the integrative effects of PsyCap on depressive symptoms after adjusting for the demographic variables.
The study procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards and approved by the Institutional Review Board of China Medical University (CMU62083011). Written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Information collected from all subjects was kept confidential and anonymous.
A cross-sectional study was carried out in Liaoning province, China, in 2016. Multi-staged sampling method was applied in our study. Firstly, according to the geographical distribution, 7 cities were randomly selected in Liaoning; secondly, from each city, a county or region was randomly selected. Finally, participants were selected from each chosen county or region by cluster sampling. After obtaining the informed consent, a self-administered questionnaire was distributed to each subject. The questionnaires were sent to 2,000 recruited general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals and 1,736 of them became the final subjects (effective response rate: 86.8%).
Depressive symptoms were measured with Chinese version of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) [33]. It is a brief, self-report questionnaire to measure individualŌĆÖs feeling in the past week, which has been reported to have good reliability and validity among rural populations in China [34]. The CES-D comprises 20 items and each item have four responses ranging from 0 ŌĆśrarelyŌĆÖ to 3 ŌĆśmost or all of the time.ŌĆÖ The total score ranges from 0 to 60, and higher score indicates severer depressive symptoms. Subjects who had a CES-D Ōēź16 were defined to belong to ŌĆśdepressive symptomsŌĆÖ group [33]. The CronbachŌĆÖs alpha coefficient for the scale was 0.887 in this study.
The Chinese version of workplace violence scale (WVS) was applied to assess the frequency of WPV experienced by healthcare workers [35]. The Chinese version of WVS, developed by Wang, was originated from Schat version of WVS [36]. The Chinese version of WVS is divided into five dimensions including physical assault, emotional abuse, threat, verbal sexual harassment and sexual assault; each dimension has one item, with 5 items in total. Each item has four responses ranging from 0 to 3 (0=never, 1=1 time, 2=2-3 times, 3=Ōēź4 times). The total score ranges from 0 to 15, with higher scores indicating a higher frequency of experiencing violence. The Chinese version of WVS has been shown to have adequate reliability and validity among individuals in China [37]. In this study, the Cronbach alpha coefficient for the total scale was 0.784.
The Chinese version of the 24-item Psychological Capital Questionnaire (PCQ) was used to measure PsyCap [38]. The 24-item PCQ consists of 4 dimensions including self-efficacy, hope, resilience and optimism [39]. Each item has six responses, ranging from 1 ŌĆśstrongly disagreeŌĆÖ to 6 ŌĆśstrongly agreeŌĆÖ. The higher average score for each dimension indicates the higher hope, optimism, resilience and self-efficacy level; the higher average score for total scale indicates more PsyCap individual has. The Chinese PCQ has demonstrated adequate reliability and construct validity of the PCQ among multiple samples [40,41]. In the present study, the CronbachŌĆÖs alpha coefficients for self-efficacy, hope, resilience, optimism and PsyCap were 0.884, 0.892, 0.731, 0.726, and 0.920, respectively.
Five demographic variables were obtained from the self-reported questionnaire, including age, marital status, monthly income, occupation and education. Age was classified as <30, 30 to 50, and >50 years old. Marital status was categorized as unmarried, married/cohabitation and divorced/widowed/separated. Monthly income was divided into <2,000, 2,000 to 4,000, and >4,000 Renminbi (RMB). Occupation was classified as doctors and nurses. Education background was divided into senior high school or under, junior college and undergraduate or above.
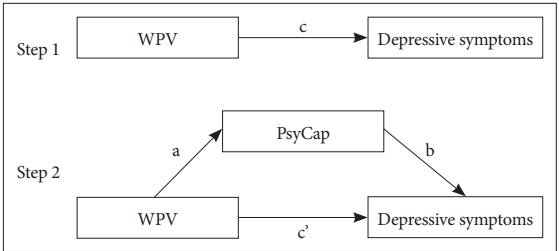
The mean depressive symptoms score in different categories of demographic factors were examined by t-test or one-way ANOVA. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between WPV, PsyCap and depressive symptoms. Hierarchical linear regression analyses were applied to explore the mediation of PsyCap in the relationship between WPV and depressive symptoms. Asymptotic and resampling strategies were used to examine PsyCap as a potential mediator on the association between WPV and depressive symptoms [42]. WPV was modeled as independent variable, with depressive symptoms as dependent variable, PsyCap and its components as mediating variables (Figure 1), and demographic factors as covariates. In the first step, the aim was to test whether the relationship between workplace violence and depressive symptoms was significant (the c path); in the second step, the aim was to examine the mediation of PsyCap (the a*b products). If the effect of WPV on depressive symptoms (cŌĆÖ path coefficient) in the second step was smaller than the c path coefficient in the first step, or was not significant, the mediation of PsyCap possibly existed. The bootstrap estimated in our study was based on 5,000 bootstrap samples. A bias-corrected and accelerated 95% confidence interval (BCa 95% CI) was conducted for each a*b product, and a BCa 95% CI excluding 0 indicated significant mediation.
All Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) values <10, was considered no existence of collinearity in hierarchical multiple regression. All the statistical analyses were performed with SPSS for Windows (version 17.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), with two-tailed probability value of <0.05 considered to be statistically significant. All statistical tests were two-sided (╬▒ = 0.05).
About 49.9% of the participants had depressive symptoms (CES-DŌēź16). The average age of the participants was 41.09┬▒ 9.84 years; the depressive symptoms score of the participants was 16.16┬▒8.99 and the WPV score was 1.67┬▒2.62 (mean┬▒SD). Demographic characteristic of subjects and distributions of depressive symptoms were shown in Table 1. Marital status and monthly income were significantly associated with depressive symptoms (p<0.05). As for marital status, the scores of those who were divorced, widowed or separated (5.1%) were higher than others. 459 (26.4%) out of the respondentsŌĆÖ monthly income were below 2,000 RMB, with higher score of depressive symptoms than others.
Correlation coefficients between continuous variables were presented in Table 2. WPV was significantly and positively associated with depressive symptoms, whereas PsyCap and its components including self-efficacy, hope, resilience and optimism were significantly and negatively associated with depressive symptoms; WPV was significantly and negatively associated with PsyCap and its components.
Given the associations between demographic variables (marital status and monthly income) and depressive symptoms, these demographic variables were added as control variables in block 1 in hierarchical multiple regression analyses, as shown in Table 3. In block 2, WPV was positively and significantly related to depressive symptoms (╬▓=0.399, p<0.01); in block 3A, PsyCap was negatively correlated with depressive symptoms (╬▓=-0.420, p<0.01) and the effect of WPV on depressive symptoms was smaller (╬▓=0.309, p<0.01) compared with that in block 2, which indicated that PsyCap could probably become a partial mediator on the association of WPV with depressive symptoms. Likewise, in block 3B, three dimensions of PsyCap including hope (╬▓=-0.187, p<0.01), resilience (╬▓=-0.095, p<0.01) and optimism (╬▓=-0.250, p<0.01) were significantly and negatively associated with depressive symptoms and the effect of WPV on depressive symptoms was also smaller (╬▓=0.299, p< 0.01) compared with that in block 2, indicating that hope, resilience and optimism could also partially mediated the association of WPV with depressive symptoms.
The mediating effect of PsyCap and its components were examined in Table 4. WPV had a negative association with PsyCap and its components (the a path); PsyCap and its components had significant and negative correlations with depressive symptoms after controlling for WPV (the b path). The product of a*b indicated that with the exception of self-efficacy, PsyCap (a*b= 0.090, BCa 95% CI: 0.066, 0.114), hope (a*b=0.037, BCa 95% CI: 0.022, 0.055), resilience (a*b=0.018, BCa 95% CI: 0.008, 0.037) and optimism (a*b=0.049, BCa 95% CI: 0.034, 0.066) all significantly and partially mediated the association between WPV and depressive symptoms.
Proportion of the total effect of the WPV on depressive symptoms (the c path) mediated by PsyCap, hope, resilience and optimism were calculated with the formula (a*b)/c to assess the mediating effect size. The proportion of mediation of PsyCap, hope, resilience and optimism were 22.53%, 9.27%, 4.51%, and 12.28%, respectively.
This large-scale cross-sectional study of general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals was conducted in Liaoning province in the northeastern region of China, which was the first one to examine the association between WPV and depressive symptoms and the mediating role of PsyCap on the relationship in China. Our findings revealed that 49.9% of the general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals had depressive symptoms (CES-DŌēź16), which was higher than the prevalence of metropolitan doctors (28.1%) [43], migrant workers (23.7%) [44], and general public in China (33.3%) [45]. Besides, the mean score of depressive symptoms among the subjects (16.16┬▒8.99) was also much higher than the average score of general population in urban China (13.24┬▒10.33) [45]. These results indicated that general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals had relatively severe depressive symptoms. Therefore, urgent efforts should be made to prevent and reduce these symptoms among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals.
In this study, WPV was found to be positively related to depressive symptoms, which echoed the findings of similar studies [16,17,43]. General practitioners and nurses devote themselves to helping patients to alleviate the pain and improve their quality of life. However, when general practitioners and nurses experience violent incidents such as accusations or abuse from patients, they are likely to have serious psychological imbalance in return, which can develop into negative emotion or stress [46]. On the other hand, since general practitioners and nurses in China are always busy at taking care of a large number of patients, there is little time left to relax themselves or communicate with others to release their negative emotion and stress [47]. Over time, medical staff may suffer from mental disorders such as depression [48].
In China, the continuous reform of the healthcare system [4], increased occupational stress [49], and the increasingly serious doctor/nurse-patient conflicts have resulted in violent incidents occurring frequently in health sector [47]. In our study, after the adjustment for control variables, WPV accounted for 15.9% of the total variance in depressive symptoms, confirming its important impact on depressive symptoms. Therefore, intervention strategies should be carried out to help general practitioners and nurses receive more respect from rural residents, improve their medical technology, and promote communication between doctors/nurses and patients in order to reduce occurrence of violent incidents and negative impact of WPV on mental health among general practitioners and nurses in township hospitals in China.
PsyCap and its components (hope, resilience and optimism) were found to play partial mediating roles in the relationship between WPV and depressive symptoms, which confirmed our hypothesis. The results suggested that workplace violence could reduce the level of general practitioners and nursesŌĆÖ PsyCap; subsequently, the reduced PsyCap could lead to their depressive symptoms. In other words, PsyCap and its components (hope, resilience and optimism) could help general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals to combat depressive symptoms. This result was in accordance with previous studies that verified the mediating effect of PsyCap in relationships among many occupational psychological outcomes. For instance, PsyCap could act as a mediator on the associations of depressive symptoms with occupational stress [50], and perceived organizational support [29]. Individuals who experienced WPV would feel angry, unfair and sad, along with decreased level of PsyCap, especially hope, resilience and optimism. Hope and optimism were found to be negatively associated with depressive symptoms, as they could help individuals to actively reduce or release psychological stress and negative emotions [51]. Previous studies also showed that resilience was significantly and negatively associated with depressive symptoms, since resilience could guide individual to bounce back from tragedy, frustration or failure [52]. As PsyCap can be measured, developed and effectively managed [38], the findings from our study encourage hospital managers to adopt effective strategies to improve PsyCap to combat depressive symptoms. In addition, in this study, we found that PsyCap as a whole had a greater mediating effect than that of each component (hope, resilience and optimism) alone, which suggested that managers might focus on the development of total PsyCap rather than its individual components. In brief, effective interventions should be undertaken to reduce WPV and to improve PsyCap so as to relieve depressive symptoms among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals.
However, several limitations must be mentioned. First, we applied a cross-sectional design, which limited us to draw conclusion on the casual relationships between the variables investigated. Longitudinal studies should be conducted in the future. Secondly, all data collected in this study were obtained through self-reported questionnaires, which could introduce recall bias or response bias. Thirdly, the participants were restricted in rural areas of Liaoning province, in northeastern region of China. Thus, caution should be taken when attempting to extrapolate the results to health workers in township hospitals in other regions of China.
In summary, based on this cross-sectional survey, our findings revealed that a large percentage of general practitioners and nurses surveyed in Chinese township hospitals had depressive symptoms and also suffered severe WPV which was significantly and positively related to depressive symptoms. PsyCap and some of its components (hope, resilience and optimism) played partial mediating roles in the relationship between WPV and depressive symptoms. Our results highlighted the importance of intervention on WPV and PsyCap for the reduction of depressive symptoms among general practitioners and nurses in Chinese township hospitals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all the administrators in the study hospitals who assisted in obtaining written informed consent for the survey and in distributing questionnaires to the subjects.
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Lie Wang, Chi Tong. Data curation: Lie Wang, Chi Tong, Chunying Cui, Yifei Li. Formal analysis: Chi Tong, Chunying Cui. Validation: Lie Wang. WritingŌĆöoriginal draft: Chi Tong. WritingŌĆöreview & editing: Lie Wang, Chunying Cui, Yifei Li.
Figure┬Ā1.
Theoretical model of the mediation of PsyCap on the association between WPV and depressive symptoms. c: associations of WPV with depressive symptoms; a: associations of WPV with PsyCap; b: association between PsyCap and depressive symptoms after controlling for the covariates; cŌĆÖ: associations of WPV with depressive symptoms after adding PsyCap as a mediator. WPV: workplace violence, PsyCap: psychological capital.
Table┬Ā1.
Demographic characteristic of subjects and the distributions of depressive symptoms
Table┬Ā2.
Means, SD and correlations of continuous variables
| Variables | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Depressive symptoms | 16.16 | 8.99 | 1 | |||||
| 2. WPV | 1.67 | 2.62 | 0.400ŌĆĀ | 1 | ||||
| 3. Self-efficacy | 4.55 | 0.93 | -0.331ŌĆĀ | -0.145* | 1 | |||
| 4. Hope | 4.46 | 0.95 | -0.430ŌĆĀ | -0.197* | 0.740ŌĆĀ | 1 | ||
| 5. Resilience | 4.38 | 0.82 | -0.415ŌĆĀ | -0.187ŌĆĀ | 0.582ŌĆĀ | 0.681ŌĆĀ | 1 | |
| 6. Optimism | 4.26 | 0.79 | -0.458ŌĆĀ | -0.192ŌĆĀ | 0.434ŌĆĀ | 0.519ŌĆĀ | 0.582ŌĆĀ | 1 |
| 7. PsyCap | 4.41 | 0.73 | -0.487ŌĆĀ | -0.214ŌĆĀ | 0.844ŌĆĀ | 0.893ŌĆĀ | 0.846ŌĆĀ | 0.740ŌĆĀ |
Table┬Ā3.
Associations of WPV, PsyCap and its components with depressive symptoms and mediating roles of PsyCap and its components
| Variables | Block 1 (╬▓) | Block 2 (╬▓) |
Block 3 (╬▓) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block 3A | Block 3B | |||
| Marital status 1 | 0.013 | -0.002 | 0.009 | 0.003 |
| Marital status 2 | 0.065* | 0.062* | 0.068ŌĆĀ | 0.057* |
| Monthly income | -0.071ŌĆĀ | -0.055* | -0.051* | -0.042* |
| WPV | 0.399ŌĆĀ | 0.309ŌĆĀ | 0.299ŌĆĀ | |
| PsyCap | -0.420ŌĆĀ | |||
| Self-efficacy | 0.013 | |||
| Hope | -0.187ŌĆĀ | |||
| Resilience | -0.095ŌĆĀ | |||
| Optimism | -0.250ŌĆĀ | |||
| F | 5.020ŌĆĀ | 330.241ŌĆĀ | 437.020ŌĆĀ | 126.510ŌĆĀ |
| R2 | 0.009 | 0.168 | 0.335 | 0.357 |
| ╬öR2 | 0.009ŌĆĀ | 0.159ŌĆĀ | 0.168ŌĆĀ | 0.189ŌĆĀ |
Table┬Ā4.
Mediating roles of PsyCap and its components on the associations of WPV with depressive symptoms
| Mediators | c | a | b | cŌĆÖ | Mediation of a and b (BCa 95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PsyCap | 0.399ŌĆĀ | -0.214ŌĆĀ | -0.420ŌĆĀ | 0.309ŌĆĀ | 0.090* (0.066, 0.114) |
| Self-efficacy | 0.399ŌĆĀ | -0.146ŌĆĀ | -0.015 | 0.298ŌĆĀ | -0.002 (-0.011, 0.006) |
| Hope | 0.399ŌĆĀ | -0.197ŌĆĀ | -0.186ŌĆĀ | 0.298ŌĆĀ | 0.037* (0.022, 0.055) |
| Resilience | 0.399ŌĆĀ | -0.187ŌĆĀ | -0.096ŌĆĀ | 0.298ŌĆĀ | 0.018* (0.008, 0.037) |
| Optimism | 0.399ŌĆĀ | -0.191ŌĆĀ | -0.253ŌĆĀ | 0.298ŌĆĀ | 0.049* (0.034, 0.066) |
REFERENCES
1. Merecz D, Rymaszewska J, Mo┼øcicka A, Kiejna A, Jarosz-Nowak J. Violence at the workplace--a questionnaire survey of nurses. Eur Psychiatry 2006;21:442-450.


2. Gao YQ, Pan BC, Sun W, Wu H, Wang JN, Wang L. Depressive symptoms among Chinese nurses: prevalence and the associated factors. J Adv Nurs 2012;68:1166-1175.


3. Da Silva AT, Peres MF, Lopes CS, Schraiber LB, Susser E, Menezes PR. Violence at work and depressive symptoms in primary health care teams: a cross-sectional study in Brazil. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2015;50:1347-1355.



4. WHO: Depression. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/. Accessed August 28, 2017.
5. Wang JN, Sun W, Chi TS, Wu H, Wang L. Prevalence and associated factors of depressive symptoms among Chinese doctors: a cross-sectional survey. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 2010;83:905-911.



6. Saijo Y, Yoshioka E, Kawanishi Y, Nakagi Y, Itoh T, Yoshida T. Relationships of job demand, job control, and social support on intention to leave and depressive symptoms in Japanese nurses. Ind Health 2016;54:32-41.


7. Gong Y, Han T, Yin X, Yang G, Zhuang R, Chen Y, et al. Prevalence of depressive symptoms and work-related risk factors among nurses in public hospitals in southern China: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 2014;4:7109




8. Shen LL, Lao LM, Jiang SF, Yang H, Ren LM, Ying DG, et al. A survey of anxiety and depression symptoms among primary-care physicians in China. Int J Psychiatry Med 2012;44:257-270.


9. Hao J, Wang J, Liu L, Wu W, Wu H. Perceived organizational support impacts on the associations of work-family conflict or family-work conflict with depressive symptoms among Chinese doctors. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016;13:326



10. National data: population. Available at: http://data.stats.gov.cn/easy-query.htm?cn=C01&zb=A0301&sj=2015. Accessed August 28, 2017.
11. Wang PS, Simon G, Kessler RC. The economic burden of depression and the cost-effectiveness of treatment. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 2003;12:22-33.


12. He Z, Cheng Z, Fu H, Tang S, Fu Q, Fang H, et al. Factors associated with the competencies of public health workers in township hospitals: a cross-sectional survey in Chongqing municipality, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:14244-14259.



13. Wang YP, Jin Y, Shi JW, Tao R, Wu P. An empirical analysis on medical service in the rural areas of Liaoning province. Med Philosophy 2010;21:48-50.
14. Zhang Y, Chen M, Shi XQ. Challenges of basic public health services provided by village doctors in Guizhou, China. Asia Pac J Public Health 2015;27:69S-76S.


15. Zhang X, Fang P. Job satisfaction of village doctors during the new healthcare reforms in China. Aust Health Rev 2016;40:225-233.


16. Wu S, Lin S, Li H, Chai W, Zhang Q, Wu Y, Zhu W. A study on workplace violence and its effect on quality of life among medical professionals in China. Arch Environ Occup Health 2014;69:81-88.


17. da Silva AT, Peres MF, Lopes Cde S, Schraiber LB, Susser E, Menezes PR. Violence at work and depressive symptoms in primary health care teams: a cross-sectional study in Brazil. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2015;50:1347-1355.



18. Hanson GC, Perrin NA, Moss H, Laharnar N, Glass N. Workplace violence against homecare workers and its relationship with workers health outcomes: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2015;15:11




19. WHO: Violence against health workers. Available at: http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/violence/workplace/en/. Accessed August 30, 2017.
20. Zhao S, Qu L, Liu H, Gao L, Jiao M, Liu J, et al. Coping with workplace violence against general practitioners and nurses in Heilongjiang province, China: social supports and prevention strategies. PLoS One 2016;11:e0157897.



21. Heponiemi T, Kouvonen A, Virtanen M, V├żnsk├ż J, Elovainio M. The prospective effects of workplace violence on physiciansŌĆÖ job satisfaction and turnover intentions: the buffering effect of job control. BMC Health Serv Res 2014;14:19




22. Magin PJ, May J, McElduff P, Goode SM, Adams J, Cotter GL. Occupational violence in general practice: a whole-of-practice problem. Results of a cross-sectional study. Aust Health Rev 2011;35:75-80.


23. Meuleners LB, Lee AH, Xia J, Fraser M, Hendrie D. Interpersonal violence presentations to general practitioners in Western Australia: implications for rural and community health. Aust Health Rev 2011;35:70-74.


24. Magnavita N. Workplace violence and occupational stress in healthcare workers: a chicken-and-egg situation-results of a 6-year follow-up study. J Nurs Scholarsh 2014;46:366-376.


25. Wang X, Liu L, Zou F, Hao J, Wu H. Associations of occupational stressors, perceived organizational support, and psychological capital with work engagement among Chinese female nurses. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:5284628




26. Estiri M, Nargesian A, Dastpish F, Sharifi SM. The impact of psychological capital on mental health among Iranian nurses: considering the mediating role of job burnout. Springerplus 2016;5:1377




27. Luthans F, Youssef-Morgan CM, Avolio BJ. Psychological capital: developing the human competitive edge. J Asian Econ 2007;8:315-332.
28. Youssef-Morgan CM, Luthans F. Psychological capital and well-being. Stress Health 2015;31:180-188.


29. Liu L, Hu S, Wang L, Sui G, Ma L. Positive resources for combating depressive symptoms among Chinese male correctional officers: perceived organizational support and psychological capital. BMC Psychiatry 2013;13:89




30. Hao J, Wu D, Liu L, Li X, Wu H. Association between work-family conflict and depressive symptoms among Chinese female nurses: the mediating and moderating role of psychological capital. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:6682-6699.



31. Li M, Wang L. The associations of psychological stress with depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese bladder and renal cancer patients: the mediating role of resilience. PLoS One 2016;11:e0154729.



32. Wang Y, Yao L, Liu L, Yang X, Wu H, Wang J, et al. The mediating role of self-efficacy in the relationship between big five personality and depressive symptoms among Chinese unemployed population: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2014;14:61




33. Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1977;1:385-401.

34. Yang L, Jia CX, Qin P. Reliability and validity of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) among suicide attempters and comparison residents in rural China. BMC Psychiatry 2015;15:76




35. Wang PX, Wang MZ, Bai Q, Jia CF, Lan YJ, Wang ZM, et al. Path analysis on workplace violence affecting work ability, job satisfaction and turnover intent in health professionals in Shangqiu City. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2006;35:785-788.

36. Schat AC, Kelloway EK. Reducing the adverse consequences of workplace aggression and violence: the buffering effects of organizational support. J Occup Health Psychol 2003;8:110-122.



37. Lin WQ, Wu J, Yuan LX, Zhang SC, Jing MJ, Zhang HS, et al. Workplace Violence and Job Performance among Community Healthcare Workers in China: The Mediator Role of Quality of Life. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:14872-14886.



38. Luthans F, Avolio BJ, Avey JB, Norman SM. Positive psychological capital: measurement and relationship with performance and satisfaction. Pers Psychol 2007;60:541-572.

39. Luthans F, Norman SM, Avolio BJ, Avey JB. The mediating role of psychological capital in the supportive organizational climate-employee performance relationship. J Organ Behav 2008;29:219-238.

40. Li X, Kan D, Liu L, Shi M, Wang Y, Yang X, et al. The mediating role of psychological capital on the association between occupational stress and job burnout among bank employees in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:2984-3001.



41. Peng J, Jiang X, Zhang J, Xiao R, Song Y, Feng X, et al. The impact of psychological capital on job burnout of Chinese nurses: the mediator role of organizational commitment. PLoS One 2013;8:e84193.



42. Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 2008;40:879-891.



43. Gong Y, Han T, Chen W, Dib HH, Yang G, Zhuang R, et al. Prevalence of anxiety and depressive symptoms and related risk factors among physicians in China: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 2014;9:e103242.



44. Qiu P, Caine E, Yang Y, Chen Q, Li J, Ma X. Depression and associated factors in internal migrant workers in China. J Affect Disord 2011;134:198-207.



45. Zhang J, Wu ZY, Fang G, Li J, Han BX, Chen ZY. Development of the Chinese age norms of CES-D in urban area. Chin Ment Health J 2010;24:139-144.
46. Tang FC, Li RH, Huang SL. The association between job-related psychosocial factors and prolonged fatigue among industrial employees in Taiwan. PLoS One 2016;11:e0150429.



47. Liu YL. Application of communication skill in new nurse patient relationship. Chin Health Ind 2015;6:133-135.
48. Goyal M, Singh S, Sibinga EM, Gould NF, Rowland-Seymour A, Sharma R, et al. Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174:357-368.



49. Ding Y, Qu J, Yu X, Wang S. The mediating effects of burnout on the relationship between anxiety symptoms and occupational stress among community healthcare workers in China: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 2014;9:e107130.



50. Shen X, Yang YL, Wang Y, Liu L, Wang S, Wang L. The association between occupational stress and depressive symptoms and the mediating role of psychological capital among Chinese university teachers: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2014;14:329











