 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 16(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) in out-of-school youths (OSYs) may be influenced by alcohol use, but there is a lack of evidence explaining how PTSS affect alcohol use problems in OSYs. The present study aimed to investigate the relationships among PTSS, quality of life, and alcohol use in OSYs.
Methods
In total, 125 OSYs (46.4% male) in South Korea completed the Korean Version of the Child Report of Post-Traumatic Symptoms (CROPS), the KIDSCREEN-27 Quality of Life Measure for Children and Adolescents, and the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption.
Results
Mean CROPS score was 18.7 (SD=11.6); 37.6% were problem drinkers. Quality of life in the domain of parent relations and autonomy significantly mediated the relationship between PTSS and alcohol use problems. OSYs with high parental satisfaction and autonomy were less likely to have alcohol use problems even with PTSS.
In South Korea, approximately 50,000 to 60,000 adolescents dropped out of school annually, with a total of 390,000 adolescents having dropped out by 2016 [1]. Accordingly, the number of out-of-school youths (OSYs), youths who do not attend school, has been increasing [2]. Approximately 14% of OSYs ultimately return to school and 20-30% of those who return leave school again. Furthermore, nearly 30% of OSYs undertake alternative learning (e.g., job skills or certification), while others remain idle, are employed part-time, or perform housework [2].
The increase in the school drop-out rate may be explained by traumatic experiences or chronic exposure to high-stress environments that may lead to or exacerbate psychiatric distress or mental illness [3-5]. Traumatic incidents, including experiencing or witnessing abuse, being a victim of a violent crime, being in a school environment with high levels of aggression and victimization, experiencing severe neglect, suffering a traumatic injury, or having the traumatic loss of a loved one can result in academic interruptions [5,6]. OSYs with high exposure to trauma have been reported to present with PTSD comorbid with alcohol use problems [7,8]. Alcohol use problems in OSYs can cause significant consequences. In alcohol studies on OSYs in the United States (US) and Nigeria, OSYs presented with more alcohol use problems than school youth [9,10]. Such adolescent alcohol abuse is often comorbid with other substance abuse (nicotine and more) and risky sexual behavior. Indeed, young adults exposed to alcohol before the age of 15 are four times more likely to ultimately develop alcohol dependence and persistent mental health and neuro-cognitive problems into adulthood [11,12]. Therefore, it is necessary to identify and scrutinize alcohol problems in OSYs who are at high risk of trauma.
Quality of life (QOL) is an important concept in health assessment, and health-related QOL represents a comprehensive multidimensional construct that defines QOL in terms of all domains of life (i.e., physical, psychological, and social), with an emphasis on mental and social stability beyond simply physical well-being [13,14]. Adolescence is a developmental stage marked by lower QOL compared with other developmental stages, and adolescents are more sensitive to traumatic events [15]. In previous research with adolescents and adults, PTSD has been shown to increased alcohol use problems, which not only decreased QOL but also increased the risk of depression and suicide [16,17]. OSYs are highly likely to have low QOL because of the high risk of exposure to traumatic events and the high likelihood of PTSD or post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS).
Previous studies [16,17] have shown that OSYs are at high risk for PTSS and alcohol use problems. PTSS have been linked to alcohol use problems, and PTSS and alcohol use problems are related to lower QOL. However, there is still limited research on trauma exposure, alcohol use, and QOL among OSYs. Therefore, this research aimed to test and explore the relationship between PTSS, QOL, and alcohol use in OSYs.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 125 OSYs who had been referred to the institution for physical and psychological health examinations from out-of-school youth support centers and youth shelters in the metropolitan centers for OSYsŌĆÖ health promotion services between September 2015 and December 2016. For the purpose of this study, OSYs are defined by the Korean Ministry of Government Legislation definition as ŌĆ£non-schooling adolescents aged between 9 and 24 yearsŌĆØ. OSYs from 9 to 24 years of age were recruited for participation [18]. As part of this examination, participants completed self-report questionnaires on PTSS, QOL, and alcohol use. The Institutional Review Board/Ethics Committee of the National Medical Center of Korea approved the study protocol in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (IRB No. H 1708-081-004).
We collected demographic information including age and gender. Alcohol use, smoking, PTSS, and QOL were assessed using the following instruments.
The Child Report of Post-Traumatic Symptoms (CROPS) [19] is a screening tool for post-traumatic symptoms in children who do/do not have an identified childhood traumatic event. The CROPS consists of 26 items that assess post-traumatic symptoms over the previous seven days. All items are rated on a 3-point Likert-scale (0=none, 1=some, 2=a lot). Survey completion takes approximately one minute. The total score is calculated by adding the scores of all item responses, with higher total scores indicating the presence of higher levels of post-traumatic symptoms. Cut-off scores have been developed to clarify what constitutes a clinical concern, and at present, the best cut-off for clinically meaningful CROPS scores is 19 [19,20]. CROPS was translated into Korean by Lee et al. [21], who also confirmed its reliability and validity (CronbachŌĆÖs ╬▒=0.93).
The KIDSCREEN instruments are self-report measures assessing the subjective health and well-being of children and adolescents [i.e., health-related quality of life (HRQoL)]. The KIDSCREEN-27-HRQoL [22], a shorter version of the KID-SCREEN-52, was used to assess the QOL measurements of children and adolescents [23]. It consists of 27 items related to five domains, including ŌĆ£Physical well-beingŌĆØ (5 items), ŌĆ£Psychological wellbeingŌĆØ (7 items), ŌĆ£Parent relations and autonomyŌĆØ (7 items), ŌĆ£Social support and peersŌĆØ (4 items), and ŌĆ£School environmentŌĆØ (4 items). Participants were asked to respond on a 5-point Likert-scale (0=not at all, 1=almost never, 2=sometimes, 3=often, or 4=very often). Considering the characteristic of OSYs, the current study selected 23 items in four domains, leaving out the ŌĆ£School environmentŌĆØ domain. Higher scores reflect a greater sense of QOL related to health. In this study, reliability was good (CronbachŌĆÖs ╬▒=0.92) [22].
The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption (AUDIT-C) [24] consists of three items that screen for drinking problems. It was developed to supplement the limitations of AUDIT [25], particularly the considerable implementation time in primary care. The AUDIT-C is a 3-item alcohol screening tool for people who are hazardous drinkers or who have active alcohol use disorders. The three items are as follows: ŌĆ£How often do you have a drink containing alcohol?ŌĆØ ŌĆ£How many standard drinks containing alcohol do you have on a typical day?ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£How often do you have six or more drinks on one occasion?ŌĆØ Subjects were asked to respond on a 5-point Likert-scale with varied response options (first item: 0=never, 1=monthly or less, 2=2-4 times a month, 3=2-3 times a week, or 4=4 or more times a week; second item: 0=1-2, 1=3-4, 2=5-6, 3=7-9, or 4=10 or more; third item: 0=never, 1=less than monthly, 2=monthly, 3=weekly, or 4=daily or almost daily). Total score of 3 or more among women or 4 or more among men is considered to indicate hazardous or harmful alcohol use [26]. For adolescents, a score of 3 or more is considered to be the cut-off for an alcohol use disorder [27]. The reliability of the K-AUDIT-C was good (CronbachŌĆÖs ╬▒=0 .93) [28].
We conducted statistical analyses using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) as follows. First, descriptive statistics were administered to examine the characteristics of participants such as gender, age, runaway history, and smoking history. Furthermore, participants were classified as problem drinkers based on a score Ōēź3 of AUDITC. Second, we used PearsonŌĆÖs product-moment correlation to examine the association between PTSS, QOL, and alcohol use problems. Finally, we used the SPSS INDIRECT MACRO [29], which is a multiple regression procedure, to test for mediating effects of parental relations/autonomy on the relationship between PTSS and alcohol use. The bootstrapping method [30] was used to test the significance of the indirect effect, using 5,000 bootstrap samples and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). CIs that do not include 0 are considered to be significant.
The mean age of participants was 16.87 years (SD=0.94), with a range from 13 to 21 years. Among the participants, 58 (46.4%) were male, and 67 (53.6%) female; 47 (37.6%) had alcohol use problems according to the cut-off score of the AUDIT-C (Table 1). Of the participants, 40.0% were smokers, 56.8% non-smokers, and 3.2% did not respond. Further, 36.0% of the adolescents had a history of at least one episode of running away, 50.4 % had no history of running away, and 13.6% of the participants did not answer this question. Based on a score Ōēź19 of the CROPS, 44.8% of participants was classified as being in the PTSD group.
Table 2 displays the bivariate correlations among the variables of interest included in the hypothetical model. First, posttraumatic symptom scores were negatively correlated with QOL total scores (r=0.670, p<0.001), as well as with the four QOL domains (rs=-0.338 to -0.709, ps<0.001). Furthermore, there were negative correlations between QOL total scores and alcohol use problems (r=-0.187, p<0.05). In particular, only parent relations/autonomy was negatively correlated with problem drinking (r=-0.301, p<0.001). However, post-traumatic symptom scores were not significantly related to alcohol use as measured by the AUDIT-C.
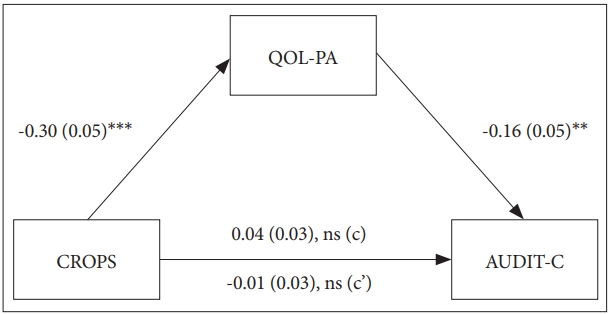
As shown in Table 3, the indirect effect analysis indicated that QOL related to parent relations and autonomy might fully mediate the effects of PTSS on alcohol use problems because both a and b paths were significant, but the c and cŌĆÖ paths were not significant. Moreover, the bootstrap analysis found that the indirect effects were significant. In other words, although PTSS have no direct effect on alcohol use problems among OSYs, PTSS might decrease the QOL related to parent relations and autonomy, in turn contributing to alcohol use problems (Figure 1). In addition, physical well-being, psychological well-being, and social support/peers had neither an indirect nor a direct effect.
This study demonstrated that PTSS decreases QOL in the domain of parent relations and autonomy, which could contribute to increased alcohol use problems among OSYs. The rate of problem drinkers in OSYs in our study (37.6%) was higher than that of Korean adolescent students (16.7%) reported in the ŌĆ£Youth Health Behavior Online Survey.ŌĆØ [18] This result is similar to previous findings on the alcohol consumption of OSYs. The lifetime prevalence of alcohol consumption of Nigerian OSYs was 61.1%, and the prevalence rates for problem drinkers were as high as 57.8% [10]. Among OSYs in the US, alcohol users accounted for 41.6%, and binge alcohol users made up 32.3% [9]. More attention needs to be given to alcohol problems in youth as alcohol use tends to disturb growth and development of youth, who are at high risk for numerous economic, occupational, and cognitive consequences and difficulties that could persist into adulthood [31].
The frequency of occurrence of alcohol use disorders has been shown to be higher in PTSS groups with trauma history compared to groups with no trauma [17]. Further, adults with PTSS are prone to increased risk of alcohol use disorders in epidemiological studies [32,33]. However, in our study, no direct relationship between PTSS and problem drinking was observed. It is presumed that the discrepancy between previous and current results is a function of differences in sample composition, research methods, and design. In this research, QOL in the domain of parent relations and autonomy may have fully mediated the effect of PTSS on alcohol use problems among OSYs. Previous studies support our findings: parental factors such as general discipline, parental monitoring, parent-child relationship quality, parental support, and general communication are related to adolescent drinking [34,35]. In another study, adolescent alcohol use was also associated with family and peer social relationships [36]. These results support the finding that alcohol use problems of OSYs are significantly associated with parental relations.
Patients with PTSS may use alcohol-containing substances to relieve psychological difficulties, which can aggravate family relationships [37]. In particular, children and adolescents are more vulnerable to substance use disorders if their emotional support resources are lacking [37]. In previous research, frequent anger outbursts and disputes due to PTSS often disrupt family or close friendships [37,38]. Numbness, hyper-arousal, and anger increase violence and aggression, leading to increased and frequent instances of domestic violence and secondary trauma to family members. This, in turn, makes family members turn aggressive and violent, worsening the relationship [39]. Moreover, traumatic experiences of children and adolescents can indirectly traumatize parents, leading to the development of psychopathology in parents and affecting the relationship between the children and their parents [40]. Indeed, when children and adolescents experience trauma, the use of family therapy has been particularly highlighted [40]. Family therapy has been demonstrated to have no direct effect on PTSS but has helped reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety as well as leading to improved relationships [41,42]. The International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies suggested behavioral family therapy and behavioral marital therapy as evidence-based therapies to relieve PTSS [43]. Therefore, it is especially important to educate and treat parents and guardians together when treating PTSS of OSYs.
This study has several limitations. First, the sampleŌĆÖs representativeness is lacking due to selection bias; participants in this study were all OSYs who were not from the entire region of South Korea but were limited to the metropolitan areas. The results of the study are difficult to generalize to all OSYs in South Korea because we did not account for characteristics and environmental differences of other regions. Second, since the range of adolescents was broadened to include youth who range in age from 9 to 24 years, we could not confirm the developmental stage differences of early, middle, and late adolescents. Future research should subdivide age groups and include larger samples.
Despite these limitations, this study provides important insights into the relationships between PTSS, QOL, and alcohol use. Our study analyzed the mediating effect of QOL in the domains of parental relations and autonomy on the relationship between PTSS and alcohol use problems among OSYs. OSYs with high parental satisfaction and autonomy were less likely to have alcohol use problems even with PTSS.
The present research demonstrated that QOL in the domain of parent relations and autonomy significantly mediated the relationship between PTSS and alcohol use problems. Therefore, when treating OSYs with PTSS, therapists should perform a family assessment and, if necessary, use a family therapy approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by a grant from the Korean Mental Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HM15C1054).
Figure┬Ā1.
Model depicting the effects of PTSS and QOL on alcohol use problems among OSYs. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. CROPS: Child Report of Post-Traumatic Symptoms, AUDIT-C: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption, QOL-PA: quality of life related to parent relations/autonomy, PTSS: post-traumatic stress symptoms.
Table┬Ā1.
Demographic characteristics (N=125)
Table┬Ā2.
Correlation coefficients of the study variables (N=125)
| CROPS | QOL total scores | Physical well-being | Psychological well-being | Social support/peers | Parent relations/autonomy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CROPS | - | |||||
| QOL total scores | -0.670*** | - | ||||
| Physical well-being | -0.474*** | 0.617*** | - | |||
| Psychological well-being | -0.709*** | 0.855*** | 0.479*** | - | ||
| Social support/peers | -0.338*** | 0.667*** | 0.297** | 0.442*** | - | |
| Parent relations/autonomy | -0.455*** | 0.857*** | 0.404*** | 0.614*** | 0.399*** | - |
| AUDIT-C | 0.119 | -0.187* | -0.103 | -0.074 | 0.037 | -0.301*** |
Table┬Ā3.
Bootstrapping result of mediation model examining the effects of parent relations/autonomy on the relationship between post-traumatic stress symptoms and alcohol use
| Paths | B | SE | t |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-traumatic symptoms ŌåÆ parent relations/autonomy (a) | -0.295 | 0.052 | -5.62*** |
| Parent relations/autonomy ŌåÆ alcohol use problems (b) | -0.164 | 0.051 | -3.20** |
| Total effect (post-traumatic symptoms ŌåÆ alcohol use problems) (c) | 0.040 | 0.031 | 1.30 |
| Direct effect (cŌĆÖ) | -0.009 | 0.033 | -0.26 |
| Indirect effects | 95% CI (BC)=0.0178-0.0923 | ||
REFERENCES
1. Ministry of Gender Equality and Family. Youth white paper. Korea: Sejong; 2016. Available at: http://www.mogef.go.kr/mp/pcd/mp_pcd_s001d.do;jsessionid=AzKR+Gfe83eQrxosIfF12na1.mogef10?mid=plc502andbbtSn=704728. Accessed August 9, 2018.
2. Gyeonggido Family and Women Research Institute. What is the solution to the problem of stopping youth study? Available at: https://www.gfwri.kr/2012/issue/no44/issue44.pdf. Suwon: Korea; 2012. Accessed August 9, 2018.
4. Schnurr PP, Friedman MJ, Bernardy NC. Research on posttraumatic stress disorder: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and assessment. J Clin Psychol 2002;58:877-889.


5. Doey T. Treating trauma and traumatic grief in children and adolescents. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2010;19:54-55.
6. Hammond C. Dropout Risk Factors and Exemplary Programs: A Technical Report. Clemson, South Carolina: National Dropout Prevention Center/network (NDPC/N); 2007.
7. Schumacher JA, Coffey SF, Stasiewicz PR. Symptom severity, alcohol craving, and age of trauma onset in childhood and adolescent trauma survivors with comorbid alcohol dependence and posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Addict 2006;15:422-425.


8. Waldrop AE, Ana EJ, Saladin ME, McRae AL, Brady KT. Differences in early onset alcohol use and heavy drinking among persons with childhood and adulthood trauma. Am J Addict 2007;16:439-442.


9. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2012). National survey on drug use and health (NSDUH), 2012. Available at: https://www.datafiles.samhsa.gov/study/national-survey-drug-use-and-healthnsduh-2012-nid13601. Accessed August 9, 2018.
10. Dada O, Odukoya O, Okuyemi K. Risk perception and correlates of alcohol use among out-of-school youth in motor parks in Lagos State, Nigeria. Malawi Med J 2016;28:19-25.



11. Grant BF, Dawson DA. Age at onset of alcohol use and its association with DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: results from the National Longitudinal alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. J Subst Abuse 1997;9:103-110.


12. Welch KA, Carson A, Lawrie SM. Brain structure in adolescents and young adults with alcohol problems: systematic review of imaging studies. Alcohol 2013;48:433-444.


13. Eiser C, Morse R. A review of measures of quality of life for children with chronic illness. Arch Dis Child 2001;84:205-211.



14. Pal DK. Quality of life assessment in children: a review of conceptual and methodological issues in multidimensional health status measures. J Epidemiol Community Health 1996;50:391-396.



15. Goldbeck L, Schmitz TG, Besier T, Herschbach P, Henrich G. Life satisfaction decreases during adolescence. Qual Life Res 2007;16:969-979.



16. Clark DB, Kirisci L. Posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, alcohol use disorders and quality of life in adolescents. Anxiety 1996;2:226-233.


17. Warshaw MG, Fierman E, Pratt L, Hunt M, Yonkers KA, Massion AO, Keller MB. Quality of life and dissociation in anxiety disorder patients with histories of trauma or PTSD. Am J Psychiatry 1993;150:1512-1516.


18. Korea Ministry of Government Legislation (updated 2018) Juvenile welfare support act, 2018. Available at: http://www.law.go.kr/LSW/lsLink-Proc.do?andlsNm=%EC%B2%AD%EC%86%8C%EB%85%84+%EA%B8%B0%EB%B3%B8%EB%B2%95andchrClsCd=010202andmode=20#0000. Accessed August 9, 2018.
19. Greenwald R, Rubin A. Assessment of posttraumatic symptoms in children: development and preliminary validation of parent and child scales. Res Soc Work Pract 1999;9:61-75.

20. Strand VC, Sarmiento TL, Pasquale LE. Assessment and screening tools for trauma in children and adolescents: a review. Trauma Violence Abuse 2005;6:55-78.


21. Lee KM, Jeong SH, Lee WK, Chung US. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the child report of post-traumatic symptoms (CROPS) and the parent report of post-traumatic symptoms (PROPS). J Korean Acad Child Adoles Psychiatry 2011;22:169-181.


22. Ravens-Sieberer U, Auquier P, Erhart M, Gosch A, Rajmil L, Bruil J, et al. The KIDSCREEN-27 quality of life measure for children and adolescents: psychometric results from a cross-cultural survey in 13 European countries. Qual Life Res 2007;16:1347-1356.



23. Hong SD, Yang JW, Jang WS, Byun H, Lee MS, Kim HS, et al. The KIDSCREEN-52 quality of life measure for children and adolescents (KIDSCREEN-52-HRQOL): reliability and validity of the Korean version. J Korean Med Sci 2007;22:446-452.



24. Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG. AUDIT: the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Guidelines for Use in Primary Care. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2001.
25. Reinert DF, Allen JP. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): a review of recent research. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2002;26:272-279.


26. Bradley KA, DeBenedetti AF, Volk RJ, Williams EC, Frank D, Kivlahan DR. AUDIT-C as a brief screen for alcohol misuse in primary care. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007;31:1208-1217.


27. Chung T, Colby SM, Barnett NP, Monti PM. Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: factor structure in an adolescent emergency department sample. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2002;26:223-231.


28. Seong JH, Lee CH, Do HJ, Oh SW, Lym YL, Choi JK, et al. Performance of the AUDIT alcohol Consumption Questions (AUDIT-C) and AUDIT-K question 3 alone in screening for problem drinking. Korean J Fam Med 2009;30:695-702.


29. Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods 2008;40:879-891.



30. Shrout PE, Bolger N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: new procedures and recommendations. Psychol Methods 2002;7:422-445.



31. Chemtob CM, Nomura Y, Josephson L, Adams RE, Sederer L. Substance use and functional impairment among adolescents directly exposed to the 2001 World Trade Center attacks. Disasters 2009;33:337-352.


32. Davidson JRT, McFarlane AC. The extent and impact of mental health problems after disaster. J Clin Psychiatry 2006;67(Suppl 2):9-14.

33. Shore JH, Vollmer WM, Tatum EL. Community patterns of posttraumatic stress disorders. J Nerv Ment Dis 1989;177:681-685.


34. Gilligan C, Kypri K. Parent attitudes, family dynamics and adolescent drinking: qualitative study of the Australian Parenting Guidelines for Adolescent alcohol use. BMC Public Health 2012;12:491




35. Ryan SM, Jorm AF, Lubman DI. Parenting factors associated with reduced adolescent alcohol use: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2010;44:774-783.


36. Zucker RA. Anticipating problem alcohol use developmentally from childhood into middle adulthood: what have we learned? Addiction 2008;103(Suppl 1):100-108.



37. Brewin CR, Holmes EA. Psychological theories of posttraumatic stress disorder. Clin Psychol Rev 2003;23:339-376.


38. Stoddard FJ, Pandya AA, Katz CL. Disaster Psychiatry: Readiness, Evaluation, and Treatment. Washtington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2011.
39. Armanini MP, Hutchins C, Stein BA, Sapolsky RM. Glucocorticoid endangerment of hippocampal neurons is NMDA-receptor dependent. Brain Res 1990;532:7-12.


40. Anticevic A, Repovs G, Shulman GL, Barch DM. When less is more: TPJ and default network deactivation during encoding predicts working memory performance. NeuroImage 2010;49:2638-2648.


41. Galovski T, Lyons JA. Psychological sequelae of combat violence: a review of the impact of PTSD on the veteranŌĆÖs family and possible interventions. Aggress Violent Behav 2004;9:477-501.

42. Jordan BK, Marmar CR, Fairbank JA, Schlenger WE, Kulka RA, Hough RL, et al. Problems in families of male Vietnam veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 1992;60:916-926.



43. Foa E, Keane TM, Friedman MJ, Cohen JA. Effective Treatments for PTSD: Practice Guidelines from the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies. New York: Guilford Press; 2008.






