 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 18(2); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of adding music therapy (MT) to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) on symptoms of smartphone/internet addiction and psychiatric comorbidities.
Methods
Overall, 155 patients diagnosed with addiction were assigned to either the CBT-MT group or CBT group. Both groups received CBT for 8 weeks, while the CBT-MT group received additional MT. The intervention was completed by 67 and 71 participants in the CBT-MT and CBT groups, respectively.
Results
The total scores of Young Internet Addiction Scale (YIAT) and Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale (SAPS) decreased significantly (p<0.001 for both) in both groups, while the total scores of State Anxiety Inventory for Children (SAIC) (p<0.001), Trait Anxiety Inventory for Children (TAIC) (p<0.001), Conners-Wells’ Adolescent Self-Report Scale-Short form (CASS(S)) (p=0.048), and Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11 (BIS-11) (p<0.001) decreased only in the CBT-MT group. The decrements in YIAT (p=0.025), SAIC (p=0.043), TAIC (p=0.011), and BIS-11 (p=0.012) in the CBT-MT group were significantly greater than those in the CBT group.
In 2018, the South Korea National Information Society Agency (NIA) reported that 19.1% of smartphone users suffered from smartphone/internet addiction in South Korea [1]. Notably, although internet gaming disorder was added in Section 3 (Conditions for Further Study) of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition (DSM5) [2], and gaming disorder was added to the World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases, 11th Revision (ICD-11) [3], the causes, concepts, and terms regarding smartphone/internet addiction are yet to be elucidated. As a result, evidence-based treatment guidelines have been difficult to establish [4].
Besides contributing to an increase in the crime rate [5], studies have implicated smartphone/internet addiction in multiple psychiatric disorders including anxiety, depression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), impulsivity, substance abuse, gambling, and behavioral problems [6-14] in teenagers. The consequences of smartphone/internet addiction could be even more devastating due to its prevalence in adolescents. In fact, it has been reported that 29.3% of teenagers aged 10-19 years suffered from smartphone/internet addiction [1]. Therefore, effective preventive and management measures are urgently required.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been considered as the first-line treatment for smartphone/internet addiction [15]. Based on the work of Davis [16] linking distortion in perception, negative reinforcement and internet addiction, studies conducted in the USA [17,18], South Korea [19,20], and China [21] have reported potential therapeutic effects of CBT in internet addiction. For instance, Home Daily Journal writing (HDJ), a form of CBT, is thought to be beneficial in the treatment of internet addiction [22].
However, a recent meta-analysis [23] found CBT to be relatively ineffective in adolescents. Indeed, not only are adolescents shy and afraid of stigma, they appear less keen for treatment as compared to adults. Additionally, CBT can seem boring, making it difficult to convince patients of its effectiveness [24].
Music therapy (MT) has also been found to be effective in depression and substance use disorder [25,26]. Several studies have used MT in teenagers with internet addiction [27-29] in South Korea. Czamanski-Cohen and Weihs [30] reported that art therapy allowed subjects to experience a supportive therapist as a ‘good-enough mother’, and to express indescribable negative emotions through the process of art in a safe environment, such that the participants could reflect upon their own cognition, behaviors, and emotions through meta-recognition processes. Importantly, Kokal et al. [31] used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to demonstrate the activation of the caudate nucleus, a region associated with the reward system.
Based on these findings, we hypothesized that group MT would be effective in smartphone/internet addiction and that combining it with cognitive behavioral interventions would result in synergistic effects. We therefore wanted to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of MT in combination with CBT homeworks (HDJ) in adolescents with smartphone/internet addiction, depression, anxiety, ADHD, and impulsiveness.
The inclusion criteria were: 1) 10-16 years of age; 2) classified as high-risk (>70) or problematic (>40) user based on Young Internet Addiction Scale (YIAT) [32], or smartphone highrisk group based on Korean Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale (SAPS) [33]; and 3) written informed consent from the participants and their parents. The exclusion criteria were: 1) medical, surgical, or neurological disorders and 2) inability to respond to the questionnaire due to severe mental disorders (such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorders), intellectual disability, or developmental disorders.
Overall, 155 students from six elementary and middle schools in Daegu Metropolitan City and North Gyeongsang Province were selected in the study through the WEE (We+ Education+Emotion) center, a school counseling office supported by the South Korean government. Of them, 70 students were randomly prescribed MT and CBT homeworks (CBT-MT group) while the remaining 85 students were only prescribed CBT homeworks (CBT group).
Before the interventions, sociodemographic information including the age, sex, marital status of parent(s), school performance, number of hours per week spent on smartphone/internet games, Children’s Social Support Scale (SSS) score [34], and Parent-Adolescent Communication Scale (PACS) score [35] were self-reported through a questionnaire. The changes in these parameters after the intervention were analyzed using clinical scales for assessing smartphone/internet addiction, depression, anxiety, ADHD, and impulsivity.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Daegu Catholic University Medical Center (Approval No. CR 19-032) and was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All the participants provided written informed consents.
We used this scale developed by NIA [33] for evaluating smartphone addiction. If the participants were classified ‘not a risk,’ they were excluded from the study. Cronbach’s α for this scale was 0.880.
Developed by Young [32], this is the most widely used scale in assessing internet addiction. Cronbach’s α for this scale was 0.880, and we used cut-off values of 40-69 and ≥70 to identify problematic and high-risk internet users, respectively.
This is a part of the Conversing Scales-Revised (CRS-R) complex test for diagnosing ADHD, and its shortened form is used in adolescents. In 2001, Bahn et al. [42] translated it into Korean with Cronbach’s α of 0.880.
The Korean Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale (SAPS) and Young’s Internet Addiction Scale (YIAT) were administered to students at three elementary and three middle schools in Daegu Metropolitan City and North Gyeongsang Province. For 8 weeks, MT and CBT homeworks were prescribed to 70 randomly selected participants (CBT-MT group), while the remaining 85 participants were required to join a CBT program, in the form of HDJ, only. MT was administered by a group of 6-8 students attending the same school as the participant, and a psychiatrist and a music therapist visited the school’s group counseling room. In both groups, MT and CBT were held for a total of 8 sessions. Each session lasted for 75 minutes, with the initial 10 minutes used to identify the CBT homework task. The CBT-only group was supervised by a psychologist. Similar to the CBT-MT group, the 10 minutes were used to identify the CBT homework task.
MT is “a clinical technique that uses music as a medium of therapy to help improve and rehabilitate the human mental, emotional, social, and physical health” [45]. MT includes improvising, composing/writing, performing, and singing, and is known to alleviate the symptoms in various mental disorders, including depression, dementia, ADHD, and autism spectrum disorders [25,26,46-51]. In this study, MT was based on the game and immersion MT program manual [52] validated by the National Association of Korean Music Therapists. The details of the program were as follows.
In the first session, the therapists and participants formed a rapport by introducing themselves using songs and various types of percussion (each selecting their desired instrument), creating a rhythm for the four nights together, and combining Nanta scores according to the direction and performance of the therapist. In the second session, the participants presented an emotional card to the group, found a matching percussion sound, wrote the lyrics suggested by the therapist, performed on the musical instrument of their choice, and read their narrated personal histories with games. In the third session, the participants drew upon their cravings of the games, explored their emotions, and checked external and internal factors through lyrics, rhythmic chanting, and playing instruments. The fourth session allowed participants to think about the consequences of behavioral patterns, express emotions, and form empathy with them, and explore the reasons and motivations for game control on their own by working on rap lyrics. In the fifth session, the participants took turns conducting and performing percussion music to improve their leadership and ability to control their behavior, and wrote lyrics by singing “My Power” songs so that they could reflect on themselves. In the sixth and seventh sessions, the participants created a song together using worksheets and performed using sheet music that the therapist produced. Each person selected a percussion instrument that matched the song and allowed them to perform while singing, which provided the experience of behavioral control through modifying the lyrics, and a sense of feeling united and belonging. In the eighth session, the notes of the first seven sessions were recorded in files that were presented as gifts to the participants, followed by a completion ceremony for the parents and teachers.
In this study, group CBT was conducted using a “Smart Me” HDJ, which is a revised version of the HDJ developed by Lee et al. [22]. The researchers [22] reported that CBT, as homebased daily journal (HDJ) writing, was effective in smartphone addiction. Furthermore, HDJ could be effective outside of schools or clinics due to the ubiquitous nature of smartphones and internet. HDJ compensates for the shortcomings of conventional CBT because it is based on the patient’s autonomy and carries less stigma. Whereas the current HDJ content focuses primarily on recording and evaluating the use of smartphones, the “Smart Me” HDJ adds a weekly cognitive behavioral therapy written task, administered by a psychologist or a psychiatrist, to the process. The revised “Smart Me” HDJ was used as CBT Homeworks every week during the entire treatment period. However, a two-week supplementary assignment and worksheet were attached to the version used at the Game Immersion Healing Center in North Gyeongsang Province.
Independent t-test and χ2 test were performed to compare the baseline sociodemographic characteristics between the groups. In order to analyze the primary endpoints of SAPS and YIAT, the change in both scales was analyzed using paired t-test. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to compare the mean pre- and post-intervention scores between the two groups. The covariates were the average weekly smartphone use time, SSS, and PACS, and were statistically significantly different between the two groups at baseline. Finally, last-observation-carried-forward (LOCF) analysis was performed on the missing data.
In order to analyze the changes in the psychological tests (SAIC, TAIC, RSES, BDI-II, CASS(S), and BIS-11) as the secondary endpoints, each group was analyzed using paired t-test before and after the treatment. Independent t-test was performed to analyze the differences between the groups.
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with p<0.05 set as the level of statistical significance.
Of the 155 participants, 17 were lost to follow-up; 3 (4.3%) in the CBT-MT group and 14 (20%) in the CBT group. Finally, 67 and 71 participants in the CBT-MT and CBT groups, respectively, were analyzed (Figure 1). The chi-square test revealed a beneficial effect of MT on treatment compliance when added to CBT (χ2=5.837, df=1, p=0.016).
There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of the age, sex, parental marital status, self-reported school performance, and weekly average time spent on internet games. However, the weekly smartphone usage time was significantly higher in the CBT group (18.61± 11.982 hour) than that in the CBT-MT group (11.85±11.648 hour) (t=3.356, p=0.001). SSS and PACS were also higher in the CBT group (98.13±16.000 and 77.73±13.422, respectively) than those in the CBT-MT group (91.24±16.883 and 71.34± 14.965, respectively) (t=2.461, p=0.015 and t=2.643, p=0.009, respectively) (Table 1).
SAPS and YIAT were significantly reduced after the interventions in both groups. SAPS in the CBT-MT group decreased from 32.75±8.619 to 26.48±10.970 (t=-5.880, p<0.001). YIAT in the CBT-MT group also decreased from 46.79±13.800 to 32.16±19.245 (t=-7.373, p<0.001). In the CBT group, SAPS decreased from 33.42±6.487 to 28.65±7.968 (t=-6.300, p<0.001) and YIAT decreased from 46.24±14.537 to 37.61±14.550 (t=-4.124, p<0.001). In terms of the differences in the mean values before and after the intervention between the groups, SAPS demonstrated no significant difference, while the magnitude of reduction in YIAT was significantly greater in the CBT-MT group than that in the CBT group (Z=5.137, p=0.025) (Table 2).
In the CBT-MT group, SAIC (t=-5.157, p<0.001), TAIC (t=-3.819, p<0.001), ADHD (CASS(S)) (t=-2.015, p=0.048), and impulsivity (BIS-11) (t=-3.859, p<0.001) decreased significantly after the interventions; however, only SAIC (t=-2.953, p=0.004) decreased in the CBT group. The CBT-MT group also demonstrated larger differences after the interventions in SAIC (t=-2.040, p=0.043), TAIC (t=-2.585, p=0.011), and impulsivity (t=-2.571, p=0.012) than did the CBT group. There was no scale in which the CBT group had bigger effect than the CBT-MT group (Table 3).
To our knowledge, our study investigating the effects of dual intervention with MT and CBT material in smartphone/internet addiction is the first of its kind. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of combined MT and task of CBT in teenagers with smartphone/internet addiction. The findings revealed that SAPS and YIAT were significantly decreased in both groups, while YIAT decreased significantly more in the CBT-MT group than the CBT group. This is consistent with the results of a prior study [22], which reported that CBT as HDJ writing was effective in smartphone/internet addiction. Particularly, YIAT<40 is classified as normal, and the average score decreased to <40 points in both groups after the intervention, thus, confirming that MT and CBT are effective in internet addiction.
Recently, there has been a huge controversy over whether smartphone and internet addictions are illnesses. Indeed, they do not have clear psychiatric definitions and further research is needed to formulate evidence-based treatment guidelines [53]. However, psychiatric interventions can be helpful if smartphone/internet addiction is severe enough to affect everyday life [54].
The effects of CBT on internet/smartphone addiction have been extensively studied, and it is currently the first-line of treatment for smartphone/internet addiction. Additionally, CBT is regarded as the primary approach to effectively correct non-adaptive automatic thinking [55]. Our findings validate previous studies and suggest that CBT as HDJ writing was effective for smartphone/internet addiction in adolescents.
The dual intervention group demonstrated significant improvements, not only in the symptoms of smartphone/internet addiction, but also in those of anxiety, ADHD, and impulsiveness. In contrast, improvements were only observed in state anxiety and smartphone/internet addiction in the CBT group. Therefore, the addition of MT to CBT was effective for comorbid psychiatric symptoms as well. Additionally, in the dual intervention group, the mean of the differences between pre- and post-intervention values decreased significantly as compared with the values in the CBT group for symptoms of internet addiction, state anxiety, trait anxiety, and impulsivity. We believe that this significant difference is due to the synergistic effects of MT and CBT.
MT not only relaxes the participant emotionally, and allows him/her to experience intimacy with the therapist and group members, but it also encourages doing CBT homeworks, induces interest in the therapy, and adaptation to it. Although a previous study demonstrated the effectiveness of MT in depression, we did not find any significant reduction in the depression scale [25]. This difference may be because the participants’ BDI-II baseline value was very low (6.93±7.828 in the CBT-MT group and 6.45±8.101 in the CBT group). Further studies are required to highlight the effects of MT on smartphone/internet addiction with depression.
One of the biggest difficulties of psychotherapy in children and adolescents is compliance [56,57]. According to one study, 22% of children and adolescents in the treatment group, did not attend their first session of therapy [58]. Of the 155 participants in this study, 3 (4.3%) in the CBT-MT group and 14 (20%) in the CBT group were excluded from the analyses because they did not complete the study. The higher participation rate in CBT-MT group is believed to be due to the strengths of a well-developed art therapy program [59]. These strengths include: 1) the use of music, art, and physical education to maximize interest; 2) the participation of parents and teachers; 3) involvement of a psychiatrist; 4) decreased stigma as compared with psychotherapy; and 5) when it is administered at school, it is similar to attending after-school classes. This is consistent with the findings of Saba et al. [60], who also reported that art therapy achieved a high rate of participation. Therefore, it can be more effective to combine CBT with art therapy.
There were some limitations in this study. First, there was a significant difference between the two groups in terms of the weekly average time of smartphone use, SSS, and PACS. Furthermore, the CBT-MT group was not similar to the CBT group; therefore, ANCOVA was performed using three covariates. In future studies, stratified randomization of sociodemographic variables should be considered. Secondly, the smartphone/internet addiction scales used in this study differed from the diagnostic criteria of internet gaming disorder in DSM-5 or gaming disorder in ICD-11. In future studies, it will be necessary to confirm whether the subjects satisfy the diagnostic criteria through psychiatric interviews. Thirdly, there was no evaluation regarding the maintenance of the effects of MT and CBT. According to Yeun and Han [61], reports on psychosocial interventions for internet addiction have failed to incorporate long-term follow-up, and the duration of the effects of psychosocial interventions is controversial. Therefore, it is necessary to include long-term follow-up as well. Fourthly, this study assumes that smartphone and internet addictions are similar because of previously reported similar pathologies between them [62]; however, Jang et al. [59] suggest that further studies are needed to prove this hypothesis. While the classical perspective was based on internet addiction due to personal computers, it is limiting because of the development of newer devices such as smartphones and tablets. In the future, psychological and biological studies are necessary to investigate the differences between such addictions.
Currently, the global COVID-19 pandemic is causing social and economic problems. Quarantine, social distancing, and suspension from school for the purpose of public health can act as great stressors on individuals [63]. In addition, social isolation from COVID-19 raises the risk of depression, anxiety, and Hikikomori, which are closely related to internet addiction [64,65]. Increased smartphone and internet usage due to COVID-19 increases the risk of smartphone internet addiction [66]. In accordance with this trend, changes are needed in the future treatment of smartphone internet addiction, and in particular, a non-face-to-face treatment method needs to be developed to reduce the risk of infectious diseases and increase accessibility. Therefore, for the next step, we plan to develop the following: 1) music therapy through a non-face-to-face video conference, and 2) music therapy and CBT using smartphone applications.
In conclusion, the findings of this study demonstrated that the use of 8 weeks of dual intervention in the form of MT and CBT in teenagers with smartphone/internet addiction resulted in a significant decrease in the symptoms of these addictions with high treatment compliance. Furthermore, combination therapy can be particularly beneficial for anxiety and impulsiveness. Future studies are required to investigate the long term effects of these therapeutic interventions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for English language editing.
We acknowledge Eun Hai Lee, So Yeoun Kim, Hyun Ju Bae, who work at Daegu Catholic Wee Center as music therapist.
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: all authors. Data curation: all authors. Formal analysis: all authors. Investigation: all authors. Methodology: all authors. Supervision: all authors. Validation: all authors. Visualization: all authors. Writing—original draft: all authors. Writing—review & editing: all authors.
Figure 1.
Flowchart depicting the study design. MT: music therapy, CBT: cognitive behavioral therapy
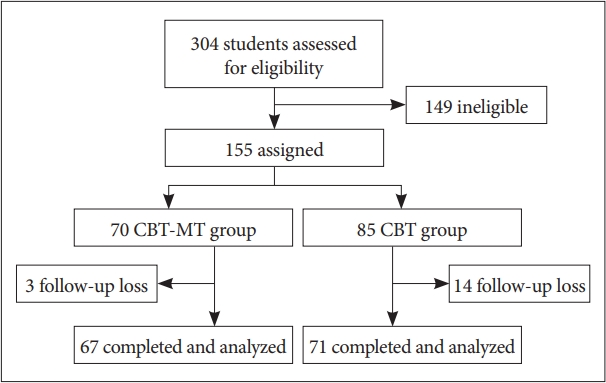
Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of the participants
Table 2.
Differences of addiction scales between before and after intervention
|
Before |
After |
Paired t test |
Difference |
ANCOVA |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | Mean±SD | t | p | Mean±SD | Z | p | |
| SAPS | 2.444 | 0.120 | |||||
| CBT-MT | 32.75±8.619 | 26.48±10.970 | -5.880 | <0.001* | 6.27±8.726 | ||
| CBT | 33.42±6.487 | 28.65±7.968 | -6.300 | <0.001* | 4.77±6.386 | ||
| YIAT | 5.137 | 0.025* | |||||
| CBT-MT | 46.79±13.800 | 32.16±19.245 | -7.373 | <0.001* | 14.63±16.237 | ||
| CBT | 46.24±14.537 | 37.61±14.550 | -4.124 | <0.001* | 8.63±17.640 | ||
Table 3.
Differences in psychometric test scores between before and after intervention
|
Before |
After |
Paired t test |
Difference |
Independent t test |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | Mean±SD | t | p | Mean±SD | t | p | |
| SAIC | -2.040 | 0.043* | |||||
| CBT-MT | 30.10±8.486 | 23.79±10.987 | -5.157 | <0.001* | 6.31±10.020 | ||
| CBT | 28.52±8.353 | 25.46±7.119 | -2.953 | 0.004* | 3.06±8.721 | ||
| TAIC | -2.585 | 0.011* | |||||
| CBT-MT | 31.79±10.531 | 25.91±13.912 | -3.819 | <0.001* | 5.88±12.605 | ||
| CBT | 28.25±7.958 | 26.93±7.586 | -1.544 | 0.127 | 1.32±7.225 | ||
| RSES | -1.319 | 0.190 | |||||
| CBT-MT | 29.88±6.193 | 28.73±11.537 | -0.914 | 0.362 | 1.15±10.293 | ||
| CBT | 32.32±5.930 | 33.06±5.813 | 1.088 | 0.281 | -0.73±5.674 | ||
| BDI-II | -0.623 | 0.534 | |||||
| CBT-MT | 6.93±7.828 | 4.85±8.794 | -1.772 | 0.081 | 2.07±9.584 | ||
| CBT | 6.45±8.101 | 5.25±8.232 | -1.482 | 0.143 | 1.20±6.805 | ||
| CASS(S) | -1.357 | 0.178 | |||||
| CBT-MT | 18.48±15.328 | 14.70±14.171 | -2.015 | 0.048* | 3.78±15.336 | ||
| CBT | 14.35±11.856 | 13.51±12.323 | -0.787 | 0.434 | 0.85±9.053 | ||
| BIS-11 | -2.571 | 0.012* | |||||
| CBT-MT | 55.91±15.218 | 45.25±23.185 | -3.859 | <0.001* | 10.66±22.606 | ||
| CBT | 60.28±13.228 | 57.62±12.702 | -1.861 | 0.067 | 2.66±12.051 | ||
MT: music therapy, CBT: cognitive behavioral therapy, SD: standard deviation, SAIC: State Anxiety Inventory for Children, TAIC: Trait Anxiety Inventory for children, RSES: Rosenberg Self Esteem Scale, BDI-II: Beck Depression Inventory-II, CASS(S): Conners-Wells’ Adolescent Self-Report Scale (Short Form), BIS-11: Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-11
REFERENCES
1. National Information Society Agency. 2018 The survey on Smarphone overdependence. Available at: https://www.nia.or.kr/site/nia_kor/ex/bbs/View.do;JSESSIONID=CDFAB20184BB8BA1AEB444174E268292.5a07860e5eb667161?cbIdx=65914&bcIdx=20876&parentSeq=20876. Accessed October 20, 2019.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
3. WHO. ICD-11 Revision 2018 Available at: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en. Accessed October 20, 2019.
4. King DL, Delfabbro PH. Internet gaming disorder treatment: a review of definitions of diagnosis and treatment outcome. J Clin Psychol 2014;70:942-955.


5. Han SA, Lee HM. Concern with online game addiction and juvenile delinquency. Korean Crim Psychol Rev 2006;2:229-244.
6. Bozkurt H, Coskun M, Ayaydin H, Adak I, Zoroglu SS. Prevalence and patterns of psychiatric disorders in referred adolescents with internet addiction. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2013;67:352-359.


7. Cao F, Su L, Liu T, Gao X. The relationship between impulsivity and internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents. Eur Psychiatry 2007;22:466-471.


8. Carli V, Durkee T, Wasserman D, Hadlaczky G, Despalins R, Kramarz E, et al. The association between pathological internet use and comorbid psychopathology: a systematic review. Psychopathology 2013;46:1-13.


9. Kim K, Ryu E, Chon MY, Yeun EJ, Choi SY, Seo JS, et al. Internet addiction in Korean adolescents and its relation to depression and suicidal ideation: a questionnaire survey. Int J Nurs Stud 2006;43:185-192.


10. Lee YS, Han DH, Kim SM, Renshaw PF. Substance abuse precedes internet addiction. Addict behav 2013;38:2022-2025.



11. Mak KK, Lai CM, Watanabe H, Kim DI, Bahar N, Ramos M, et al. Epidemiology of internet behaviors and addiction among adolescents in six Asian countries. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 2014;17:720-8.


12. Yen JY, Ko CH, Yen CF, Wu HY, Yang MJ. The comorbid psychiatric symptoms of Internet addiction: attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, social phobia, and hostility. J Adolesc Health 2007;41:93-98.


13. Yoo YS, Cho OH, Cha KS. Associations between overuse of the internet and mental health in adolescents. Nurs Health Sci 2014;16:193-200.


14. Young KS, Rogers RC. The relationship between depression and internet addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav 1998;1:25-28.

15. Beck AT. Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders. Oxford: International Universities Press; 1976.
16. Davis RA. A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use. Comput Hum Behav 2001;17:187-195.

17. Young KS. Cognitive behavior therapy with internet addicts: treatment outcomes and implications. Cyberpsychol Behav 2007;10:671-679.


18. Young KS. Treatment outcomes using CBT-IA with internet-addicted patients. J Behav Addict 2013;2:209-215.



19. Kim SM, Han DH, Lee YS, Renshaw PF. Combined cognitive behavioral therapy and bupropion for the treatment of problematic on-line game play in adolescents with major depressive disorder. Comput Hum Behav 2012;28:1954-1959.

20. Kim SH, Yim HW, Jo SJ, Jung KI, Lee K, Park MH. The effects of group cognitive behavioral therapy on the improvement of depression and anxiety in adolescents with problematic internet use. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2018;29:73-79.

21. Du YS, Jiang W, Vance A. Longer term effect of randomized, controlled group cognitive behavioural therapy for internet addiction in adolescent students in Shanghai. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2010;44:129-134.


22. Lee H, Seo MJ, Choi TY. The effect of Home-based Daily Journal writing in Korean adolescents with Smartphone addiction. J Korean Med Sci 2016;31:764-769.



23. Stevens MWR, King DL, Dorstyn D, Delfabbro PH. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for Internet gaming disorder: a systematic review and meta analysis. Clin Psychol Psychother 2018;26:191-203.


24. Chae YG. The development and effect of arts psychotherapy program for game overflow of adolescents. Kor J Counsel 2006;7:885-898.
25. Aalbers S, Fusar Poli L, Freeman RE, Spreen M, Ket JC, Vink AC, et al. Music therapy for depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;11:CD004517


26. Hohmann L, Bradt J, Stegemann T, Koelsch S. Effects of music therapy and music-based interventions in the treatment of substance use disorders: a systematic review. PLoS One 2017;12:e0187363



27. Cha ES, Kim TH. Effects of the group music therapy on behavior, self-control, social interaction and stress for the Internet-Addicted students in elementary school. Youth Facilities Environ 2013;11:79-91.
28. Lee EH, Bang SA. The effectiveness of music therapy program on self efficacy of juveniles with Internet game addiction. J Korea Acad Industr Coop Soc 2012;13:2520-2527.

29. Yeo JY. A case study of individual music therapy on adolescent with internet addiction. Korean J Music Ther 2010;12:16-40.

30. Czamanski-Cohen J, Weihs KL. The bodymind model: a platform for studying the mechanisms of change induced by art therapy. Arts Psychother 2016;51:63-71.



31. Kokal I, Engel A, Kirschner S, Keysers C. Synchronized drumming enhances activity in the caudate and facilitates prosocial commitment--if the rhythm comes easily. PLoS One 2011;6:e27272



32. Young KS. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction and a Winning Strategy for Recovery. New York: John Wiley; 1998.
33. Kim D, Lee Y, Lee J, Nam JK, Chung Y. Development of Korean smartphone addiction proneness scale for youth. PLoS One 2014;9:e97920



34. Kim MS. Development of the Children’s Social Support Scale. Fam Environ Res 1995;33:37-47.
35. Barnes HL, Olson DH. Parent-adolescent communication and the circumplex model. Child Develop 1985;56:438-447.

36. Beck AT. Beck Depression Inventory-II. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation; 1996.
37. Sung HM, Kim JB, Park YN, Bai DS, Lee SH, Ahn HN. A study on the reliability and the validity of korean version of the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II). J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry 2008;14:201-212.
38. Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory for Children. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press; 1970.
39. Cho SC, Choi JS. Development of the Korean form of the State-Trait anxiety Inventory for Children. Seoul J Psychiatry 1989;14:150-157.
40. Rosenberg M. Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (SES). Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 1965.
41. Jeon BJ. Self-esteem: a test of its measurability. Yonsei Nonchong 1974;11:109-129.
42. Bahn GH, Shin MS, Cho SC, Hong KE. A preliminary study for the development of the assessment scale for ADHD in adolescents: reliability and validity for CASS(S). J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2001;12:218-224.
43. Barratt ES. Anxiety and impulsiveness related to psychomotor efficiency. Percept Motor Skill 1959;9:191-198.

44. Lee SR, Lee WH, Park JS, Kim SM, Kim JW, Shim JH. The study on reliability and validity of Korean version of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale11-Revised in nonclinical adult subjects. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 2012;51:378-386.

45. National Association of Korean Music Therapists. What is Music Therapy? Available at: http://www.nakmt.or.kr/sub/sub2_1.asp. Accessed September 30, 2019.
46. Edgerton CL. The effect of improvisational music therapy on the communicative behaviors of autistic children. J Music Ther 1994;31:31-62.

47. Edwards J. The Oxford Handbook of Music Therapy. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2016.
48. Geretsegger M, Elefant C, MÖssler KA, Gold C. Music therapy for people with autism spectrum disorder. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;2014:CD004381



49. Pavlicevic MJ. Improvisation in music therapy: human communication in sound. J Music Ther 2000;37:269-285.


50. Soshensky R. Everybody is a star: recording, performing, and community music therapy. Music Ther Perspect 2011;29:23-30.

51. Zhang F, Liu K, An P, You C, Teng L, Liu Q. Music therapy for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;2017:CD010032


52. Choi TY, Jang HJ, Lee HJ, Seo ES, Jang SY, Chung YK. Game immersion music therapy program manual. Game Culture Foundation. Available at: http://www.gameculture.or.kr/boad/bd_news/5/egoread.php?bd=8&itm=&txt=&pg=1&seq=1020. Accessed October 20, 2019.
53. Winkler A, D?rsing B, Rief W, Shen Y, Glombiewski JA. Treatment of internet addiction: a meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev 2013;33:317-329.


54. Sakong JK. Internet addiction. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry 2002;8:176-185.
55. Lee H, Choi TY. The psychosocial approaches of Internet/Game addiction. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry 2015;21:65-72.
56. Bolton OK, Scherer DG. Therapeutic engagement with adolescents in psychotherapy. Psychother-Theor Res 2003;40:215-225.

57. Kazdin AE. Dropping out of child psychotherapy: issues for research and implications for practice. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 1996;1:133-156.

58. Minty B, Anderson C. Non-attendance at initial out-patient appointments at a hospital-based child psychiatric clinic. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 2004;9:403-418.

59. Jang HJ, Kim JW, Choi TY. The effect of group therapy using art program on Internet/Smartphone addictive behaviors of adolescents: a pilot study. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry 2017;23:171-180.
60. Saba L, Byrne A, Mulligan A. Child art psychotherapy in CAMHS: which cases are referred and which cases drop out? Springerplus 2016;5:1816



61. Yeun YR, Han SJ. Effects of psychosocial interventions for school-aged children’s Internet addiction, self-control and self-esteem: meta-analysis. Healthc Inform Res 2016;22:217-230.



62. Seo MJ, Choi TY, Woo JM, Kim JH, Lee JH. A comparative study of smartphone and internet addiction on adolescent psychopathology. J Korean Soc Biol Ther Psychiatry 2013;19:154-162.
63. Wong PWC. Potential changes to the hikikimori phenomenon in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. Asian J Psychiatr 2020;54:102288



64. Kato TA, Sartorius N, Shinfuku N. Forced social isolation due to COVID 19 and consequent mental health problems: Lessons from hikikomori. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2020;74:506-507.










