|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 16(8); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
Reaction time is defined as the time from the start of a stimulus to the start of the voluntary movement. Time plays an important role in undertaking daily living activities. Reaction time is an important factor in respect of both quality of life and of capabilities demonstrated in the work environment. Alcohol and some addictive substances have effect on RT. The aim of this study was to compare the visual and auditory reaction times of patients with opioid use disorder with healthy control subjects.
Methods
The study was applied to two groups as the opioid use disorder group and the control group. A Sociodemographic and Clinical Data Form was prepared for each patient including age, gender, marital status and education level. Using a computer program the response to visual screen color change (red/blue) and to an auditory ŌĆśbeepŌĆÖ sound of the computer system were recorded. The StudentŌĆÖs t-test was applied as a statistical method.
Alcohol and substance use disorder are chronic relapsing disorders, characterized by compulsive drug-taking with the inability to limit intake and bouts of intense drug craving. Data derived from animal models have reported that opioids are initially abused due to the reward or hedonic effects. With repeated use, opioids are known to induce alterations in the neurotransmitter and neuropeptide systems that regulate incentive-motivation and stress-responsiveness and the dysregulation of these systems results in opioids and other substance use disorders characterized by compulsive use and loss of control of drug-taking. Substance use disorders are becoming increasingly widespread. It is suggested that, in 2015, 91.8 million (37.8%) U.S. civilian used prescription opioids; 11.5 million (4.7%) misused them; while 1.9 million (0.8%) had a use disorder. Among adults with prescription opioid use, 12.5% reported misuse [1].
Reaction time (RT) is defined as the time from the start of a stimulus to the start of the desired movement. The stimulus may be visual, auditory or tactile. The time from a simple stimulus to a simple response to the stimulus is known as simple reaction time (simple RT) and when the practitioner notices a difference between a specific stimulus and a paired specific response, the time between forming the specific response paired to that stimulus is known as the selective reaction time (selective RT). Simple reaction time plays an important role in undertaking daily living activities [2].
In studies that have investigated the effects of substance use disorder on RT, it has been shown that the absence of nicotine extended RT, alcohol had a negative effect on RT, but codeine injection and marijuana had no effect on RT [3-5]. The use of more than one substance, which is often seen in opioid use disorder, and head trauma are known to cause a high rate of impairment in cognitive areas such as memory, information processing, learning, organizational functions and general cognitive functions [5]. In a previous longitudinal brain imaging study, it was confirmed that opioid use over a certain period leads to a measurable degeneration on brain [6]. In the study made by Monnelly et al. [7], the effect of methadone which is a synthetic long acting ╬╝-opioid agonist, on fetus brain development is evaluated since it crosses the placenta freely and exposes the developing fetus to exogenous opioid at the period of brain development. They showed that prenatal methadone exposure is associated with microstructural alteration in major white matter tracts, which is present at birth. It is clear that these negative effects of opioid use on brain, thereby on general cognitive functions have a negative effect on RT. However, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no study in literature that has investigated the effect of opioid use disorder on RT.
The aim of this study was to compare visual and auditory reaction times, which are accepted as an important factor in both private life and working life performance, of patients with opioid use disorder and of a healthy control group.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 [8]. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. Approval for the study was granted by the Local Ethics Committee (September 29, 2016-14/11). A total of 27 patients undergoing in-patient treatment in the Alcohol and Substance Addiction Treatment and Research Centre (AMATEM) in the Mental Health and Diseases Hospital with a diagnosis of ŌĆśopioid use disorderŌĆÖ according to the The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (DSM-5) [9] were included as the addiction group (Group 1). The control group (Group 2) was formed of 27 individuals with no substance or alcohol use disorders according to DSM-5 and no diagnosed disorder.
Body mass index (BMI) was calculated for all the cases. A Sociodemographic and Clinical Data Form was completed for all the cases including information on age, gender marital status and level of education.
The Sociodemographic and Clinical Data Form used was prepared taking into consideration the aims of the study and appropriate information obtained from the scanned literature and clinical experience. This form was a semi-structured form including sociodemographic information such as age, gender marital status and level of education, occupation, place of residence, economic status and family structure and clinical data such as duration of the disorder, number of hospitalizations, and the presence of psychosocial stress factors at the onset of the disorder.
Due to the difference in cognitive procedure load, simple RT is generally shorter than selective RT. For ease and practicality of measurement, simple RT was used in this study.
Using a computer program specially prepared on a MATLAB┬« basis, the response with clicking mouse button to visual screen color change (red/blue) and to an auditory ŌĆśbeepŌĆÖ sound of the computer system were recorded in milliseconds. For each measurement, the program gave a median value of 10 samples. Each measurement was repeated 3 times and the average was taken for analysis. Before the measurements, all the subjects were examined for auditory and visual adequacy and at least one trial test was made. The RT measurements of the patients were made on the admission day to the hospital.
This group was formed of 27 in-patients undergoing treatment in the AMATEM unit in the Mental Health and Diseases Hospital with a diagnosis of ŌĆśopioid use disorder.ŌĆÖ Inclusion criteria were to be aged 18-65 years, to have a diagnosis of opioid use disorder according to DSM-5, to have no other DSM-5 disorder, no history or current neurological disease, no physical disease (diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy, neuroendocrine diseases, other metabolic diseases etc) or significant physical pathology which could affect the distribution of psychiatric symptoms.
The control group was formed of 27 healthy individuals, age and gender-matched to the patient group, with no substance or alcohol use disorder diagnosis and no other DSM-5 disorder diagnosis, no current or history of neurological disease.
Any cases in either groups with a history of head trauma were excluded from the study.
All the individuals recruited in the study signed an informed consent form.
Statistical evaluation was made using SPSS software SPSS for Windows version 22 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The data obtained from the groups were stated as mean┬▒standard deviation (SD). The StudentŌĆÖs t-test was applied as a statistical method. The post hoc power test was applied with the PASS 2008 program. ŌĆśA significance level of p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.ŌĆÖ
The mean age was determined as 24.41┬▒6.48 years (range, 18-40 years) in Group 1 and 28.07┬▒8.26 years (range, 18-42 years) in Group 2. No significant difference was determined between the groups in respect of age (p=0.075). The cases in both groups were all male. In Group 1, the level of education was determined as no education in 2 (7.4%) cases, primary school level in 9 (33.3%), middle school in 12 (44.4%), high school in 3 (11.1%) and university in 1 (3.7%) case. Of the total cases, 6 had dropped out from school (22.2%). In Group 2, the level of education was determined as primary school level in 5 (18.5%), middle school in 7 (25.9%), high school in 11 (40.7%) and university in 4 (14.8%). There were no cases of abandoned schooling. A statistically significant difference was determined between the groups in respect of the duration of education, which was 7.5┬▒3.40 years in Group 1 and 10.26┬▒3.61 years in Group 2 (p<0.01). On first presentation at the polyclinic, 16 (59.2%) of the patients in Group 1 were in regular employment and 11 (40.7%) stated that they had a job that provided an income. In Group 2, 23 (85.1%) were in regular employment and 4 (14.8%) were unemployed. The marital status was determined as single in 18 (66.6%) cases and married in 9 (33.3%) cases in Group 1 and single in 15 (55.5%) cases and married in 12 (44.4%) cases in Group 2. In Group 1, 1 (3.7%) case lived alone and 26 (96.2%) lived together with family. In Group 2, all (100%) the cases lived together with family.
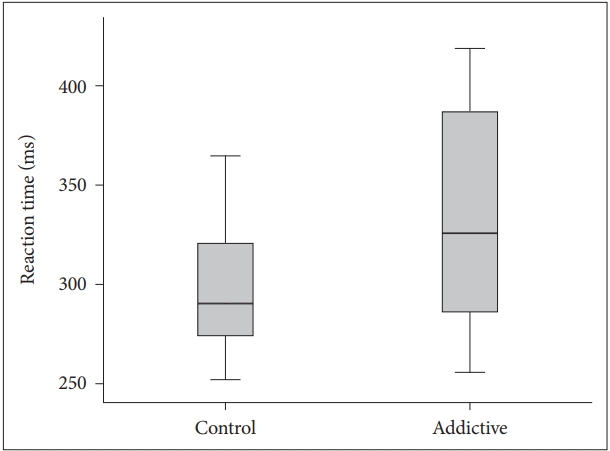
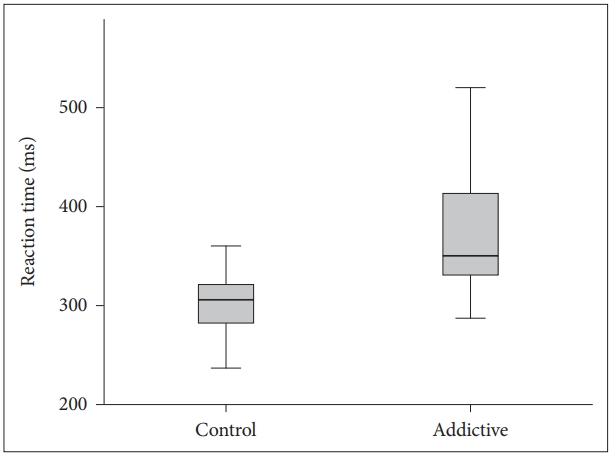
The visual and auditory reaction times of the addiction group were determined to be longer than those of the control group (Table 1, Figures 1 and 2). There were no correlation between age, BMI and RT.
As a result of the Post Hoc Power test, the auditory reaction time parameter achieved 81% power to detect a difference between the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis, with a significance level (alpha) of 0.05 using a two-sided two-sample t-test.
Reaction time is affected by factors such as age, gender, education level, type of stimulus, habits, alertness, tiredness, and alcohol and nicotine intake [10,11]. It shows a strong relationship with age; while it is 0.5-0.6 seconds in childhood, it becomes shorter up to the age of 30 years. In adults, the mean time is approximately 0.1-0.2 seconds [5]. With advancing age, it becomes longer and variable [12]. At advanced ages, both simple and selective reaction times show slower activity in measurement tests compared to younger ages [13]. The cases in the current study were in the age range of 18-40 years with a mean age of 24.41┬▒6.48 years, which is approximately the period when reaction time becomes shorter. And there was no significant difference between the study and control group in respect of age. So ŌĆśageŌĆÖ was not accepted as a confounding factor. There is a relationship between gender and reaction time. In a study conducted on male and female short-distance runners, the RTs of the females were determined to be longer than those of the males, and the reason for this was stated to be that the leg muscles of females could produce plantar flexor and isometric power to a more limited degree than males [14]. It has been reported that the auditory RT of females is superior to that of males [15]. In a study which researched gender difference in selective RT, the mean RT of females was determined to be slower than that of males [16]. In the current study, all the patients were male because of the hospitalŌĆÖs conditions and the Group 2 was formed with male healthy controls.
BMI is obtained from height and weight values and is a variable determining the weight range appropriate to height. It is an accepted marker of obesity. There are studies which have reported that obesity has a negative effect on motor skills [17]. In a study which determined a significant positive correlation between simple RT and the body weight of the subjects, the simple RTs of overweight individuals were found to be longer compared to those of lower weight [18]. In contrast to literature, although the mean BMI of Group 1 in this study was statistically significantly lower than that of Group 2 (p<0.001), the visual and auditory reaction times of Group 1 (352.68┬▒89.45; 388.32┬▒106.59) were found to be longer than those of Group 2 (306.48┬▒49.70; 318.43┬▒73.83). This result could be due to the effect of negative conditions such as the high rate of unemployment generally seen in substance addicts, low socio-economic level and associated inadequate and poor nutritional habits and a sedentary lifestyle. It is known that physically active and fit adults exhibit shorter simple and selective reaction times, which indicates that they can make decisions more rapidly [19]. Conversely people with opioid use disorder mostly have unhealthy and inappropriate life conditions which affect the physical and psychological features negatively.
Psychotropic substances have an effect on RT. While D-amphetamine and venlafaxine shorten RT, chlorpromazine and exposure to lead lengthen RT [20]. In the current study, Group 1 comprised individuals who were undergoing in-patient treatment for opioid use disorder and had no DSM-5 diagnosis other than opioid use disorder, they had no disease requiring treatment other than psychiatry and they were not taking additional medication that would affect the RT. The RT is measured on the admission day when they were still on opioids but no any other substance according to the urine samples and the patientsŌĆÖ statements as well. The patients had neither craving no withdrawal symptoms which could affect the RT. The studies dealing with the effects of alcohol and substances on RT reveal different results. In studies investigating the effects of cigarette smoking on RT, nicotine administered before the RT test to smokers and non-smokers was seen to shorten RT, but the absence of nicotine created in smokers as a result of not smoking before the test was determined to increase RT in these individuals [21,22]. In the current study Group 1 was formed of all (100%) smokers and, there were 18 (66.6%) smokers in Group 2. When the shortening effect of nicotine on RT is taken into consideration, if this effect could have been discounted in the opioid use disorder group, it can be predicted that the measured RT would have been much longer. In studies examining the effects of alcohol on RT, just as it has been reported that alcohol has negative effects on RT [23], in another study examining selective RT values, no statistically significant difference was determined between social drinkers and those who drank no alcohol at all [24]. In another study which examined differences in respect of visual motor rate between alcoholics and social drinkers, the alcoholics were found to be significantly disadvantaged [25]. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study by Bradley and Nichonlson [26], the effect of codeine on RT was investigated. Participants were administered 30, 60, or 90 mg codeine injection and in measurements made 45 mins and 2 hours later, a difference was determined between the study and control groups in respect of RT. Abnormal functional connections in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) network have been determined in patients with opioid use disorder and this has been shown to be related to weak decision-making performance. There is a significant reduction in the dopamine and serotonin transmission systems in in patients with opioid use disorder and this has been related to reduced cognitive performance [27,28]. The use of more than one substance, which is often seen in opioid use disorder, and head trauma are known to cause a high rate of impairment in cognitive areas such as memory, information processing, learning, organizational functions and general cognitive functions [3,29]. In a previous longitudinal, brain imaging study, it was confirmed that opioid use over a certain period leads to a measurable degeneration on brain morphology [5]. Although studies have confirmed a relationship between opioid use and reduced decision-making performance, there has been insufficient explanation of by what mechanism this result occurs. Nevertheless, this impairment could be explained by the mechanism that; long-term opioid use could reduce decision-making performance by leading to structural changes in the brain. Experimental animal studies have shown that the exposure of opioid reduced OFC functions and negatively affected decision-making performance [30]. It can be predicted that these negative effects of opioid use on cognitive functions influence to perceive a suddenly occurring signal and create a response to this signal adversely.
Although there have been previous studies examining the effects of alcohol, cigarettes and other addictive drugs such as codeine on RT, to the best of our knowledge there is no study in literature showing the effect of chronic opioid use on RT. Therefore, the current study is the first in this respect. This study can be considered a preliminary study on this subject and further research with more large samples and case series could investigate to what extent opioid use disorder affects RT, which is accepted as an important factor with an effect on both private life and work performance. To add improving reaction time approaches in opioid use disorder may contribute to treatment by increasing quality of life and work performance.
The present study has some limitations. Due to the conditions of the hospital that the study was conducted, only male patients were recruited, and the number of patients was relatively small. These factors may make it difficult to generalize the results. Further studies including both sexes with large samples would be more beneficial.
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Sema Baykara. Data curation: K├╝bra Alban. Formal analysis: Sema Baykara. Funding acquisition: Sema Baykara. Investigation: Sema Baykara. Methodology: Sema Baykara, K├╝bra Alban. Project administration: Sema Baykara. Resources: Sema Baykara. Software: K├╝bra Alban. Supervision: Sema Baykara. Validation: Sema Baykara. Visualization: K├╝bra Alban. WritingŌĆöoriginal draft: Sema Baykara. WritingŌĆöreview & editing: Sema Baykara, K├╝bra Alban.
REFERENCES
1. Han B, Compton WM, Blanco C, Crane E, Lee J, Jones CM. Prescription opioid use, misuse, and use disorders in US adults: 2015 National survey on drug use and health. Ann Intern Med 2017;167:293-301.


2. Babayigit I. Pilates exercise positively affects balance, reaction time, muscle strength, number of falls and psychological parameters in 65+ years old women. Dissertation. Ankara: Department of Physical Education and Sports-School of Social Sciences of Middle East Technical University; (Doctor of Philosophy Degree). 2009.
3. Schmidt RA, Lee TD. Motor Control and Learning: A Behavioral Emphasis. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics; 1999.
4. Schmidt RA, Lee TD. Motor Control and Learning: A Behavioral Emphasis. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics; 1988.
5. Ricci B. Physiological Basis of Human Performance. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1967.
6. Colgate TP. Reaction and response times of individuals reacting to auditory, visual, and tactile stimuli. Res Q 1968;39:783-784.


7. Monnelly VJ, Anblagan D, Quigley A, Cabez MB, Cooper ES, Mactier H, et al. Prenatal methadone exposure is associated with altered neonatal brain development. NeuroImage Clin 2018;18:9-14.


8. Riis P. Perspectives on the fifth revision of the Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2000;284:3045-3046.


9. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®). Washington DC: American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
10. Ricci B. Experiments in the Physiology of Human Performance. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1970.
11. Ma─Łdikov I, Makarenko N, KolŌĆÖchenko N, Serebrovskaia T, Kienko V. Human higher nervous activity during adaptation to moderate altitude. Zhurnal vysshei nervnoi deiatelnosti imeni IP Pavlova 1985;36:12-19.
12. Kolev V, Falkenstein M, Yordanova J. Motor-response generation as a source of aging-related behavioural slowing in choice-reaction tasks. Neurobiol Aging 2006;27:1719-1730.


13. Lord SR, Sturnieks DL. The physiology of falling: assessment and prevention strategies for older people. J Sci Med Sport 2005;8:35-42.


14. Lipps DB, Galecki AT, Ashton-Miller JA. On the implications of a sex difference in the reaction times of sprinters at the Beijing Olympics. PLoS One 2011;6:e26141.



15. Don M, Ponton CW, Eggermont JJ, Masuda A. Gender differences in cochlear response time: an explanation for gender amplitude differences in the unmasked auditory brain-stem response. J Acoust Soc Am 1993;94:2135-2148.


16. Der G, Deary IJ. Age and sex differences in reaction time in adulthood: results from the United Kingdom Health and Lifestyle Survey. Psychol Aging 2006;21:62-73.



17. Gunstad J, Paul RH, Cohen RA, Tate DF, Spitznagel MB, Gordon E. Elevated body mass index is associated with executive dysfunction in otherwise healthy adults. Compr Psychiatry 2007;48:57-61.


18. T├╝ren U, Kaya B, Akkocao─¤lu H. An experiment on the factors affecting simple reaction time. Int J Human Sci 2013;10:637-654.
19. Trombly CA, Radomski MV. Occupational Therapy for Physical Dysfunction. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002.
20. Grunberger J, Saletu B, Linzmayer L, Barbanoj MJ. Clinical-pharmacological study with the two isomers (d-, l-) of fenfluramine and its comparison with chlorpromazine and d-amphetamine: psychometric and psychophysiological evaluation. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 1993;15:313-328.

21. Parrott A, Garnham N, Wesnes K, Pincock C. Cigarette smoking and abstinence: comparative effects upon cognitive task performance and mood state over 24 hours. Hum Psychopharm Clin 1996;11:391-400.

22. Froeliger B, Gilbert DG, McClernon FJ. Effects of nicotine on novelty detection and memory recognition performance: double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of smokers and nonsmokers. Psychopharmacology 2009;205:625-633.



23. Moselhy HF, Georgiou G, Kahn A. Frontal lobe changes in alcoholism: a review of the literature. Alcohol Alcohol 2001;36:357-368.



24. Snel J, Lorist MM. Nicotine, Caffeine and Social Drinking: Behaviour and Brain Function. Routledge: Harwood Academic Publishers; 1998.
25. Kokavec A, Crowe SF. A comparison of cognitive performance in binge versus regular chronic alcohol misusers. Alcohol Alcohol 1999;34:601-608.



26. Bradley CM, Nicholson AN. Effects of a mu-opioid receptor agonist (codeine phosphate) on visuo-motor coordination and dynamic visual acuity in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1986;22:507-512.



27. Cheng GL, Zeng H, Leung MK, Zhang HJ, Lau BW, Liu YP, et al. Heroin abuse accelerates biological aging: a novel insight from telomerase and brain imaging interaction. Transl Psychiatry 2013;3:e260




28. Liang CS, Ho PS, Yen CH, Yeh YW, Kuo SC, Huang CC, et al. Reduced striatal dopamine transporter density associated with working memory deficits in opioid-dependent male subjects: a SPECT study. Addict Biol 2016;21:196-204.